- February 23, 2020
- Construction
- Daisy Angel
Concrete is one of the most popular materials in construction. The most suitable conditions for its hardening are considered to be an ambient temperature of + 20 ˚С. But sometimes you have to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures. In this case, it is better to use the services of specialists.
Water can become an obstacle to quality work. It is needed in concrete not only for fluidity. Water performs an important function in the hardening process. At low ambient temperatures, it changes from a liquid state to a solid state (turns into ice). This stops the hardening process and promotes the destruction of bonds formed before freezing.
Concrete can harden even at a temperature of -4 °C. However, if it drops below + 5 ˚С, then the hardening process slows down, and the strength gain is suspended and resumed only when it becomes warmer outside. The longer the stagnation in the hardening process, the less strength the material will gain. This means that at low temperatures it is necessary to provide conditions under which the concrete will not freeze and will continue to gain strength.
Use of additives
If you are interested in knowing how to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures, then you should familiarize yourself with the technology of using additives. Antifreeze substances are not very expensive and are widely available. If you purchase ready-made concrete, then all additives should already be in it. In this case, the temperature values in a specific area are taken into account.
Additives contain chemical impurities - salts of monocarboxylic acids, sodium formate and nitrite. They speed up the hardening process, prevent water from freezing, and also increase the final strength of the material. The main disadvantage of using various additives is that such substances cope with their work only at -5 ˚С. If you are interested in at what negative temperature concrete can be poured, then you should know that in severe frosts, although some additives will work, hardening will not begin as quickly as required by technology. Ultimately, the lack of strength can be 30%. Some additives are aggressive towards metal reinforcement. They destroy it, causing the structure to lose strength.
What to add to concrete at sub-zero temperatures
Special anti-frost additives allow outdoor work to be carried out at low temperatures. These are chemical additives that are divided into several groups:
- Additives that prevent water from freezing are usually used with heating, which reduces the period of setting and hardening.
- Antifreeze-based additives; their task is to enhance the activity of cement at negative ambient temperatures. These additives are used without heating the structure; the concrete will gain the required strength without freezing the mass.
- Additives are accelerators of hardening of the cement mass with the release of heat, therefore, the monolithic mass is heated without the use of additional means - independently.
From a material point of view, the use of frost-resistant additives is the cheapest option, which is acceptable for any structure. The main rule is to fill the trench evenly, with tamping and compaction.
The peculiarity of these additives is the precise dosage during use, taking into account the massiveness of the product in each specific case. Some additives increase corrosion of the reinforcement belt, while others, on the contrary, increase the anti-corrosion properties of concrete. Therefore, they are often used together.
Benefits of Using Supplements
Many people want to know how to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures. In order not to make a mistake, you first need to familiarize yourself with all the advantages and disadvantages of a particular method. The most common technology is the addition of additives. They have one significant advantage - this approach allows concreting to be carried out at any time of the year.
Using additives, it is possible to transport concrete mortar at low temperatures. To ensure high-quality setting of the material, it is not necessary to use additional heating systems. When antifreeze additives are added, a concrete monolith receives additional strength, and the solution consumption is reduced (if compared with a material prepared according to a conventional recipe).
Possible consequences of winter concreting
Failure to comply with concrete laying technologies in winter results in concrete products of reduced strength, with cracks, efflorescence and other defects, as well as poor adhesion to reinforcement. The products are short-lived in use.
Important!
It should be remembered that the critical strength of concrete is 30–50% of the design strength, and stripping - 70%. Once concrete reaches critical strength, frost no longer harms it, and heating measures can be curtailed. But at this moment it is still impossible to strip the formwork and put a load on the concrete.
Concrete work in winter is most often a necessary measure, but even in this case there are advantages. When choosing a technology for winter work, many factors are taken into account: the type of structures, the composition of the concrete mixture, the availability of equipment and the economic effect of their use. Antifreeze additives are desirable for use when choosing any method of conducting concrete work in winter.
The main disadvantages of antifreeze additives
In order to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures without compromising the quality of the material, it is necessary to become familiar with the disadvantages of anti-frost additives. Firstly, they can lead to the appearance of salt crystals on the surface, which are almost impossible to remove. Secondly, sometimes they reduce the strength of concrete stone. This happens if the proportions are calculated incorrectly, and the cooking or setting technology is broken. Thirdly, individual components may be unsuitable for use in residential areas as they are toxic.
Technology and features of pouring in autumn
At what average summer temperature should construction begin? The warm season - from +15 to +30 degrees is suitable for construction work. Pouring concrete in summer is acceptable. The only condition is to protect the freshly laid monolith from rain.
