What is caulk? Essentially, this is the process of compacting a log house with fibrous materials - moss, tow and others; in this case, heat-insulating material can be used as inter-crown insulation - flax-jute fiber, polyurethane foam, for example. But caulking correctly is not so easy - you will learn about all the intricacies and features of this process from this article. So, how to caulk a log house - with moss, tow, tape and sealants.
- 3 Video selection of examples of caulking
- 4 What tools are needed for caulking
Why do you need to caulk a bathhouse?
Craftsmen usually answer such a question simply - so that the log house does not rot or fall apart. Without a seal, a log box becomes a cold, eternally creaking hut. If you do not caulk the bathhouse and seal the seams hermetically, then the supporting surfaces of the crowns will rot in a year or two and the log house will simply “sit down” or fall on its side to the north.
In addition to choosing how to caulk a log bathhouse, it is important to do the job correctly, so we will try to understand the means, tools and rules for caulking a bathhouse.
For high-quality seam sealing you will need:
- Packaging jute, flax tow, proven over the years, or any other type of sealant with a fiber structure;
- A set of tools - a wooden hammer, a spatula, a wedge knife and a hook for stripping a seam or an electric groove;
- Brush with stiff bristles;
- Carpentry measurer.
Advice! There are few tools, but they will all be needed for the job. The first time you can rent them. After your first practical experience, it will become clear how to properly caulk a bathhouse, then you can buy a good kit or make it yourself.
If you want to seal the seams with sealant, fortunately there are quite a lot of different brands and types of them sold for bathhouse needs, then in this case no tool other than a nozzle gun for a tube with liquid polymer will be needed at all. It is possible and necessary to spray the joints with sealant for a log bathhouse in one day; the technology requires laying the paste-like mass in two passes with a difference of no more than four hours. Any disruption of the process can lead to peeling of the sealant, whereas caulking the frame of a bathhouse can be done in a couple of days with interruptions.
Moss as insulation
Moss has been used for house insulation for a long time. Thanks to its properties and qualities, it has always coped well with its tasks. It retains heat well, absorbs excess moisture, is vapor permeable and environmentally friendly. Moss contains amazing antiseptic substances that prevent the development of mold, fungi, rot, and insects in crown joints. There are hundreds of its varieties, but only cuckoo flax (red moss) and sphagnum are used in construction. They are low cost. You can also find and collect them yourself in swampy places. They are also slightly different from each other. Red moss is tough and durable. It has long fibers, the top of which is greenish and the bottom red or even brown. It has good moisture capacity, but still to a lesser extent than sphagnum. It is easy to lay between logs. Basically, the fibers of red moss on the crowns are placed crosswise so that the moss is firmly fixed and after it is completely dry it does not blow out of the seams. But without proper experience, working with him is still not easy.
Sphagnum moss is easier to prepare than red moss. It has shorter fibers and is completely light green in color. For the first stage of insulation, laying between logs or crowns, it is less suitable than cuckoo flax, because after a certain time, due to its small size, it will begin to be blown out of the seams by the winds. At the same time, it absorbs moisture well and is not afraid of temperature changes, which is why it is indispensable in insulating a bathhouse.
And to the question of which moss is best to use when assembling a log bathhouse, we answer: for a bathhouse it is best to choose, buy and use white moss called sphagnum.
How should you caulk a log house?
A number of requirements apply to materials for insulation: it must be resistant to sudden changes in temperature and moisture, prevent heat loss, not be toxic and not lose its properties for many years. There are several types of materials used for these purposes.
A material with a long history, it has unique properties: it provides good thermal insulation, has a long service life and has an antibacterial effect. However, it must be selected very carefully: moss that is too wet causes the timber to rot, and moss that is too dry causes it to break and crumble. The cost of moss is higher than other materials; it is quite difficult to install. Therefore, experts recommend caulking the log house with tow mixed in equal parts with moss. Before laying in the cracks, the moss must first be wetted and slightly dried in air.
Being an environmentally friendly insulation material, jute is characterized by high strength, good thermal insulation properties and natural composition. It practically does not absorb moisture, thereby extending the service life of the log house. There are several varieties of it:
- Jute tow. Rigid insulation of low density, they will have to be caulked several times.
