- Dense sand (coarse, medium, with gravel). An excellent foundation for building a house: the water drains quickly and the foundation is reliable. On such soils, you can build a house on a shallow foundation (laying depth from 50 cm).
Quick sands (fine and dusty). If the groundwater is deep, construction is possible. But these soils are dangerous because they float when saturated with water.
It is necessary to determine what kind of soils are in each layer.
Difficulties often arise when trying to distinguish clay-containing soils. Sometimes it is enough just to look at them: if sand predominates and there are inclusions of clay, you have sandy loam in front of you. If clay predominates, but there is also sand, it is loam. Well, the clay does not contain any inclusions and is difficult to dig into.
There is another method that will help you make sure how correctly you have identified the soil. To do this, roll a roller from moistened soil with your hands (between your palms, like you used to do in kindergarten) and bend it into a donut. If everything has crumbled, it is low-plasticity loam; if it has fallen into pieces, it is plastic loam; if it remains intact, it is clay.
Having decided what kind of soil you have in the selected area, you can begin to choose the type of foundation.
What is a strip foundation
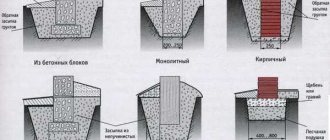
Figure 1. Construction of a strip foundation
A strip foundation is the most common type of foundation for cottages and other buildings. This is a reinforced concrete structure, usually in the shape of a rectangle, which is characterized by increased strength. The use of tape not only allows you to freely transfer the weight of the walls, but also provides the building with a long service life.
The main advantages of a strip foundation for a house are:
- simple and quick installation;
- Possibility to equip basement premises.
Types of strip base:
- not buried;
- shallow;
- recessed
Each type of strip foundation implies its own depth . This parameter is important, as it has a significant impact on other indicators and characteristics. Before starting construction work, it is necessary to correctly calculate how deep the foundation should be .
Important: do not confuse concepts such as foundation depth and trench depth. The size of the latter can be many times larger if an additional pillow is used.
Preparing a foundation pit and load-bearing cushion for a two-story house.
Strip foundation depth for the house.
Preparing a pit for a two-story building.
Having developed a foundation pit, the bottom is measured using a level and the edge and area are cleared of crumbling soil. Then markings are made for the load-bearing concrete pad. The width of such concrete preparation is 100−1200 mm, with a thickness of 150−250 mm. It can be used to mount both a monolithic foundation and a block one. The formwork is prepared according to the diagram, installed around the perimeter, using reinforcement as stops, simply driving them into the ground.
Reinforcement is done in one tier, with class A 1-3 reinforcement. The mesh cell has a size of 200×200 mm, the joints are knitted with wire. The laying depth of the load-bearing belt is at least 1.8−2.2 meters for medium heaving soils of type 2. What is important when laying is to make a cushion of crushed stone under the base. The thickness of the pillow for a two-story house must be at least 120 mm. Crushed stone is laid on compacted soil. Then water drainage measures are installed or waterproofing material is laid. If construction is frozen for the winter, a pit is dug at the lowest point of the pit to collect water. The size of the sump (storm pit) must be at least 6 cubic meters.
Deepening the strip foundation
Before determining the depth of the strip foundation , you should decide on its type. When constructing a foundation for a one-story house made of foam blocks, wood or brick, a shallow type is suitable. The standard depth is 70 cm.
The recessed type is used for buildings with considerable weight, and is also used in the construction of houses where the presence of basements is expected. In this situation, the depth will be GFP (soil freezing depth) + 20-30 cm.
For heated buildings, it is allowed to calculate how much to deepen the foundation, without taking into account the GPP. However, it should be borne in mind that the work will need to be completed before the onset of frost.
The minimum depth of a strip foundation for objects without heating is: average GPP + 20-30 cm. For heated objects, the value decreases by 20-30%. If the building involves a basement, then measurements are taken from its floor.