Choosing the right time
In the fall, the weather is unpredictable, so it is important to know at what temperature you can pour concrete in the fall.
The optimal air temperature is from +20 to +5°, so it is recommended to start laying the foundation in September-October before frost. In the process of arranging the foundation, it is important to consider to what point on the thermometer the work needs to be completed before the cold snap. It should be +10 degrees Celsius. The concrete mass gains strength within 1 month. Before frost, it is recommended to make a shelter, and in the first two days, protect the mixture with film from rain.
Advice! Before pouring your foundation in the fall, check the weather forecast.
Factors influencing dough setting in autumn
Pouring a monolith will be of high quality if you take into account several points:
- air temperature. At what temperatures can concrete be poured in the fall to start building a house? The normal value is plus 16°. During this period, the solution hardens slowly, which ensures the quality of construction. Frosts occur at the end of October, so it is better to start construction in mid-September;
- humidity characteristics. Damp weather and wet soil promote the curing process. Freshly laid mortar does not need to be regularly sprayed with water, and slow drying ensures increased strength;
- presence of precipitation. If you have figured out the optimal temperatures at which you can pour the foundation, then you need to take into account the presence of rain. Overmoistening of the monolith leads to the leaching of cement laitance;
- ground water level. In swampy areas there is less water in the fall, which makes it possible to make a pile foundation. You can check whether the water has risen by digging a trench. If water has risen in it, the foundation cannot be poured.
Important! If at least one factor does not comply, the structure will lose strength.
Heating technology
Many novice craftsmen do not know at what temperature concrete should be heated. It is important to take into account one rule: if the thermometer drops below + 5 ˚С, then the hardening process slows down. To avoid this, heating must begin when the ambient temperature drops below this mark. You can do this as follows:
- pass current through the concrete using an electrode;
- pass current through a wire pre-laid inside the material.
The first method is cheaper, since metal rods can act as electrodes. If you follow the rules, you will need special equipment for these purposes. However, some craftsmen connect a welding machine to the reinforcing electrodes, passing current through the solution and heating it. Reinforced concrete is heated at a voltage of up to 127 V. Without metal reinforcement, voltages of up to 380 V should be used.
The second method involves additional costs for the heating cable. It is laid with a reinforcement frame. Current is connected to it through substations. This method is more expensive, but is more effective compared to heating using electrodes.
The main disadvantage of the above method can be called financial costs. In addition, when heating, you need to constantly monitor the temperature. If it rises excessively, this will cause the material to dry out and may compromise the strength of the structure. If frosts are severe, the formwork should be additionally insulated. Now you know at what temperature you need to heat concrete.
At what temperature can the foundation be poured: we understand the nuances so as not to make mistakes
The reliability and durability of the entire structure directly depends on the strength of the foundation. When planning such a “zero” cycle of construction work, it is necessary to take into account many factors. Particularly important is the information at what temperature the foundation can be poured.
At what temperature can the foundation be poured?
If you do not take into account the weather conditions during the process of pouring the foundation, the quality and brand of the solution, the use of additives that can reduce the temperature crystallization of water, measures to maintain the necessary conditions for the maturation of concrete, then the work may be done in vain, and the constructed foundation of the building will begin to crumble immediately after hardening.
Expert opinion: Afanasyev E.V.
Chief editor of the Stroyday.ru project. Engineer.
Some owners of suburban areas are in a hurry to build permanent structures on their newfound territory, not paying attention to the time of year. In some, rather rare cases, this may be justified; however, there are many difficulties with this approach, and they begin already at the stage of preparatory work.
Preparing to pour the foundation
Regardless of the time of year, preparatory activities will include a whole list of mandatory work:
- The place where the foundation for the construction of the structure will be laid must be cleared of the top layer of soil and marked accordingly. Removing the top layers of soil in frosty weather is a rather labor-intensive task.
- When the general location has been determined, the internal boundaries of the trench are marked, which must be dug under the foundation. Its depth should be from 500 to 800 mm - this value will depend on the type of soil in the area where construction is taking place, the depth of their freezing, the characteristics of the building being constructed (its number of floors, material of walls and roof, etc.) Earth-moving equipment for excavating narrow and It is not always possible to use sufficiently deep trenches with smooth walls. Manual digging of frozen soil is another difficulty when carrying out winter work.
- A waterproofing and reinforcing cushion is placed at the bottom of the trench pit. Sand is laid first and compacted well; the layer thickness can be from 100 to 150 mm. Crushed stone is poured onto it and it is also compacted well. Very often in winter, both sand and gravel are in a frost-bound state. There is a high probability that as the temperature rises, the pillow may lose the required density, even with the best tamping.