- Jute felt. Dense and flexible eco-material, which must first be treated against parasitic insects and rotting.
- Flax-jute. Non-woven fabric that looks like flax wool. Flax-jute is resistant to mold, parasites and rot, and also removes excess moisture from the room.
Lnovatin
Tape natural insulation, which is made from flax fibers and has good thermal insulation properties. At high humidity it absorbs water, and at low humidity it returns it, thereby preventing the logs from rotting. However, it quickly becomes infested with insects, and its service life is only 3 years. It must be treated with special solutions against parasites before installation.
Tow
The most inexpensive and popular environmentally friendly material for sealing seams. Insulating a log house with tow makes it very warm. But its main drawback is its fragility. During the shrinkage of a wooden house, the tow begins to rot, becoming dust. The maximum period of its use is 3 years. After this time, it needs to be changed and the log house must be re-caulked with tow, which is quite problematic and time-consuming.
Sealant
Modern sealants make it possible to quickly and easily insulate a house or bathhouse. They are usually used in tandem with natural inter-crown seals (jute or flax). The sealant applies smoothly and neatly, providing an aesthetically pleasing appearance to the wooden structure. However, it is only suitable for log houses made of rounded logs and is applicable only after shrinkage has completed. After coating the cracks with sealant, re-caulking is not required.
How to caulk a log house correctly?
Caulking the cracks of a wooden house or bathhouse is a rather painstaking process. First, inter-crown insulation is laid between the logs during construction. After the wood shrinks (after about a year), gaps form and the procedure must be repeated. The timber finally dries out 3-5 years after construction, during which time the final caulking is carried out. In this way, maximum thermal insulation of the building is achieved.
You can caulk a log house with natural insulation after shrinkage at any time of the year. The exception is when working with sealant: seams can only be sealed at temperatures above 0 degrees, otherwise the composition will not dry out.
There are two ways to insulate cracks:
- To the set. This technology is used when working with large gaps: the sealant is twisted into a ball and, gradually unwinding it, is hammered into the space between the logs. When filling large voids, it is necessary to twist the loop or turn the rope. You should start laying out loops from the top of the gap and gradually work your way down.
- Stretch. This method is suitable for closing small cracks: a strand is formed from the insulation, placed across the log and pushed inside the hole so that the material protrudes by about 5 cm. Thin rolls are formed from the protruding part and hammered inside.
For caulking, a wooden tool is more often used, since it is more gentle and causes less damage to the timber. When choosing tools, you should pay attention to their hardness - they should be made of softer rocks than walls. It is necessary to caulk the log house not only from the outside, but also from the inside. This process is carried out in a circle from the bottom up, since if you caulk each wall separately, the structure may warp. Particular care must be taken to fill the cracks at the corners of the log house, where the most noticeable gaps form.
Caulking log houses is a long and labor-intensive process that requires certain knowledge and experience. For this reason, it is worth entrusting this work to professionals. has been engaged in the construction of turnkey wooden buildings in Moscow, the Moscow region and the Central region of Russia for more than 15 years. Our team consists of 40 teams of experienced specialists with at least 7 years of experience. From us you can order a log house based on a ready-made project from the catalog, or create an individual project to suit your taste. You can get expert advice, calculate an estimate and place an order by calling 8(495)128-21-53, or request a call back on the website.
Choosing material for padding
Traditionally, seams and joints between wooden parts are sealed with a moisture-resistant, durable and necessarily easily deformable material. Interventional insulation for a bath can be made from:
- Synthetic polypropylene fibers, for example, in the form of a tape of woven and non-woven structure;
- Organic fiber, primarily jute cords and flax tow;
- Natural plant fibers from certain types of moss for baths.
For your information! Sometimes the problem arises of choosing whether moss or jute is better for a bathhouse, or they try to determine before starting work whether it is better to caulk with synthetics or organics. You need to choose based on the degree of shrinkage of the bathhouse frame and the size of the seam between the crowns.
What to put between the crowns?
