It is well known that without a supply of hot water, a steam room in a bathhouse loses its attractiveness. Even the simplest heat exchanger in a sauna stove will provide plenty of boiling water for spraying the heater and washing in the shower. But not everything is so simple, the performance and reliability of heating depends on how well the design of the water heating circuit is chosen, how well the heat exchanger is located in the sauna stove. And also the comfort and mood of bathhouse visitors. Not to mention the need to maintain basic sanitation. Therefore, there is no point in running with buckets to the next room when there is a simpler solution.
Installation and connection
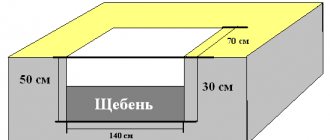
How to mount the heat exchanger is shown in photo No. 1:
Photo No. 1 Connecting the heat exchanger
Photo No. 2 - required slopes and dimensions
Step-by-step instruction:
- Let's determine a suitable location for the remote container. It is hung on the wall, 100-300 mm above the heat exchanger.
- The tank should not be hung directly on the wall of the bathhouse. First, we attach the guides with dowels - 2-3 wooden dies. Then, already on them, we hang the tank. The gap between the wall and the container must be at least 20 mm.
- To strengthen the structure, use special brackets, securing them under the bottom of the container. When assembling the container, do not forget to provide holes through which it will be attached.
- We will need 4 pipes: one for direct supply, the second for reverse supply, the third for filling with cold water, the fourth for the consumer. Place a check valve on the third pipe, and connect the tap and shower to the fourth.
- Using fittings, connect the remaining 2 pipes (forward and return) to the heat exchanger using good copper or steel corrugated pipe. Don't forget to seal all connections.
- We install a valve on the return line to drain the liquid. It must be installed so that it is at the lowest point.
- We attach a low tank with a heat exchanger to the wall of the furnace. How to install a heat exchanger on a sauna stove is shown in photo No. 1, and the necessary slopes are also shown there (photo No. 2). It can be built-in. Work must be carried out in compliance with safety regulations.
- Using fittings, we connect the forward and return supply pipelines.
Tank with water circuit connection
The heat exchanger in the form of a tank located around the chimney is made of stainless steel or galvanized sheet. In this case, the design of the furnace should be taken into account. If it has a combustion mode for flue gases, and the smoke temperature at the furnace outlet does not exceed 200 degrees, you can use any material to make the heat exchanger.
In simple stoves without smoke circulation, the smoke temperature at the outlet can reach 500 degrees Celsius. In this case, it is necessary to use stainless steel, since the zinc coating releases harmful substances when heated strongly.
Most often, heat exchangers of this type are installed on a sauna stove and used as a water heater for domestic hot water. The tank is equipped with fittings in its upper and lower parts, and pipes leading into the system are connected to them. The hot water tank is installed in the shower or steam room. It is possible to use such a system for heating a utility room or garage.
Making a tank: step-by-step instructions and video
Heat exchangers for industrial furnaces are sold complete with some modifications; when installing a new furnace, you can choose a suitable model with a ready-made water circuit. You can also make a heat exchanger for the chimney with your own hands. To make it you need the following materials:
- pieces of stainless steel pipe of different diameters with a wall thickness of 1.5-2 mm, sheet steel;
- 2 1-inch or ¾-inch fittings for connecting to the system;
- storage tank made of stainless steel or galvanized steel with a volume of 50 to 100 liters;
- copper or steel pipes or flexible connections for hot water supply;
- ball valve for draining coolant.
Manufacturing sequence for a sauna stove or potbelly stove:
- Work begins with preparing a drawing. The dimensions of the tank installed on the chimney depend on the diameter of the pipe and the type of stove. Furnaces of a simple design with a direct chimney are characterized by a high temperature of the flue gases at the outlet, so the dimensions of the heat exchanger can be quite large: up to 0.5 m in height.