Formwork for strip foundation
- In addition, there is no complete certainty that with the general thawing of the soil in the spring and its possible movements, the entire structure of the foundation being built will not “lead”, and this can lead to the formation of internal stresses and cracks.
- The next step is the installation of formwork from boards or wooden panels, which is waterproofed with thick polyethylene film. In severe frost, polyethylene often loses its elasticity, becomes brittle, and the waterproofing can be damaged.
In the cold, waterproofing film can lose its plasticity and become brittle
- Permanent formwork made of extruded polystyrene foam can also be used, which, in addition to its direct function, also serves as insulation.
Fixed formwork made of extruded polystyrene foam
- Next, it is necessary to install a reinforcement structure into the formwork, which is welded or twisted with steel wire. The reinforcement for this design is taken with a thickness of 10 to 15 mm. We must not forget that reinforcing steel has a fairly significant coefficient of linear thermal expansion. A reinforcement frame welded in severe frost will certainly tend to change in size as temperatures rise. This is another significant “additive” to the unnecessary internal stresses of the foundation structure.
Reinforcement of the foundation strip
However, as already mentioned, there are situations when, for one reason or another, the construction of a foundation in the winter season is justified:
- This may be caused by soil characteristics. If the area where the construction is taking place is dominated by sandy loose soils, then it is better to build the foundation in frozen solid soil, which retains the shape required for the foundation pit.
- The impossibility of carrying out construction in the summer due to the special climatic conditions of the region should not be discounted.
- In a number of areas, due to the poor development of road networks, the delivery of large volumes of construction materials or the movement of heavy special equipment is only possible on frozen ground.
- Sometimes winter construction is resorted to in order to save money, since during this period the prices for necessary materials decrease. This will be beneficial if the work is carried out independently.
- Often there is an opportunity to save money by reducing the cost of services by construction firms, due to a sharp decrease in demand for their activities during the cold season.
When all the preparatory processes are completed, you can calculate the density and composition of the solution, the parameters of which will depend on the temperature at which it will be poured into the formwork.
Pouring the foundation with concrete
- Whenever pouring is carried out, the foundation mortar should not be too thin, so it is most often made from cement and medium-sized crushed stone.
- Plasticizers are often added to the solution, which improve the condition and strength of concrete, increase its adhesion to reinforcement structures, and increase the moisture resistance of the foundation. In addition, according to manufacturers, when pouring, plasticizers reduce the consumption of cement mortar by 20%.
One of the types of modifying additives in concrete mortar
Due to the fact that plasticizers have a positive effect on the frost resistance of the mortar, they are often added in cases where it is necessary to pour the foundation at subzero air temperatures.
Optimal conditions for pouring concrete are temperatures from 15 to 25 degrees
- According to all recommendations, concrete should be poured at a temperature of at least 5 degrees - this, in fact, is a critical indicator for normal maturation. However, the summer heat is also not suitable for carrying out these construction processes. The optimal temperature for pouring the solution into the pit is +15 ÷ 25 degrees. Such conditions will make it possible to obtain the most solid foundation for the construction of walls without unnecessary costs and technological techniques and in the shortest possible time.
What are the general recommendations for pouring a concrete foundation:
- In the case when the solution is made independently directly at the construction site, all materials used for it should not be frozen and should not contain snow or ice crystals. Therefore, it is better to purchase them from companies that are guaranteed to provide them with proper storage.
- The solution must be poured and distributed over the formwork quickly so that frost does not have time to capture the moisture in the solution. Therefore, the entire volume of concrete is poured under such conditions only at one time. If the foundation has a large volume and area, then it is better to take advantage of the offers of specialized companies that are engaged in the manufacture, delivery and unloading of the necessary solution into the prepared formwork.
The foundation should be poured in one go
- It is not recommended to pour concrete in layers, since, due to low temperatures, gaps may form between them, which will make the foundation less strong.
If circumstances are such that you have to carry out work at critical temperatures, you need to know that the setting and hardening processes will be increased several times. Therefore, pouring the foundation in winter is carried out only when absolutely necessary.