When placing the base on sandy soils, penetration above the GLP line is allowed if the base is located no closer than 50-60 cm to the soil level. If water passes nearby, or the soil is very heaving or deeply frozen, then it is better to abandon the tape.
Important: the foundations of the main building and the small structures adjacent to it must be located at the same depth. Different levels are only allowed if there is a large difference in the loads on the base.
Average values for different types of buildings
Another indicator that should be taken into account when calculating is soil resistance. For the main types of soil it is as follows
- dry dense clay – 1.6-3.0;
- coarse sand – 3.6-4.6;
- medium-grained – 2.5-3.6;
- fine-grained – 2.2-3.4;
- sandy loam – 2.6-3.6;
- loam – 1.6-3.0;
- gravel, crushed stone, pebbles – 5.1-6.5.
After this, you need to determine the weight pressure of the building. For main building structures these indicators are as follows (in kg/cm2):
- plank walls with insulation – 30-50;
- log – 80-120;
- expanded clay concrete – 460-580;
- brick – 570-970;
- overlap on wooden beams – 120-160;
- basement – 170-300;
- reinforced concrete – 320-550.
By calculating the weight of the building and comparing the result with the calculated soil resistance, you can determine whether a strip foundation is suitable for your building. It also happens that you have to think about how to make the building lighter or choose a different type of foundation. We provided a complete example of calculating a strip foundation here.
What factors influence depth
Figure 2. Strip foundation
When planning to make a strip foundation, the main attention is paid to depth, since this parameter is key and affects many characteristics. The higher the sole is located, the less money the owner will have to spend. However, strong savings are unacceptable, as they can lead to unsatisfactory results.
When determining the depth, take into account:
- GLP level;
- location of waters;
- heaving;
- structural features;
- type of soil.
Important: the upper layers are characterized by changes in properties depending on weather conditions, so it is advisable to bury the base in stable soils.
How to reduce the impact of freezing soil:
- create a sliding layer on the sides of the base using a material with a minimum coefficient of friction;
- fill the base in a trapezoidal shape, narrowing upward;
- protect the foundation with systems configured against waterlogging.
Modern materials
Non-buried or slightly buried types of foundation require additional measures to distribute the load. The use of geological textiles here is justified by both price and quality of the material.
Using the method of continuous monofilament weaving, manufacturers make beautiful geotextiles. By placing it at the bottom of the trench under the foundation pad, you will increase the percentage of stability of the building. On slightly heaving soils its use is justified.
Capillary-type waterproofing, a roll of thick dynamic plastic with recesses, will serve to remove moisture in the foundation areas. Not allowing moisture to pass through and collecting capillary moisture in the recesses, such waterproofing has all the advantages when arranging the base.
And the level (depth) of the foundation can be any. The use of bimetallic reinforcement for reinforcement has become justified. A material that does not rust, which allows it to be used for different laying depths.
Insufficient depth leads to subsidence, but this can be corrected. By installing piles along the bottom of the trench, you can strengthen the structure with them by pouring concrete on top. It is not difficult to calculate what the depth of the strip foundation will be; you need to take into account the weight of the building with all the finishing work.
Formula for determining value
To correctly determine the depth of the tape, you must first calculate the GPP in the area. Calculations are made according to the formula: Df=kx Dfn, where:
- Dfn – standard indicator of GPP;
- Df – calculated indicator of GPP;
- K – coefficient taking into account the influence of heating.
After the calculations have been made, the properties of the soil are determined at the site where the foundation will be located, for which soil samples are taken. This procedure is best left to professionals.
Then they calculate at what depth the groundwater is located. This is done by drilling a hole up to 3 m deep, into which a tube is lowered, which is used to measure the liquid level at different times of the year. A similar procedure is necessary to determine whether groundwater is capable of rising above 2 m to the GLP.
Based on the data obtained, the depth can be calculated using Table 2 of SNiP 2.02.01-83.