- The diameter of the inner walls of the tank must ensure a tight fit of the heat exchanger on the smoke pipe. The diameter of the external walls of the tank can exceed the diameter of the internal ones by 1.5-2.5 times. These sizes will ensure quick heating and good coolant circulation. It is better to equip furnaces with low flue gas temperatures with a small tank to speed up its heating and avoid the formation of condensation and deterioration of draft.
- Using a welding inverter, the parts of the workpiece are connected, ensuring the tightness of the seams. Fittings for supplying and withdrawing water are welded into the lower and upper parts of the tank.
- The tank is installed tightly onto the smoke fitting of the furnace, coating the connecting seam with heat-resistant silicate sealant. An adapter from a non-insulated pipe to an insulated one is placed on top of the heat exchanger tank in the same way and the chimney is removed from the room through the ceiling or wall.
- Connect the heat exchanger to the system and storage tank. At the same time, the required degree of inclination is maintained: the cold water supply pipe connected to the lower fitting must have an angle of at least 1-2 degrees relative to the horizontal plane, the heated water supply pipe is connected to the upper fitting and, with a slope of at least 30 degrees, is led to the storage tank. The storage tank must be located above the heat exchanger level.
- A drain valve is installed at the lowest point of the system. In the bathhouse it can be combined with a tap for drawing warm water for the steam room.
- Before starting operation, the system must be filled with water, otherwise the metal will overheat and leak, which can lead to poor sealing of welds and leaks.
- The water supply to the storage tank can be done either manually or automatically using a float valve. When filling manually, it is recommended to place a transparent tube on its outer wall to monitor the water level in the tank, so as not to run the system dry.
For good coolant circulation, it is necessary to use pipes with a diameter of at least ¾ inches, and their total length to the storage tank should not exceed 3 meters!
A do-it-yourself water heater exchanger is shown in the video.
All about heat exchangers
The heat exchanger is used to heat the water in the bath. Its operating principle is based on the physical properties of hot water to expand and rise, while cold water remains at the bottom.
Typically, heat exchangers are small in size and the water in them heats up quickly. Two pipes are connected to the heat exchanger - bottom and top. Thus, hot water through the upper pipe, displaced by cold water from below, rises into the water tank, which can be located either in the steam room or in an adjacent room, usually in the sink. In this case, cold water through the lower pipe is constantly independently added to the heat exchanger for heating in it. No additional mechanisms or pumps, engines or motors – pure physics!
The Termofor company produces two types of heat exchangers for heating water in a bath:
1. Built-in heat exchanger installed inside the Termofor sauna stove;
2. Kostakan “samovar” type heat exchanger, installed on the stove chimney and using the heat of the gases escaping into the pipe to heat water (purchased separately from the stove).
All Termofor heat exchangers are made of high-alloy heat-resistant steel with a chromium content of at least 13%.
Open siphon type heat exchanger
A very interesting and effective option is to heat water on a stove, but, unfortunately, not very common. An inclined pipe, sealed at the end, is welded into the furnace. Its second end - an open cut - is welded at the bottom of the water tank. When water is poured into the tank, some of it flows into a pipe located in the oven, where it is heated until it boils. The steam released during boiling rises in bubbles. Once in a cold environment, the bubble bursts, transferring a significant part of the heat to the surrounding water. In addition, heat transfer occurs due to the same convection (the movement of hot water up and cold water down).
Siphon heat exchanger. Effective option, but rarely used
One of the practical implementations of such a heat exchanger is shown in the photo. The design has been slightly changed, but the principle remains the same.
DIY heat exchanger for a sauna stove
In this option, the tank is located on a stand in the next room. A hole was made in the wall and in one side of the stove (the stove stands on its side). The length of the pipe is such that it almost reaches the opposite wall of the firebox. The pipe is sealed at the end, the hole in the furnace is slightly larger than the diameter of the pipe, and is not insulated or sealed. The inlet hole is located quite low - firewood is placed directly on this unusual heat exchanger, and then, after burning, coals are heaped onto it if necessary.