Below is a table from which you can clearly see how the ambient temperature affects the time of maturation and full set of the required strength of conventional concrete mortar grade M200 - M300, made on the basis of Portland cement M-400 or M-500.
| concrete hardening time, days | -3° C | 0°C | +5° C | +10° C | +20° C | +30° C |
| 1 | 3% | 5% | 9% | 12% | 23% | 35% |
| 2 | 6% | 12% | 19% | 25% | 40% | 55%٭ |
| 3 | 8% | 18% | 27% | 37% | 50%٭ | 65% |
| 5 | 12% | 28% | 38% | 50%٭ | 65% | 80%٭٭ |
| 7 | 15% | 35% | 48%٭ | 58% | 75%٭٭ | 90% |
| 14 | 20% | 50%٭ | 62% | 72%٭٭ | 90% | 100% |
| 28 | 25% | 65% | 77%٭٭ | 85% | 100% | — |
Notes:
— percentages are calculated in relation to the reference strength of mature concrete of a given grade.
— under the icons (٭) the so-called conditional normative and safe periods for stripping a poured concrete structure are indicated.
— icons (٭٭) are the ripening dates for the start of completely safe further work.
To ensure the required minimum permissible temperature conditions, several technologies are used:
- The process is carried out with heating of the reinforcement structure or with the installation of special heating cables. In this case, the appropriate electrical voltage must be supplied to the foundation. There are several technologies, both using high voltage currents (up to 380 volts) and low current ones (12 volts). Once warmed up, the reinforcement structure or heating cable will prevent the wet, unset solution from freezing.
However, such methods are justified only for large-scale industrial construction - such technologies are very dangerous and require the highest qualifications of specialists. In addition, it will be important to consume a large amount of electricity, which means you will have to pay a hefty amount. As a result, the total budget for such foundation arrangement is hardly acceptable for the average Russian private developer.
The technology of electrical heating of ripening concrete is quite complex, expensive, and requires the mandatory participation of specialists
- Another technology that can be used is the use of permanent insulated formwork for constructing the foundation.
For this method, hollow blocks of extruded polystyrene foam are used, which are convenient to install on top of each other, thanks to the existing teeth on the side and top surfaces. They fit perfectly with each other, leaving no gaps (a kind of analogue of a children's Lego construction set). Reinforcement structures are installed in the internal space, which give the foundation the required overall rigidity.
Fixed EPS formwork solves the insulation problem only partly
Expanded polystyrene is not removed from the foundation, and after the concrete has hardened, the surface is covered with reinforcing mesh, plastered and waterproofed.
However, this approach will only reduce the negative impact of negative temperatures during concrete maturation, but will not completely eliminate the problem.
- In any case, for reliable setting of the poured foundation at sub-zero temperatures, it must be covered with a thick plastic film on top. To do this, a temporary structure made of wood or reinforcing bars is erected over it, which is also covered with polyethylene. In the resulting enclosed room, which looks like a greenhouse, the temperature necessary for high-quality hardening is maintained using heat guns. It is clear that this will also require very significant material costs.
As you can see, even from an economic point of view, carrying out foundation pouring work in winter raises great concerns. Therefore, before starting such work during cold weather, you need to very carefully weigh all the financial risks and the justification of such a rush.
Video: work on “winter” laying concrete in the foundation
Cement prices
Cement
Are anti-frost additives a “panacea”?
There is a very widespread opinion that the problem of pouring a concrete foundation in winter can be completely solved by using special salt additives in the prepared solution. Judging by numerous advertisements, it is worth adding this component when mixing, and then everything will go as usual. It is worth looking into this in more detail.
Video: one of the options for anti-frost additives in concrete
Prices for various types of antifreeze additives in concrete
Antifreeze additive in concrete
First of all, it is necessary to understand how the process of hardening and maturation of concrete stone actually occurs.
When the solution is poured into the formwork, it goes through two stages until it is ready - setting and hardening.
- The poured concrete sets within 24 ÷ 30 hours. During this time, the liquid consistency turns into a solid state, however, it still does not have sufficient strength. It is during this period that crystalline bonds begin to form, and free water and cement components of the solution bind.
- Then the second stage begins - this is the final hardening, maturation and strengthening of the concrete structure - it takes place over a much longer period. This period depends on several factors, such as the brand of the prepared solution, the level of humidity and temperature conditions, as well as the presence of special strengthening additives.
As mentioned above, the optimal temperature for the chemical reactions of both processes varies from 15 to 25 degrees. The higher it is in this range, the faster the final crystallization, the transition of water into a gel-like state, will occur. But even in optimal conditions, we can talk about the readiness of the foundation no earlier than after 4 weeks - the foundation is completely ready for the construction of walls.
The danger of negative temperatures lies in several reasons:
- First, the expansion of frozen water unbound by cement causes internal pressure on the porous structure of concrete, which leads to its destruction. This becomes especially noticeable after the temperature rises to positive levels - such concrete cannot be compared with “normal” concrete in terms of strength.
