You are on a page that is a guide on the topic “painting a bathhouse”. This means that here we briefly consider all the options for painting a bathhouse - inside, outside, in rooms, on surfaces, and you will find more complete and detailed materials on the links that are given right there. If a question has not been addressed in any of our materials, a detailed answer is given.
Types of paints
In the bathhouse we will use the same set of paints and varnishes that you could use in a residential building . Of course, there are nuances associated with the steam room, but there are few of them, and you are almost unlimited in your choice.
You can use a variety of varnishes, paints, and impregnations in the bath. If finances allow, then at least inside it would be nice to use water-based varnishes and paints - these are acrylic, acrylic-silicone varieties. They are non-flammable and safe for humans both during application and during operation. But they are still not cheap.
A more detailed overview of the available options for what and how to paint a bathhouse can be found at this link.
Method of protection
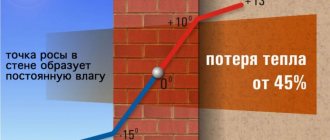
To prevent moisture from damaging the door, you need to prevent it from getting inside. For this purpose, the door is painted. During polymerization, the layer of dye forms a protective film. For best protection, apply two coats of paint. Now moisture will not penetrate inside.
But the process of moisture penetration will resume when the protective layer of paint or varnish cracks. And this happens quite quickly, because the doors experience dynamic load during operation: in other words, they are opened and closed several times a day and not always lightly.
Many manufacturers are trying to use elastic coatings. They change their geometry along with changes that occur under dynamic loads. In addition to oil and varnish coatings, oil processing of products began to be used. This method of moisture protection works as follows:
- the oil penetrates into the wood, closes its pores, making it impossible for moisture to enter them;
- in the connections of individual parts, a single solid structure is formed from a polymerized oil coating. The joints are filled, all existing cracks are closed.
Painting inside
Let's briefly go through all the issues related to interior painting. First, we will touch on issues related to surfaces made of different materials, then we will move on to the specifics of the premises. You will find details here in the article about painting the inside of a bathhouse.
Types of surfaces
Depending on the material and location of the surface, the requirements for coating change.
Floor (concrete, wood)
In the bathhouse you can find floors either made of wood (more often) or concrete (less often and only in wet rooms).
Wooden floors can be treated with impregnations that protect against moisture, biological hazards and fire. This can be either a separate impregnation with certain properties, or a multifunctional composition that combines several useful properties.
Impregnations can be used as a finishing coating or as a precursor to the application of the finishing coating.
The final coating for a wooden floor can be either
varnish or paint. Both can be of very different compositions, of which those with the addition of polyurethane have the greatest strength. (Although there is also a pure polyurethane varnish).
Concrete floors also need protection - they will last longer if they are treated with varnish or paint. Both are produced simultaneously for stone, brick and concrete.
If we are talking about floors in the steam room and washing room, then you need to understand that these are floors along which used water flows. Therefore, you should pay attention to waterproof paints , for example, those made for painting concrete pools.
You can read more about all the available options for painting bath floors made of concrete and wood here.
Ceiling and walls (wood)
Walls and ceilings are usually coated with the same composition . And the material in the vast majority of cases will be wood.
Wood can be coated with water-dispersed acrylic and silicone paints, alkyd and oil paints. Regarding varnishes, the picture is the same: you are free to use any varnish, and there is no need to even look at its wear resistance.
You should pay attention not only to the price, but also to toxicity, drying time, hiding power (the number of layers and paint consumption depend on it).
If you want to know which option is the best, let us tell you our opinion - water-soluble varnishes and paints. Then decide for yourself.
Another option is impregnation, which makes the wood waterproof, protects it from mold (contains an antiseptic) and dirt. Such impregnations can be either oil or acrylic. Adding color can change the color of the impregnation, and without color it will be colorless or pearlescent (the Finns have such