To create a gasket between the crowns of a log house, there are many insulating materials. But not all of them are ideal for these purposes. First, you need to safely cross out synthetic and artificial materials from the list of candidates for inter-crown insulation. They will cope with the thermal insulation task well, but the price of their work will be damaged crowns of the log house. Artificial materials allow air to pass through well only when they are in a fluffy form, and when they are compressed by logs, they cannot do this, which will negatively affect the wood; it may begin to rot.
There is another drawback to these insulation materials - they are made from non-ecological components. And it seems to me that many people choose wood for construction in order to be closer to everything that is clean, safe and natural. The use of artificial, synthetic insulation will disrupt the entire beneficial microclimate of the room. It is for these reasons that I do not recommend focusing your attention on these insulating materials.
And it is advisable to lay insulation between the crowns from natural materials, which consist of fibers of natural plants. They also have good thermal insulation characteristics, but they are in perfect harmony with the wood and do not cause any harm to it. Among such materials are:
- Moss.
- Jute.
- Tow.
Many builders cannot make the final choice of insulation, deciding which of these three materials is better.
Moss can safely be called the best insulation material. Even with the advent and development of technology, they have not yet been able to invent and create insulation that is superior to moss, unless they came close to its characteristics by producing jute insulation. There are more than a hundred varieties of moss, but only brown and white moss have shown excellent results in construction. They practically do not differ in their properties, they only have differences in appearance. White moss consists of small light green fibers. It does not have a root system, despite this it grows well. White moss produces a very valuable product - peat. Brown moss consists of longer and tougher fibers that are greenish on top and brown on the bottom. Its stems resemble flax in appearance, which is why its second name is cuckoo flax.
What is better, moss or tow for a bath?
Today, both materials are recognized as the most durable and reliable of all traditional fiber seals. In both cases, the decisive factor is not even the type, but the quality of the preparation of the material.
Moss is recognized by all craftsmen as a universal means for sealing crowns. Most often they try to caulk the bathhouse with red or white moss. Bunches of plants are prepared 2-3 weeks before the start of work. Before caulking the bathhouse, remove debris and dry the moss under a canopy, periodically turning over and shaking the layers.
The organic matter should remain slightly moist. After drying, the fibers turn into a springy and strong wire-like structure.
Caulking walls with moss is not difficult; you just need to correctly measure the amount of material and the force of hitting the shovel with a hammer. The easiest way is to caulk the seams immediately on the new log house, after assembling the walls of the bathhouse. After shrinkage, after a year and a half, the procedure will have to be repeated with the same material.
For your information! Often, craftsmen who undertake to caulk the walls of a bathhouse tell stories about the bactericidal properties of mosses, the ability of the plant to germinate and completely fill the gap between the crowns.
In fact, the seal can bloom and turn green only if the birds have collected seeds and grass in the spring. If you caulk with organic matter, the seal can easily become a source of problems, from the appearance of fungus to green sprouts. Therefore, you still need to be able to prepare the moss for the bathhouse for caulking. If it’s too dry, the material becomes brittle and doesn’t hold well in the gap; too wet moss is very difficult to caulk into the seam.
Where to buy?
- The collected moss is sold in bags. Moss in bags should not be compacted too much, as this will disrupt its structure.
- It is better to buy moss collected from mid-June. It's almost ready to go.
- It is better to transport bags of moss separately from the log house. This will preserve its structure and will not crush it during transportation.
- It is better to bring moss, and therefore buy it, immediately before assembling the log house.
- After delivery, the moss should be poured onto a litter or into a container (an old bathtub). If you see that the moss is dry, you should moisten it by lightly watering it from a watering can.
- After wetting the moss, gently rub it, and at the same time remove forest debris (cones, branches, etc.).
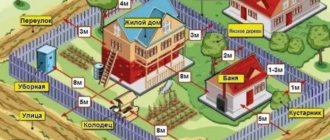
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Distance from the bathhouse to the fence: construction rules
Both of these interventional seals can be purchased from our specialized company. You can buy by going to our online store page here.
How to harvest moss for a log house
Collecting moss is a rather painstaking and time-consuming process, as it is harvested by hand. Each species has its own collection method and drying technology.