- Secondly, the complex chemical process of cement hydration itself requires a certain temperature regime. Already at temperatures below +5° C, the activity of these processes decreases to critical levels, and the colder it is, the more sluggish the maturation of concrete will be. And even in this case, such an “intermittent” process significantly degrades the quality of the finished concrete structure.
Potash is a very common additive for increasing the frost resistance of freshly poured concrete.
In order to minimize the negative impact of frost to some extent, special additives have been developed. Technologists are trying to solve both problems in this way. By adding salt solutions, the density of water is increased, sharply reducing its crystallization temperature. Special additives, in addition, are designed for a kind of catalysis and additional involvement of air in the processes of chemical aging of concrete stone in conditions of negative temperatures. Typically, such compositions are made based on potash, lignosulfonate, calcium hydrochloride, nitrite or sodium formate.
Sodium nitrite is often used as an additive
However, if the issue is resolved positively to one degree or another with the freezing of water, then it is much more difficult to “deceive” the laws of chemistry. The ripening process is still not fast, and takes much longer than under optimal conditions.
The table below shows, as an example, the approximate maturation times for concrete at subzero temperatures using antifreeze additives:
| Type of antifreeze additive | average temperature during ripening | 1 Week | 2 weeks | 4 weeks | 3 months |
| Sodium nitrite | -5° C | 30% | 50% | 70% | 90% |
| -10° C | 20% | 35% | 55% | 70% | |
| -15° C | 10% | 25% | 35% | 50% | |
| Potash | -5° C | 50% | 65% | 85% | 100% |
| -10° C | 30% | 50% | 70% | 90% | |
| -15° C | 25% | 40% | 60% | 80% | |
| -20° C | 23% | 35% | 55% | 70% | |
| -25° C | 20% | 30% | 50% | 60% |
You can be sure that even at -5°, complete readiness of the concrete structure can only be discussed after 3 months. In a colder atmosphere, the period increases even more.
A completely reasonable question arises: does it make sense for the owner of an individual plot to “get involved” with the winter laying of the foundation (if this is not caused by some special circumstances), to spend significant material resources and physical effort on this, if the real gain in time is practically unattainable. Moreover, with antifreeze additives, things are also not so simple:
- Some types of additives cause active corrosion processes on metal reinforcement frames. Not all steel grades are suitable for these purposes.
- Mixing “winter” concrete mortar is much more difficult than regular one. Carrying out such work manually is simply impossible, since it requires particularly thorough mixing of the components to an absolutely homogeneous consistency. The mixing time increases significantly, the components must undergo certain preparation (heating to the required temperature), a strictly verified order of feeding materials into the mixer is necessary, etc. you need a very precise dosage of additional additives, depending on both the brand of concrete and the air temperature - this requires a professional approach. Another option is delivery of a ready-made modified mortar made in a factory - but this again comes down to the question of the profitability of such construction.
- Even with the use of additives, temperatures below -20 ° C are still critical, and such a sharp drop in winter, for example, at night, is by no means uncommon.
- You cannot pour such solutions even if a thaw suddenly begins, it rains, or the relative air humidity jumps above 60%.
- The use of such additives does not at all exempt you from the necessary measures to construct a “greenhouse” after pouring, and maintaining the required temperature using heat guns. If this is not possible, then the foundation will have to be covered with insulation (for example, a layer of dry sawdust, grass or turf, about 300 mm thick, and then covered with film until maturation. Still, most likely, it will be necessary to remove the formwork only in the spring, after the end of persistent cold weather.
Caring for a poured foundation
It would be a serious mistake to believe that even in ideal conditions you can only fill the formwork with concrete and then wait for the results of maturation. No matter how strange it may sound, a freshly poured foundation always, under any circumstances, needs some care. The main objectives of such technological activities are:
- Minimizing shrinkage of poured concrete structures.
- Provide the most optimal conditions for the ripening process.
- Protect the hardening foundation as much as possible from temperature changes, including daily ones.
- Do not allow the poured solution to dry out or the rapid evaporation of unbound water - this will most likely result in cracking of the surface.
- Create protection for a structure that has not hardened and has not gained strength from mechanical damage.
Measures for such maintenance should begin literally from the moment the foundation is poured, and can be considered fully completed only when the concrete reaches at least 70% of its brand strength, that is, at the optimal time for removing the formwork (as indicated in the first table).
- Immediately after pouring, you should make sure that the formwork has not lost its given geometric shapes - before the initial setting (the first 1 ÷ 2 hours) there is still an opportunity to make adjustments.