How to connect a heat exchanger to a water tank
The owner of such a siphon-type water heat exchanger has been using this unit for more than 6 years. He says that smoke does not enter the room. Sometimes, if you close the door to the steam room too quickly, a small portion of smoke may escape, but this happens very rarely and does not cause any trouble. It is not recommended to make the tank large - it is more convenient to fill the water several times than to wait until a large volume of it heats up. The tank in the photo has a volume of about 50 liters.
Water jacket
Another heat exchanger is simply implemented - a water jacket (water circuit) on the pipe. A larger diameter pipe with two pipes for water supply/discharge is welded onto the chimney section. The principle of operation is still the same: hot water rises up, colder water flows down from the remote tank.
This method is more attractive for several reasons:
- heating occurs due to heat that previously simply flew away;
- making such a heat exchanger with your own hands is not difficult, although there are factory-made options;
- can be installed on any metal chimney and for this you do not need to disassemble the stove and make holes in it;
- a heat exchanger on the pipe prevents the penetration of gases from the chimney into the room.
All these advantages make such a device quite attractive. But this solution also has disadvantages:
- complete sealing of seams is required;
- when adding cold water, condensation may form;
- You cannot pour water into a heated system - it may tear the walls of the chimney due to the temperature difference.
The water circuit for the stove is made in a similar way, but in this case, a container with water is built around the body. Almost always, such a heat exchanger is made for round stoves. Firstly, you can select a larger pipe and weld the bottom and top, which is unlikely to be possible with rectangular stoves, and secondly, water moves in a circle easily and the system is efficient, which is difficult to achieve with a square casing.
System installation methods
Correct placement of all system components allows for its ideal functioning. To achieve this result, the tank is placed on the wall above the level of the heat exchanger. The larger and smaller containers are connected by two pipes. Installation is carried out according to certain rules:
- the hot water supply pipe to the large tank has an inclination to the horizon of up to 30 °;
- another pipe passes below, cold water flows through it for heating towards the stove, its angle of inclination is approximately 1 - 2 °. A water drain tap is located on the lower pipe, and the water tank is equipped with a tap for disassembly.
An important condition for the reliable operation of the system is the mandatory filling of it with water before starting the fire, otherwise depressurization of welds or connecting areas may occur. Filling a hot tank with cold water can lead to a breakdown of the entire system.
Experienced craftsmen advise installing the tank so that the distance from the firebox to it is no more than 3 meters, and the connecting pipes should correspond in diameter to the selected type of equipment. It is generally accepted that the use of pipes with a minimum cross-section of 1 inch will be acceptable. Otherwise, the process of convection exchange between hot and cold liquid will be hampered, and the liquid will not be able to move efficiently through the pipes. If such a problem bothers you, then the use of electric pumps is recommended; they pump water through the system, improving its circulation.
The easiest way to install a heat exchanger in a bathhouse is when it comes complete with a purchased metal stove. You just need to carefully study the operating instructions and perform assembly in accordance with the diagram. All that remains is to connect to the system, this will be discussed below.
On the Internet you can often read a recommendation that the area of the heat exchanger, that is, its surface, should be 1 m2. The statement is not entirely correct, because ovens are different, and calculating this indicator is quite difficult. In this case, it is better to make a coil according to the principle of analogy.
As for chimney heat exchangers operating on the principle of a water economizer, such an element can either be purchased ready-made or welded from two pipes of different diameters. Remember, the longer the circuit, the more efficiently it will exchange heat with the chimney.
Installation of a furnace with a heat exchanger - features of the work
To install a stove with a heat exchanger for a bath without any problems, you need to follow a certain sequence of actions.
- The structure must be installed on a foundation poured to a depth of up to half a meter.
- The heating system is enclosed by a masonry of refractory bricks on a mortar of clay and sand.
- In the room where the stove is installed, the main heat exchanger is placed, and the firebox is led out into a hole pre-arranged in the wall of the bathhouse.