Key points
- The foundation must be supported by soil that provides sufficient bearing capacity;
- In some types of soil (for example, clayey), the foundation must separate layers where seasonal movements caused by moisture and other reasons are likely. And also “cut through” those layers of soil that move when frozen;
- The strip foundation cannot be supported on soils whose bearing capacity is lost with increasing soil moisture.
There are several reasons why the depth of the tape depends. There is a possibility that after the calculations are completed, the “ribbon” will have to be abandoned in favor of another structure, for example a slab. For a competent calculation, you first need to know the structure of the soil, the level of subsurface water and the freezing depth. Without this, nowhere.
If the soil on the site is homogeneous, this is already good. This means that the foundation will settle evenly and will not crack.
Methods for reducing depth
The depth of the strip foundation directly affects construction costs. To build a one-story house, a deep foundation is not required, therefore, the costs will be low. However, for heavier and more massive buildings, considerable costs will be required, which owners are trying to reduce by reducing the depth.
One of these methods is soil replacement - first, they dig a pit much larger than required and replace the heaving soil with non-heaving soil. This method is quite complex and difficult, as it involves large-scale work.
Another option is to use blind areas - concrete platforms to lower the GPP and prevent it from becoming waterlogged. The blind areas must have a slope of up to 10 degrees, and their width is determined based on the properties and type of soil.
It is possible to lower the boundary of the passage of groundwater passing under the object due to ditches equipped with outlets for liquid. Such designs are very effective and eliminate excess liquid in spring or rainy weather.
Dependence on groundwater level
Underground springs, which are located in the upper layer of the earth, oversaturate the soil with moisture and gradually destroy the integrity of the reinforced concrete foundation. This factor must be taken into account when designing the foundation. The developer can hire a surveyor to perform a hydrogeological analysis or do the research themselves.
Deep occurrence of hot water
When groundwater passes below the frost line, the house is practically unaffected by it. The defining dimensions in this case are calculated only taking into account the geology of the site and the weight of the structure.
Above or at the level of the frost line
For the developer, such hydrogeological conditions are considered unfavorable and require compensatory measures. To avoid destructive effects, the tape is lowered below the frost line by 0.15 - 0.2 m.
Such a foundation should be classified as a buried type. Several layers of waterproofing are prudently laid between its layers.
Rocky, coarse-grained, gravel and similar rocks are dense enough that the engineer does not have to take into account the occurrence of sources in the calculations.
Insulation of strip foundations
Professionals and engineers argue that a shallow foundation needs to be insulated at the time of its construction. High-quality thermal insulation will not only protect the building from dampness, but also protect it from the cold in the winter season.
In what cases is thermal insulation necessary:
- when using a shallow foundation;
- if there is heating on the ground floor.
This procedure is also recommended in areas with heaving soils, since when they freeze, they increase in volume, which leads to the pushing out of the foundation, and when heat sets in, uneven thawing occurs. This contributes to the formation of cracks and destruction of the building.
How to insulate the foundation:
- Expanded polystyrene - this material has proven itself well and is perfect for insulation in all regions of Russia, including the northern part.
- Polyurethane foam - the material is applied in an even layer, forming a durable coating that does not deform under external influence. However, its use requires special equipment and skills.
Important: regardless of what material was chosen for thermal insulation, waterproofing the foundation remains a mandatory item. Without it, insulation becomes a useless procedure.
Frost-resistant soils under the foundation
On unstable soil, it makes sense to replace its top layer with coarse rocks that do not support the capillary supply of water, do not heave and do not destroy the foundation.
Experts advise installing a sand and crushed stone cushion, sometimes mixed with old soil, not only under the tape monolith, but also around it.
The listed methods can be combined to achieve better geological conditions and reduce the depth of the base.
Common mistakes when pouring a foundation
When pouring a strip base, many people make common mistakes that lead to unsatisfactory results. Among them:
- Filling above the GPP level, which ultimately contributes to the formation of cracks and destruction of the building.
- Ignoring the load on the base of the foundation, which leads to the collapse of the house.