Covering the poured foundation with film
- No one is safe from sudden rains. To prevent erosion of the fragile surface or its mechanical damage, immediately after pouring the surface should be covered with plastic film, burlap or tarpaulin.
- Do not forget that too high temperatures are also quite destructive for the normal course of ripening processes. This is primarily due to the active evaporation of water, drying out of the surface layer and the appearance of cracks. Steps must be taken to moisten the surface and retain moisture. In addition to covering with a vapor-proof film, sometimes it is necessary to resort to more radical measures, for example, after initial setting, covering the surface with a layer of material that absorbs moisture well. This can be wet sawdust or coarse cloth - a kind of constant wet compress is created under a plastic cover.
To maintain the humidity regime, wet sawdust is often used, which is regularly moistened with water.
In a word, each temperature regime requires its own concrete care measures. To make it easier to select what you need, you can give the following table:
| Actions taken to ensure normal maturation of concrete | less - 3 ° C | from - 3° to + 5° С | from + 5° to + 10° C | from + 10° to + 15° С | from + 15° to + 25° C | over + 25° C |
| Covering with film, constantly moistening the poured surface and formwork, covering the concrete with moisture-saving material | No | No | No | No | in severe windy weather | Always |
| Covering with film, moistening the concrete surface | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | not enough |
| Covering with film and thermal insulation material | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Covering with film and thermal insulation material, creating a greenhouse maintaining a temperature of +10° C for at least 3 days | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Constantly maintaining a thin layer of water on the concrete surface | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
A few more important notes:
- Even if a shallow strip foundation was poured under ideal conditions, it should not be left “bare” and unloaded for the winter. This will inevitably lead to the onset of surface erosion processes, and the structure will lose its strength, begin to crack and crumble. Thus, it is necessary to plan construction work in such a way that during the season we can proceed to the construction of walls on the created basis.
- Immediately after the concrete structure reaches the required 100% strength, it is recommended to immediately waterproof and insulate the foundation walls . More details about these technological processes are described in the relevant articles on our portal.
What general conclusion can be drawn?
Despite the fact that modern construction technologies, in principle, make it possible to fill the foundation at temperatures quite far from the optimal 15-25 degrees, the best option would still be to plan such work in the most favorable conditions. This way the foundation will be guaranteed to be reliable and of high quality. If, however, circumstances force you to carry out the “zero cycle” under other conditions, you should strictly follow all technological recommendations for pouring and caring for concrete, in relation to the actual temperature conditions.
Video: labor intensity of foundation pouring processes in winter
Warming during hardening
It is allowed to use conventional insulation methods. This is true if the ambient temperature is not lower than 5 degrees Celsius. Most often, the formwork (if any) is insulated, as well as visible parts of the concrete. For this purpose, you can use all kinds of materials, such as sawdust or polystyrene foam.
One of the most popular ways is to create a tent around the object. Heating guns can be installed inside such a structure. This method has the disadvantage that the concrete must be at a predetermined temperature when supplied. In addition, conventional insulation without additional heating will be ineffective if there is severe frost outside.
Caring for concrete after pouring the foundation
After laying the concrete mixture, it is important to create comfortable conditions for its maturation. They must provide:
- minimizing plastic shrinkage;
- strength;
- protection from sudden temperature changes;
- prevention of crack formation.
Depending on the season, the rules for caring for the foundation vary significantly.
Curing
Protecting concrete after laying in summer
Protecting a freshly poured foundation from water evaporation consists of:
- in a shelter with moisture-absorbing material with constant moistening, for example, sawdust;
- using polymer reflective film;
- constant wetting of wooden formworks with water.
The more time the concrete foundation is moistened, the higher its strength will be. The minimum period of care is 28 days.
Using polymer reflective film to protect concrete
Concrete care in winter
The basic rule for winter maintenance of concrete is to insulate it and conserve hydration energy. Foundations for modern monolithic buildings are initially insulated with foam formwork. It remains to cover the upper, open part of the concrete:
Preventing Concrete Freezing
- it is covered with wet sawdust, which will prevent the mixture from drying out;
- cover with wide plastic film;
- a thick layer of dry sawdust is placed on top.
You can use other available materials for covering concrete - mineral wool, straw, rags.
Related video: Is it possible to pour concrete in winter?
Publications on the topic
Technology for laying paving slabs on concrete
How to correctly calculate the thickness of the foundation slab
How long does it take for the concrete mass to dry under the influence of different environmental conditions?