For example, ordinary white moss has a fairly fragile texture so as not to be damaged; the collected material is piled up (like hay) to dry. It is best to collect this moss in sunny and dry weather. It is in this weather that the moisture concentration in it is lower, which means the drying process will be easier.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Do-it-yourself pitched roof for a bathhouse
The best time to collect cuckoo flax is a cloudy day. The fact is that this species reacts poorly to direct sunlight. The quality of flax is also affected by the place where it is collected. For example, the one found in the forest under the trees will be of better quality, since its humidity will be much lower than that collected in the swamps. This will also reduce the drying time of the material.
The collected cuckoo flax is laid out on a straight surface in strips. After drying using this technology, you get something like a tape heat insulator. This material is very convenient to use as an interventional gasket.
In total, it takes from a week to two to dry moss for a log house.
About choosing insulation for a log bathhouse
Traditionally, a truly Russian bathhouse should be built only from larch, pine or spruce wood that grew far in the north. And no matter how precisely the beams or logs for its walls are adjusted to each other manually or in production, it is impossible to do without the use of insulating materials. Thanks to them, the bathhouse will quickly warm up to the desired temperature and retain heat inside the steam room for a long time. It is recommended to use only natural inter-crown insulation in the process of laying a log house.
Despite the wide variety of modern synthetic materials for insulation, none of them has such unique properties as plant fibers. In addition to being unconditionally natural and, accordingly, environmentally friendly, such insulation materials themselves are durable and help extend the service life of construction wood. By regulating the level of humidity, they prevent rot, which is the main enemy of wooden buildings.
Neither wool fiber, nor batting and padding polyester, nor sealants, nor thermal insulation tapes can provide that amazing microclimate of a wooden bathhouse, for which log houses made of timber and logs are especially valued today. Only moss, flax and jute as inter-crown insulation ideally correspond to the image and spirit of a truly Russian bathhouse.
Moss insulation
Moss has always been used in Rus' as a sealant for wooden log houses. And not only because its habitats, damp forests and swamps, occupy a significant part of the country’s territory. The unique qualities of this plant are valued: it does not rot at all and does not allow organic bodies and objects to decompose in the dampness of swamps.
Dismantling the log cabins of centuries-old wooden buildings, insulated from roof to floor only with layers of moss, one can observe perfectly preserved wood at the junction of the crowns. And the excellent heat-insulating properties of this plant have been tested by Siberian snowstorms and frosts. And a better alternative for sealing the frame of a wooden bathhouse has not yet been found.
Not every type of moss is used in construction. The so-called red moss copes best with the task of insulation. The biological name of this plant is cuckoo flax; it grows in the wetlands of the northern territories. It is less widespread in nature than white sphagnum moss, which is also used for thermal insulation of log houses.
Qualities that allow mosses to be considered the best inter-crown insulation:
- pronounced bactericidal properties that prevent the development of mold and rot;
- the strength and elasticity of plant fibers that form a well-retaining heat-retaining layer;
- vapor and gas permeability, allowing you to maintain a healthy microclimate indoors made of logs or timber;
- the ability to absorb excess moisture, promoting rapid drying of wood;
- natural environmental safety.
Compared to cuckoo flax, sphagnum is less durable. And although it is more convenient and preferable to use red moss for laying a bathhouse in a log house, white moss always turns out to be more accessible.
Jute insulation
The use of jute spacers between the crowns of the bathhouse frame is possible in the absence of moss.
This insulation is no less environmentally friendly, it prevents rotting due to the lignin content in its fibers, but is inferior to moss in terms of thermal insulation properties. But it is easier to install and visually more aesthetic. As a result of special processing, insulating materials are obtained from the annual jute plant: tow, felt and flax-jute. Long fibers of tow are suitable for compacting crowns during manual felling and as caulking. And tapes of felt and linen-jute, uniform in density and layer thickness, are convenient for insulating walls made of timber and rounded logs.
The disadvantages of this material include its ability to cake over time and its high cost.
Linen insulation
Flax has been used as a natural heat-insulating material in the construction of wooden baths for as long as moss. Today, tow and flax wool (eurolin) are made from it. Both types of insulation are durable and environmentally friendly, their density allows you to reliably isolate the inter-crown space of any type of log house from heat loss.