- Hot liquid flows through pipes wrapped in thermal insulation material into a water tank or heating radiators.
- The chimney is discharged through a hole in the roof.
- All joints are properly sealed.
Well as a source of water supply for a bathhouse
difference between an artesian and a sand well
All wells that can be used to supply water to a bathhouse are divided into two categories:
Artesian wells are deep, they reach powerful aquifers (35-300 meters). Artesian water supply systems for houses and baths are drilled using special mechanisms and are quite expensive. Water from artesian wells flows by gravity, under pressure.
Artesian water is clean, the well will never clog or silt, the volume of water is practically unlimited.
The only negative is the high cost of arrangement. But the problem can be solved by organizing simultaneous water supply to the houses and baths of several owners.
Sand wells are usually drilled no deeper than 30 meters to the top layer of sand. When supplying baths with water, such wells can become clogged with sand. To prevent this, a filter column is made from alternating layers of fine mesh and gravel.
The advantages of water supply to baths from a sand-type well: low cost and quick construction.
How to choose a sauna stove with a water heat exchanger?
Of course, it is important that the equipment is safe and effective. All stoves presented in the R-sauna.ru catalogs meet these requests, but it is important to choose based on the characteristics of the bath
Taken into account:
Heat exchanger power. This parameter is responsible for the speed and amount of water heating, as well as the area of the room for heating
Remember that a sauna stove with a heat exchanger is not used as actively as a household one, so it is important to choose it with some power reserve. This is important to ensure rapid heating of the room from room temperature or sub-zero in winter. Type
There are two types of heat exchangers: coil and container (jacket). It is more important to choose a coil if the steam room has a small area. Volumetric steam rooms require intense heating, so it is better to choose stoves with a mounted heat exchanger, so the surface area that releases heat will be larger. Dimensions. The selected type of heat exchanger also plays a role here. If this is equipment with a coil, then the space occupied will be less, if with an external heat exchanger - more. You should choose based on the dimensions of the bath itself.
Choose based on the size of the steam room and the volume of water that needs to be heated.
Bath water supply: choosing a suitable system
Modern bathhouse with autonomous water supply
For bath procedures to bring real pleasure, it needs to be properly equipped. And first of all, make sure that the water supply system in the bathhouse is reliable and works all year round, including the coldest months.
However, not everyone needs this. For many people, the bathhouse is located at their summer cottage, and there is simply no point in investing in a complex system. Therefore, here we will consider all possible water supply schemes for a bath, from the simplest to the most functional.
How does a heat exchanger installed in a sauna stove work?
The design of a furnace with a heat exchanger has proven itself so well that various heat removal design options have emerged, with varying degrees of efficiency. The most common:
- Classic coil.
- Built-in flat-plate heat exchanger (similar to two hollow plates connected to each other).
- Samovar heat exchanger installed on a chimney.
A water jacket surrounding the combustion chamber is used extremely rarely and is found in only 1-2 models of factory-made stoves.
Meanwhile, sauna stoves with a heat exchanger have become the subject of consumer debate. Some argue that the use is not practical, others, on the contrary, point to convenience and comfort during operation.
What does a built-in or samovar heat removal device provide?
- A heat exchanger in a sauna stove is needed to produce hot water for washing. This task was the main one when designing the structure.
- The possibility of heating the bathhouse from a stove with a water circuit - in fact, a metal stove becomes a kind of heating boiler. During combustion, enough heat is released to warm up the coolant and heat the required volume of hot water.
The operating principle depends on the device used. Efficiency is determined by several parameters:
- Reliability.
- Sufficient heat dissipation.
- Possibility of operation without the use of a heat exchanger.
According to their design, all water heating devices can be divided into built-in and built-on (samovar type).
Built-in heat exchanger
Stoves for baths with a water circuit for heating and DHW needs began to appear after conventional water heat generators received good reviews. According to their design, furnace equipment with an integrated water heating circuit is divided into several classes:
- The coil is the simplest device used in classic solid fuel boilers. Inside the structure there is a bent metal tube. The shape is different and depends on the internal design of the furnace. The coil is positioned so that the flame does not directly affect it, and heating is carried out through flue gases.