Types of antifreeze additives
To pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures, which additive should I choose? The following types of these products are available on the market:
- Antifreeze.
- Sulfates.
- Antifreeze additives.
Antifreezes are substances that reduce the crystallization temperature of a liquid and speed up the setting time of the material. Sulfates are additives that accelerate hardening as much as possible and generate heat, so that the components of the solution mix faster and become a homogeneous mass. This lowers the freezing point. On sale you can find antifreeze additives called accelerators. These components are able to increase the rate of dissolution of silicate components, which react with the products of solution hydration. This ensures the formation of basic and double salts, which reduce the freezing point of the mixture.
Features of hydration
After mixing concrete, a hydration reaction begins in it, that is, a chemical interaction between cement and water with the formation of crystalline hydrates. As a result, the plastic mass turns into hard stone. However, when stirring the mixture in a mixer, the setting process is slowed down due to the vibrations to which it is exposed. An intense reaction starts after the foundation is poured. Hydration occurs in two stages.
At the stage of setting or thickening of the solution, the crystallization process begins with the further formation of spatial bonds between the particles. 10 hours after the start of the reaction, a lattice is formed from the hydration products of calcium aluminates.
Subsequently, the process of hardening of the cement mixture occurs. The hydration products of calcium silicates displace the aluminate structure, and after 28 days they gain the required degree of strength.
Hydration reaction
Antifreeze additive CemFrio
Among the inexpensive offers on the market, CemFrio should be highlighted. It is designed to increase the strength of material poured at sub-zero temperatures. This complex additive is used not only for concrete, but also for other mortar mixtures. It accelerates hardening and provides a plasticizing effect. Concreting with its use can be carried out at temperatures up to - 20 ˚С.
Prefabricated monolithic or monolithic concrete, as well as reinforced concrete structures can be erected with its help. The additive prevents the possibility of their destruction when exposed to negative temperatures. This substance should be dosed with a larger margin, focusing on the approximate readings of the thermometer during the day (not only during the day, but also at night) throughout the entire stage of hardening of the solution. In this case, the strength gain of concrete at sub-zero temperatures will be ensured in the range from + 10 to - 20 ˚С. At the same time, the need to add water to mortar mixtures is reduced by 5%, and the strength characteristics increase by 10%.
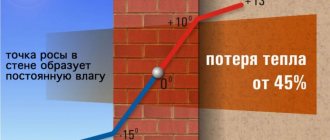
The influence of negative temperature on concrete hardening
At temperatures above +5°C, cement hydration occurs normally. If the temperature suddenly drops below 0°C, the water in the mixture will freeze and the process will freeze. In this case, the crystals that began to form in the warm mixture will remain in the solution. Winter concrete hardens much longer. If additives are not added to it and it is not heated, the monolith will be heterogeneous, with cracks.
If, after freezing, the solution is heated and the water is melted, then new bonds will form incorrectly and the monolith will not receive the necessary strength.
How to heat concrete yourself
Now you know that you can pour concrete in cold weather in different ways. If you do not want to use the appropriate additives, use the solution heating method. For this purpose, they most often work with electrodes. This is due to the simplicity and low cost of the method, because there is no need to use heating wires and transformers. This method is based on the physical properties of electric current, which passes through a conductor and releases a certain amount of heat.
The conductive material is concrete. When current passes through a water-containing solution, it heats it. If the concrete structure contains a reinforcement frame, it is not recommended to apply a voltage of more than 127 V to the electrodes. If such a structure does not exist, you can use both 220 V and 380 V. It is not recommended to apply a higher voltage.
If we pour concrete in cold weather, we can use different materials for heating, for example, rod electrodes. To create them, you should take metal reinforcement with a diameter of 8 to 12 mm. Such rods are inserted into concrete at a certain distance from each other and connected to different phases.
If the design is complex, heating electrodes will be indispensable. Fiberglass reinforcement is not suitable for such purposes, since it is a dielectric. Electrodes in the form of plates can be used. In this case, the heating circuit is very simple. The plates must be placed on opposite sides of the poured solution and connected to different phases. The passing current will heat the concrete.
Sometimes craftsmen use narrow stripes. The principle of their operation is the same as that of the plates. Electrodes can also be string electrodes. They are used when pouring columns, pillars and beams. The principle of operation is similar. The strings should be connected to different phases. Warming up with electrodes must be carried out with alternating current, since direct current passing through water promotes electrolysis. In this case, the water will chemically decompose without fulfilling its role in the hardening process. Now you know whether concrete is poured at sub-zero temperatures.