Ordinary tow, packaged in bales, is used to caulk cracks, and for laying in log houses, material is used in the form of a tape. Flax batting, which is also a tape made from weaves of flax fibers, has good thermal insulation properties, is cheaper than jute and more accessible than moss. But the hygroscopicity (ability to absorb moisture) of the material is much worse.
In order for the Russian bathhouse to be hot, but “breathable”, and the steam in it to be not just light, but healthy, by purchasing a beam or log of excellent quality, you should not skimp on inter-crown insulation. Its naturalness and optimal hygroscopicity will provide for many years maximum comfort, a charge of vigor and pleasure with every visit to a warm and cozy wooden bathhouse in any season.
How difficult is it to caulk the walls of a bathhouse with tow?
Tow or combed flax fibers twisted into bundles are safer than moss or jute. Due to its soft and thin structure, working with linen material is more difficult than with any other sealants. Tow is convenient for caulking the seams on the walls of a rounded bathhouse. Interventional gaps on log buildings are too large, so the fiber has to be folded into several loops. Technologically, this does not affect the quality, but it can seriously delay the caulking process over time.
Flax tow, thanks to the small amount of non-drying oils remaining in the fabrics, has the best damping properties of all possible sealants, both natural and synthetic. Tow for a bath is very well suited for sealing corner locks, especially hand-cut ones. When shrinking, the bathhouse log does not make frightening creaks and sounds; the process itself occurs without any complications.
The only drawback is the low durability of flax fiber. In a log house, tow caulk will last up to 5 years; in a bathhouse, the fiber burns out in 2-3 years.
Materials unsuitable for insulation
Option #1 - mineral wool
Ordinary mineral wool also cannot serve as a heat insulator for timber in any way - its threads have moisture absorption close to zero. All the moisture in this material is retained by the tension of the fibers and does not disappear anywhere. In addition, this material allows heat to pass through and even creates a dew point when lighting a bath. And yet, unscrupulous builders sometimes manage to use it.
Option #2 - isover
As for Izover, which has recently become incredibly popular, in those places between the rims where there is no gap, it is compressed almost 100%, and here its heat transfer is somewhat less than that of other material under the same conditions. But in the gaps, Izover is a little fluffy and copes quite well with its functions as a heat insulator. On the other hand, Izover’s ability to absorb and remove moisture is almost the same as that of many other inter-crown insulation materials, but this material does not burn, does not rot, does not need to be caulked, and over time it does not crumble like dust. Unpleasant dust can be eliminated with a sealed finish.
So, let's summarize. This is what Izover is preferred by many as an interventional insulation:
- Doesn't burn, doesn't rot;
- Convenient to use;
- It compresses well and leaves no gaps;
- Birds don't like it;
- Does not require additional caulking.
But this fashionable material also has a significant drawback: it is not very environmentally friendly, and when slightly torn, it emits caustic and allergic dust. It also quickly accumulates moisture... And many lazy builders convince future owners of bathhouses to use this inter-crown insulation - after all, it’s much easier for them to work: it cuts easily, just rolling out over the log, construction goes quickly and costs are less. That is why, despite advertising from neighbors, not many people want to install Izover in the walls of bathhouses - especially those who saw it in use: even with dry timber, the insulation turned out to be 2/3 wet.
Also, similar synthetic materials often serve as a dangerous source of phenol. So, let’s conclude: mineral wool in a compressed state does not remove moisture at all, and Izover, if not covered with a vapor barrier, completely turns into a sponge. The decision is yours.
Option #3 - polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is also used as inter-crown insulation. It is valued for the following properties:
- Fast technological installation.
- Good adhesion, thanks to which the timber sticks tightly together. When drying, it will not twist, and the steam room will not warp.
- Foam seals corners in a log house much better than moss or tow.
- Hardened one-component foam is not flammable and does not emit toxins, which, however, multi-component foam cannot boast of.
- The process of caulking after foaming is quite simple.
But with all its advantages, foam as an interventional insulation does not please with the following qualities:
- It is not elastic, which is why microcracks may appear over time (and wood, like any living material, can slightly change its volume).