- A flat heat exchanger is a more complex device compared to the previous one. A flat heat exchanger for a sauna stove looks like two hollow plates connected to each other. In terms of thermal efficiency, the design is superior to the coil and is used in modern models of furnace equipment.
- Built-in tank - a separate container is made in the furnace and installed on top of the combustion chamber. The built-in horizontal heat exchanger heats up quickly and maintains temperature while the oven remains hot.
- Water jacket - represents the cavity surrounding the entire combustion chamber and smoke channels. The design is often used in the production of solid fuel boilers, but is not widely used in the manufacture of sauna stoves.
The operating principle of the integrated heat exchanger in a sauna stove is as follows. The spiral or plate is heated by flue gases, the temperature of which reaches 450-500°C. When heated, pressure arises, forcing the coolant to circulate in the heating system. In schemes where an indirect heating boiler is used, the hot water supply is heated using heating heat.
Samovar type
Installing a heat exchanger on a sauna stove is a budget solution to the problem of hot water supply and heating. The water heating device is manufactured in two ways:
- Coil - a coil made of aluminum or copper is installed on the chimney pipe. For systems with natural circulation, up to a storage tank or water distribution taps, the dimensions of the coil should not exceed 3 m. The optimal dimensions of a heat exchanger with forced circulation are 5 m.
- The design of a samovar-type heat exchanger - experts agree that this particular design is optimally suited for a bathhouse. Hot water for showering is prepared gradually, preventing the liquid from boiling.
The movement of water in a samovar-type heat exchanger occurs according to natural physical laws. The heated liquid rises, creating pressure in the container.
The optimal volume of a samovar-type heat exchanger is selected so that the water reaches the required temperature after 2-3 hours of intense combustion. The design is optimal for providing hot water supply.
Coil for furnaces
One of the easiest heat exchangers to manufacture is a coil. All you need is to find a pipe made of a sufficiently ductile metal. Copper or aluminum are most often used, as both metals are resistant to corrosion and bend easily. Then the pipe is bent, and in principle it can be any shape.
In order for the water to actively move by gravity (without a pump), the total length of the coil should not exceed 3 meters (this includes the connection to the remote tank). When creating your own heat exchanger, “try” it on the stove: it should not come into contact with an open flame, but should be heated by hot air. An external thread is cut at the ends, to which a remote tank is then connected through fittings.
The coil can be located not only inside the firebox, but also outside. It is hardly worth wrapping the stove, but a metal chimney will heat water quite effectively. After all, if the furnace does not have an afterburner, the temperature at the furnace outlet can be up to 500°C. For an example of such a heat exchanger on a pipe, see the photo.
In the simplest version, the heat exchanger can have the shape of a horseshoe. Then you can use stainless steel - this way you can bend it. For example, the video clearly shows a similar shape that was used in the Vitra sauna stove (for a video on how to move the heat exchanger in a Vitra stove from the left side panel to the right, look at the end of the article).
The simplest type of heat exchanger for a sauna network is a curved tube with threaded ends
One type of coil is a register. This is, as a rule, a welded structure made of pipes, which is often somewhat reminiscent of heating ones. The register for a sauna stove is most often made of stainless steel, since only it can withstand harsh operating conditions for a long time. Welded structures are large in size and weight, and therefore they are more often installed in brick kilns. In an iron furnace it is not always possible to find a place to place a small heat exchanger tube, let alone a bulky welded structure. And when designing brick sauna stoves, you can allocate space for a register.