- Ignoring the level of groundwater - if they lie in close proximity, then upon contact with the foundation they will contribute to its destruction.
When determining the depth of the strip foundation, it should be remembered that this is an extremely important parameter, the calculation of which must be approached with all responsibility. Only by taking into account all the nuances, features and indicators can you build a reliable house that will last for a long time.
Basic Ribbon Options
Over the years, cracks may appear in a reinforced concrete monolith if the foundation was not laid deep enough during the construction phase. The dimensions of the tape are determined taking into account the characteristics of the soil masses in the built-up area.
The relationship between the geological characteristics of the soil and the depth of the belt is reflected in the table below:
| Underground part of the base, m | Freezing level | |
| non-heaving soil, m | medium heaving soil, m | |
| 0,50 | up to 2.0 | up to 1.0 |
| 0,75 | 2,0 – 3,0 | 1,0-1,5 |
| 1,00 | more than 3.0 | 1,5-2,0 |
Concrete floor height
This is a calculated value that is directly dependent on the degree of heaving of soil masses, the occurrence of groundwater and the massiveness of the structure.
As a rule, a trench for reinforced concrete tape is dug at a depth of 0.2 - 0.3 m below the freezing level of the ground. The base protruding above the ground should not be larger than the underground part of the base.
Read more about the height of the strip foundation in this article.
Width
An equally important parameter is the width of the tape .
To make calculations, the engineer needs to know the resistance of the soil masses, as well as the weight and dimensions of the building. By correctly calculating the width of the tape, the master will ensure uniform distribution of pressure on the ground under the structure.
The basis for calculations will be the results of geodetic, geological and hydrometeorological surveys. If the developer does not have the opportunity to order such a service, he can rely on reference information for his region.
Peculiarities
The strip foundation is supposed to be installed around the perimeter of the house, including under the internal load-bearing walls. Often such a foundation is built under heavy houses made of natural stone, brick or concrete blocks. But it is also compatible with buildings with reinforced concrete floors. Another advantage of the tape is its suitability for placing basements and cellars. It is much more difficult to equip slab structures with such premises, and sometimes even impossible.
Already a general description shows that the depth of the tapes is usually quite large. However, the simplicity of the technology used justifies its use in low-rise buildings and in the construction of auxiliary facilities. Strip foundations also work well even where there is a risk of uneven shrinkage of the building. This is usually due to the heterogeneous composition of the soil, which has different mechanical characteristics. When constructing a basement, you can use foundation structures in the form of ready-made main walls.
The service life depends greatly on the material used. Thus, concrete and rubble stone can last up to two centuries in a row. But a lot depends on:
- applied load and its changes;
- quality of materials used;
- characteristics of the solution;
- soil properties and climatic parameters of the area.
The tape can be made in monolithic form, from prefabricated blocks, or a combination of these two approaches.
To make the foundation, in addition to concrete and rubble stone, sometimes a mixture of them or brickwork is used. The tape is made both in the form of a straight contour and with breaks, the geometric shape is a rectangle or trapezoid. In any case, the width is taken no less than that of the supported wall, and ideally 100-150 mm more. The wide variety of types of strip foundations does not mean that they can be chosen arbitrarily; there are quite strict construction standards.
Features of the arrangement of the MZLF
The task of building a foundation with your own hands is quite feasible. The fulfillment of a number of conditions will help ensure the strength and durability of the MFFL:
- The strip foundation is poured in one go; reinforced concrete M200-M300 is used for the solution.
- The width of the trench exceeds the size of the supporting structure for further thermal insulation and bedding design.
- Accelerated drainage and uniform load distribution are facilitated by a drainage cushion under the base of the strip foundation.
- The insulation of the EPP sole helps reduce the impact of heaving forces during frost.
- Waterproofing and insulating the side surfaces of a strip foundation significantly increases its service life.
Correct calculation of the laying depth and compliance with the construction conditions during the construction process will ensure the integrity of the strip foundation and the entire structure for a long period.