- In winter it does not tolerate the cold well - it crumbles.
- Less resistant to ultraviolet radiation. Over time, it turns to stone and discolors from the sun.
- Not environmentally friendly enough.
And, let us note that polyurethane foam is used relatively little today as inter-crown insulation, and therefore many other negative consequences of such insulation are not yet known. But the foam itself is also used as inter-crown insulation in the following alternative:
- Option #1. The beams are laid half a meter apart, and after construction is completed they are foamed. This way it supposedly dries faster, and then the remaining wide gap can be foamed. Fast, airtight and no caulking required. From the inside of the bathhouse, the cracks are caulked with linen rope.
- Option #2. Before using the foam, allow the bathhouse to sit completely on the tow. After all, the settlement of the building occurs due to the shrinkage of the timber itself - and this is at least a year and a half. After that, a 5-centimeter gap is punched in the tow and the groove is foamed, and finally, the seams are protected with sealant.
As for the choice of foam brand, “Macroflex Pro” is so far most suitable for this purpose. In a word, there is a lot of material, and, as they say, as many people as there are so many opinions. There are also bathhouse owners who built their steam rooms ten years ago and are quite satisfied with Izover as a sealant. They claim that after rains the timber will be wet in place of the insulation, regardless of the type of insulation: it is moss or a modern material. And the main advantages become the decisive factor: they are cheap and easy to build. It’s just important not to take the cheapest Izover (also called Chinese) - you can really get poisoned from it.
Linen
Flax is a plant growing in Russia, Belarus, and Europe. Linen is very durable, has heat-saving, heat-transfer, and antiseptic properties. Linen fiber is used to produce fabrics that are used in various branches of light industry. Insulation (flax wool and tow) is made from flax. Ligin in flax is only 7%, which makes it unstable to the conditions of our climate. Rolled insulation - flax wool - is used as insulation in wooden houses and bathhouses. This is a special material for inter-crown gaskets. Linen is the most unstable insulation material. The service life of flax fiber is 1-3 years. It quickly rots when moisture gets on it and quickly disintegrates. Birds and rodents love this material.
It is loved by bedbugs, moths and many other insects. In view of this, it is necessary to antisepticize wood and all lumber. The roof extension in buildings where flax was used as insulation must be at least a meter. The main advantage of this material is environmental safety and excellent thermal conductivity.
Flax fiber insulation has proven itself to be excellent when caulking seams between logs, filling gaps when installing windows, doors, and insulating roofs, floors and ceiling surfaces. Linen is an excellent soundproofing material.
Eco-insulation materials
These invisible and at the same time irreplaceable helpers for creating home comfort are:
- synthetic (mineral-based, with two types of pores);
- natural (rope jute, moss, flax, hemp).
Synthesized insulation materials, despite the rapid technological development, are still not able to satisfy all the requirements for quality and durability. It is often their fault that the walls of houses “sink” and rot. This problem especially concerns buildings made of rounded logs, which are deprived of their protective coating during the production process and are therefore more susceptible to constant contact with moisture.
Types of natural interventional and artificial insulation
There are different ways to maintain a comfortable temperature inside a log house or bathhouse. However, no matter what type of wooden house is preferred by the owner, inter-crown insulation naturally helps to maintain heat in it.
Materials with these characteristics include:
- ribbon linen;
- moss;
- rope jute;
- hemp;
- tow.
The general properties of natural insulation materials are:
- low thermal conductivity;
- antifungal properties;
- bactericidal.
Each of the listed materials also has its own unique properties, which attracts an equal number of consumers.
Jute fiber
Mechanically combed stems of jute hemp Jute Tassa produce a tough and at the same time durable fiber, which is used not only as a sealant on the walls of the bathhouse, it is an ideal material for containers and technical fabrics. Jute is produced in the form of coils, ribbons, and ropes, which allows you to caulk cracks on the walls of a bathhouse many times faster than using tow and moss.
Technical jute has only two disadvantages:
- High hygroscopicity;
- Susceptibility to rotting when soaked for a long time.