Heat exchanger-register. You can’t put one like this in a ready-made metal oven. This is an option either for a homemade iron stove or for a brick one (more likely judging by the size)
Sometimes the heat exchanger is made in the form of a small container with water (volume up to 3 liters), which is also located inside the firebox without direct contact with the fire. The principle of its operation is no different from others. To make such a heat exchanger tank last longer, when making it yourself, try to make the structure so that there are as few welds as possible. For example, take a stainless steel sheet (1-2 mm thick is enough) and use a sheet bending machine to create the required geometry. There will be only one seam on the body, plus the side panels and inlet pipes will be welded.
Heat exchanger for sauna stove - unique design
When making any of the heat exchangers located inside the furnace, you need to remember that they can take no more than 10% of the furnace power without damaging the heating of the room. So it is irrational to make registers that are too large. It is difficult to place them and they will negatively affect the air temperature in the steam room. It’s better to design the system so that you can heat the water several times during your visit to the bathhouse: you don’t need 150 liters of boiling water at once, do you? First you need a little hot water to steam the brooms, then a little more to wash yourself before the steam room, and then some more to rinse. As a result, you need maybe 150 liters of hot water, but in portions. So why make a system for 150 liters and wait several hours until it is at an acceptable temperature, if you can make a tank for 50-70 liters and heat water in it several times, which will be used as needed...
Heat exchanger for the Termofor sauna stove on the chimney
If you want to increase the efficiency of your sauna stove and use the heat of gases escaping into the chimney to heat water, a Kostakan “samovar” type heat exchanger is suitable for you. Named after a lake in Kamchatka, it has an increased volume and allows you to quickly heat water in large capacity tanks. The Kostakan heat exchanger is usually installed as the first element of the chimney in order to remove heat from the very first hot gases, as well as to maintain the height difference between the heat exchanger and the tank. The Kostakan heat exchanger is available in 4 modifications for different chimney diameters: Ø115 – 8l, Ø120 – 8l, Ø140 – 9l, Ø150 – 9l; The connecting thread for all is standard - G ¾.
As you can see, the installation of a water heating system with a remote heat exchanger is identical to the installation of a water heating system using a sauna stove with a built-in heat exchanger.
For efficient operation of the water heating system, the height difference between the heat exchanger and the tank must be significant - at least 30 cm between the upper fitting of the heat exchanger and the bottom of the tank. It happens that it is not easy to comply with this requirement, since the ceilings in the baths are low, the heat exchanger is installed on the stove quite high, and most water tanks are vertical.
For such cases, the Termofor company produces a horizontally oriented external Zeppelin tank, with a shape and shine reminiscent of the German airships of rigid construction of the last century, after which it was named. It heats up better and is much more convenient to maintain. The large, long neck makes it easy to fill the tank with water, clean the tank and service the fittings.
Precautionary measures
Please note that any water heating system, like the sauna stove itself, is a fire hazard and requires a responsible approach during operation, therefore we strongly recommend that you carefully read the instructions for Termofor products and strictly follow all safety precautions!
Here are the basic requirements for the installation and operation of water heating systems in a bath using heat exchangers:
- Do not operate the oven with an empty heat exchanger and hot water tank or an unconnected water heating system.
- It is prohibited to pour water into an empty tank, heat exchanger or water heating system after lighting the stove - you must wait until the stove and tank have completely cooled down.
- Do not connect a heating system to the heat exchanger. For this purpose, the Termofor company produces tube heaters, which are identical in principle to a “samovar” type heat exchanger, only designed not for water, but for hot air.
- The bottom of the remote hot water tank must be at least 30 cm above the level of the upper fitting of the heat exchanger.
- When installing pipelines, the use of pipes with an operating operating temperature of less than +95 ° C is not allowed. It is recommended to install pipes for hot water at an upward angle of at least 30°, and for cold water – 1-2°. Sagging of pipes in horizontal sections is not allowed. Connecting pipes expand as the water temperature rises, so they cannot be fixed to the walls.
- The maximum length of the pipeline for hot water is 3 m.
- Threaded pipe connections must be sealed with plumbing sealant.
- Fill the water heating system only with clean water. It must meet quality requirements in terms of the content of salts, iron, lime, etc. It is prohibited for corrosive substances to enter the tank.