Concreting in dry, hot climates
Concrete does not like not only frost, but also heat. When the air temperature rises to +35 and above, and the humidity is at 50%, water evaporates too quickly, which provokes a violation of the water-cement balance. Hydration slows down or stops altogether, and therefore the concrete must be protected from too rapid loss of moisture.
To lower the temperature of the mixture, use chilled (or diluted with ice) water. This prevents rapid evaporation of water during the laying of the mixture. After a certain time, the mixture heats up, so it is important to ensure the tightness of the formwork (so that water does not evaporate through the cracks). Formwork can also absorb moisture, and therefore, to limit the adhesion of concrete and structural material, it is treated with special compounds before pouring.
Hardening concrete is protected from direct ultraviolet rays - the surface is covered with tarpaulin (burlap), and the surface is wetted every 3-4 hours. Moisturizing may be necessary during the entire 28 days of the monolith gaining strength.
The following method is often used to protect concrete from heat: an airtight cap made of PVC film with a thickness of at least 0.2 millimeters is created above the surface.
Concrete prepared according to the recipe is able to set, harden and acquire all design characteristics at an ambient temperature of +20 degrees and a humidity of about 100%. If work is carried out in frost or heat, it is necessary to take care of heating or cooling measures that will guarantee the strength and durability of the finished structure.
Infrared and induction methods
If you are thinking about how to pour concrete in sub-zero temperatures, you can also use the induction method. It is mainly used in crossbars, beams and purlins. This method is not very common due to the complexity of the device. It consists in the fact that the insulated wire creates induction and heats the fittings around which the element is wound.
Warming up using infrared rays is based on the ability of the latter to heat the surface of transparent objects with heat transfer throughout the volume. When using this method, the concrete should be wrapped in a transparent film, which will transmit the rays through itself, preventing the heat from quickly evaporating. The advantage of such heating is that transformers do not need to be used. The method also has a drawback. It is expressed in the inability of infrared radiation to uniformly heat large structures.
If you plan to pour concrete in sub-zero temperatures, you should know that the method described above is only suitable for thin structures. Regardless of what type of electric heating is used, you need to monitor the temperature. If it rises above +50˚C, it will create dangerous conditions. The heating rate (as well as cooling) should not exceed 10 ˚C per hour.
Advantages of a winter foundation
Constant changes in climatic conditions have led to the fact that “winter” construction conditions can occur even in September. This is due to the fact that sudden frosts and subsequent thaws make adjustments to the concrete pouring technology used by specialists. It is worth noting that there may not be snow, but in the northern regions of the country, where there are very few warm days, the average annual temperature does not exceed +5 ˚ C. That is why innovative foundation construction technologies have been developed, which are designed to extend the construction season.
Now you can pour high-quality concrete even at a temperature of -25˚ C. This significantly speeds up the construction of new buildings, since with the arrival of the first spring days you can safely begin building walls. If the house is built of wood, then its construction can continue - regardless of the temperature.
What other substances can be used to heat concrete mortar?
We looked at how many degrees below zero it is possible to pour concrete. It should be said that antifreeze additives are most often used. Among others, it is allowed to use calcium carbonate, which is also called potash. This crystalline antifreeze component accelerates the hardening of concrete and is recommended for use exclusively together with sodium tetraborate (sulfide-yeast mash). Many people know it better under the name “borax”.
Calcium carbonate added in its pure form may reduce the strength of the structure. The amount of sodium tetraborate and mash should be no more than 30%. When choosing additives for concrete at sub-zero temperatures, you must take into account that potash is a dangerous substance. It can only be used in compliance with safety precautions. Sodium tetraborate can be used as a stand-alone additive. This additive is a mixture of sodium, ammonium and calcium salts. The sodium tetraborate impurity preserves the structure of the structure. Borax eliminates the occurrence of cracks and reduces the water permeability of concrete. Its strength increases by 30%.
How long does it take to warm up concrete?
The concrete is heated until it reaches critical strength (30-50% of the design strength). This usually happens on the 4th-6th day.
The strength of concrete is determined by the actual temperature conditions using graphs.
To more accurately determine the timing, laboratory tests are used, for which sample castings are made and allowed to gain strength under the same conditions as the main structure.
The use of anti-frost additives during winter concrete work guarantees the production of high-quality concrete structures even in conditions of negative temperatures. Combining the use of antifreeze additives with the thermos method or heating the concrete not only guarantees strength gain, but also reduces the duration of heat treatment, which means it saves energy and increases the turnover of expensive equipment and formwork. Proper use of warming measures and anti-frost additives in accordance with the technological map allows us to obtain high-quality winter concrete.