Jute for a bathhouse is interesting because during the shrinkage process it ideally fills the inter-crown space, especially if the log house is built from chopped logs. In this case, you only need to caulk with jute fiber and rope.
If, according to the project, the bathhouse building is planned to be covered with decorative finishing, the jute rope will simply rot in a couple of years. The tapes are laid to seal the crowns of the new log house; the rope is good for finishing the open surfaces of the walls of the bathhouse.
In fact, jute occupies an intermediate position between dense and hard moss and soft flax tow.
What is the time frame for caulking baths?
When can the final stage of insulation begin after the construction of the log house?
If the frame was laid with moss, then it is necessary to cut off its excess. Then the remaining material is tucked into the cracks and carefully pushed inside. All. You should not be particularly zealous - the first caulking will take place six months after the completion of construction. During this time, the tree will finally shrink and excess moisture will evaporate. After completing the first caulking, you can install windows and doors.
A year after the first caulking, the second one is carried out as the last stage of insulation. After about five years, another caulking procedure may be used, which is optional and depends on what specific materials were used.
Advantages of moss insulation
Natural materials are especially highly valued in construction today. Technologies that have long been used in construction in Rus' are today regaining popularity among those who want to avoid artificial, often toxic synthetics as much as possible. Many common insulation materials reduce the environmental friendliness of a building because they impede the passage of air and water vapor. Moss is free from this drawback, as it fits harmoniously into the structure of the house, providing it with protection. Another plus is that cuckoo flax itself has antiseptic properties, so it also helps to increase the durability of the building.
Properly performed insulation using ancient technologies allows you to forget about drafts and ventilated corners, and the room will always be warm and comfortable. One of the advantages will be the forest aroma, which many people like.
Is it possible, using modern tape insulation, to do without secondary caulking?
No you can not. Despite the high surface density and uniform thickness of the insulation layer along its entire length, when settling a house, linen and jute fabric still shrinks up to 5–6% in its height, which is 10–15 cm per floor. This means that the resulting cracks will have to be sealed. This can only be avoided in the case of a building made of laminated veneer lumber, and not at all because of the special properties of the insulation, but only because such buildings themselves are practically not susceptible to sedimentary processes and lose only 1–1.5 cm of height per two floors .
Seam filling technology
The process itself looks easy. In theory, it is necessary to caulk the crowns of a successfully constructed bathhouse twice, immediately after construction and upon completion of the shrinkage processes. In practice, caulking is done every three years, especially if the log has not been sanded and rounded.
First of all, before caulking the bathhouse, you need to inspect the seams, check and free the joint line from the old burnt-out seal. If the gaps in the inter-crown space of the bathhouse are supposed to be caulked with a cord or rope, then you will first need to measure the maximum drawdown of the crowns with a gauge.
This is done in order to determine the uniformity of shrinkage of the bathhouse building. If on one side the seal is pinched and compressed, and on the other it has fallen out of the cracks, then before caulking the box you need to determine the reasons for the uneven settling of the log house. At the same time, we specify the required thickness of the jute or flax hemp rope.
How much material will be needed?
It is impossible to accurately derive a formula by which you can calculate the amount of material for sealing cracks.
Natural material, be it jute or moss, is highly compacted and compressed when processing cracks. So its consumption can be quite large. First of all, material consumption depends on the methods of processing logs and cutting grooves.
In any case, you need to buy material for caulking with a large supply - it will not go to waste and will be useful for a repeat procedure. As for industrial sealants, as a rule, the manufacturer indicates a method for calculating the approximate number of packages.
Sealing the material with tape
The easiest way to caulk a bathhouse is with a tape seal. After measuring the cracks, it becomes clear what width of tape should be used in this section of the log house. One end of the roll is secured in the gap at the corner, the sealing strip is carefully unrolled along the wall without twisting, a margin of 20-25 cm is left and cut off.
The ribbon laid out on the gap is carefully tucked into the gap so that the material does not sag or be stretched. Caulking begins from the widest edge, using a hammer and a wooden spatula with a rubber tip. The ribbon is pressed into the slot with light blows. It will be necessary to make 3-4 passes so that the sealant evenly and completely fits end-to-end between the crowns.
It will be necessary to caulk three or four pieces of tape before the desired joint seal can be achieved.
For your information! In this way, the cracks along the entire perimeter of the crown are sealed before it is possible to move to the next higher level.
If you caulk the entire wall at once, then one edge of the log house may rise by more than the thickness of the log, which will lead to the breakage of the upper rows of the bathhouse.
Application
Technique for laying inter-crown sealant on a log
Let's look at how to properly use the material in your work.
Laying moss.
Moss must be laid in the following way:
- If it is dry, then tamp it in a barrel and fill it with 20 - 30 liters of water. Leave for half an hour, drain the water, and squeeze out the moss.
Remember! Dry moss does not allow itself to be manipulated, so pre-washing will allow the material to become more pliable.
- Take ready-to-install moss.
- Lay it across the log without compacting it. Please note that the seal must lie evenly.
- Make sure that the width of the layout is 200 - 250 mm, and the thickness is 40 - 50 mm.
- Laying in the bowl is made with a thickness of 4–5 cm, and the protrusion beyond its limits is 5–10 cm.
Advice! Lift one end of the log and place it on the bowl, then lift the other end, about 50 - 60 cm higher from the place of laying, so as not to move the moss, and release it into the opposite bowl.
- Tap the entire surface with the headstock.
- Perform all subsequent actions as described in paragraphs 2 – 7.
- Take a construction stapler and secure the laid material every 30–40 cm.
Tow is less problematic to work with, since the finished canvas does not require additional time for cleaning and even laying on the log.
Tape jute is especially convenient to use.
It differs only in the installation methods:
- If the timber is for a bathhouse, profiled, glued, then we lay the insulation without bends. We don't use a stapler.
- If the log is ordinary, profiled with natural moisture, then the material must be folded once with a lock. Make sure that the canvas does not extend beyond the edge of the end.
- If the bathhouse is built from a wild log house, a fire monitor structure, or from a milled log, lay the tow in two layers. Use a stapler to secure the fabric.
Attention! Crumpling the canvas is prohibited, as this leads to poor shrinkage and further damage to the wood.
Log caulking technology
Caulking is a stage in the construction process whereby gaps and crevices are filled with a special material to prevent the inside of a room from coming into contact with the outside environment.
Kinds:
- stretch (photo);
Caulking of a stretched log house.
- set (photo).
Caulking set.
The goal of the work is to fill the visible cracks tightly, without gaps.
Progress:
- Select a specific area as the primary task.
- If the material is in a log (just insulated), push the protruding part into the gap.
- Take the caulk in one hand and insert the tool into the crack.
- After it stops falling into the gap, proceed to tapping it with a mallet.
The caulking process goes like this.
- Next, compact the next section on the same log, and so on, along the entire length in a circular direction.
- After external caulking of the bath, proceed to the internal filling.
Remember! One log needs to be compacted, both on one side and on the other.
Modern caulking tool.
After 12 months the process must be repeated.
Caulk joints of tow
The procedure for sealing the inter-crown space with bundles of fibers, such as tow or linen yarn, is a little more complicated. After cleaning the seam between the logs, the future place where the tow will be laid is rubbed with a mixture of formaldehyde, alcohol and linseed oil. You can impregnate individual cords with a disinfectant mixture before laying them in the wall of the bathhouse.
You need to caulk the bathhouse wall in the same sequence as when using tape. If the thickness of the seam is small, then the material can be laid by immediately rolling cords of 2-3 mm thick from the fiber. A tightly rolled roll of tow applied to the gap, without blows, is carefully pressed into the gap with a spatula.
For the next pass, roll up a thicker cord from tow, about 3-4 mm; this time you need to caulk the seam with force. For the last pass, a thick rope is rolled up, sometimes up to 8 mm. The material is hammered into the gap so that the edge protrudes above the line of the bathhouse crowns by no more than 3-4 mm.
If there are wide cavities between the crowns, they are caulked with additional ropes made of tow with a lubricant of any rubber-based elastic adhesive. In the same way, cracks in the logs of the bathhouse walls are clogged. The repaired areas are rubbed with additional acrylic paste.