- It is necessary to ensure that the hot water tank is secured to the wall as securely as possible to avoid burns and injuries. The wall must be able to support the weight of a fully filled tank.
- Do not pour water into the tank right up to the lid, otherwise the water may splash out when boiling. When boiling, drain the hot water and add cold water.
- Do not operate the hot water tank under pressure other than atmospheric pressure. When operating a stove with a built-in heat exchanger, it is not allowed to exceed the operating pressure in the water heating system by more than 0.05 MPa (0.5 kgf/sq.cm). Pressure testing of the system with higher pressure should be carried out with the heat exchanger turned off.
- Do not use a heat exchanger or a faulty tank that has visible damage and/or leaks. Do not use the water heating system if the water circulation is not possible.
Tank location options
Water tanks can be placed anywhere: on the wall of a washroom or shower, in the attic, near the stove in the steam room. It is always better to insulate external options, otherwise the water will heat up for a very long time and cool down quickly.
The option when the tank is located directly next to the sauna stove is the most optimal, since the water is heated by the flame. This visually makes the bathhouse smaller, but holds the heat well.
Often the stones are placed in the chimney, and the tank is placed under the firebox. This design takes a long time to heat up, but also maintains the temperature for several hours. The heat from such a stove will be good, as will the steam.
The external location option is more expensive in terms of fuel. In this case, you will have to heat it longer, since you need to warm up the water in the pipes. However, the external location is very convenient for the shower room, when you need to rinse off after the steam room.
Both options have their drawbacks - their water pressure is very low due to the small installation height, and the ceiling height in the bathhouse is rarely higher than two meters. It will be difficult to install a shower, and you will have to wash no higher than one and a half meters. This problem can be solved by moving the tank, for example, to the attic. Then the pressure will increase; you just need to add water in a timely manner. You can’t run around with buckets; it’s better to install a water supply. It is made with a float so that when the tank is full, the water supply automatically stops.
As the tank is moved to the external circuit, heat loss increases. It is necessary to insulate the heat exchanger itself and the pipes that are supplied to it. Calculations should be carried out based on the design features of the bathhouse. For example, the over-pipe option, when a coil encircles a pipe, is well suited for a shower room. But there are volume restrictions - you can heat no more than 50 liters of water this way.
If it is possible to install a water supply, it is better to automate this process. Then the tank will always be full and the water in it will be hot all the time while the sauna stove is burning.
Do-it-yourself heat exchanger for a bath
The heat exchanger is made of metal of at least 2.5 mm or pipes bent into a snake or spiral.
The water tank is located above the level of the stove - this is necessary for water circulation. Then these elements are connected to each other by pipes: upper and lower contours.
To drain water (when flushing the system or during periods of long downtime in winter), a tap is cut into the return circuit at the lowest point of the pipe.
Installing a heat exchanger on a sauna stove requires high-quality connection of all elements and tightness of welds. The heat exchanger itself can be checked with compressed air by lowering it into water. After assembly, check the tightness of the connections of the entire system.
Note: to heat adjacent rooms, the water tank can be thermally insulated - in this case it will have the additional function of a heat accumulator.
Water supply for a bathhouse in winter
trench for laying pipes
How does the water supply work for a bathhouse that is used all year round? If the water supply and heating scheme for the house and bathhouse is the same, no problems arise. It is more difficult when the bathhouse is not heated and freezes in winter.
The water supply pipes for the bathhouse are buried in the ground to a depth exceeding the freezing point of the soil. In the middle zone, the freezing depth is about 1.5 meters, therefore, we lay the pipes at 1.7 - 1.8 m. The best pipes for such work are made of polypropylene foam, additionally insulated with moisture-resistant material. To ensure that frost does not reach the pipes, they are additionally placed on a thermal insulation cushion and sprinkled on all sides, after which they are covered with soil.
If the room is not heated, care must be taken to completely drain the water from the system after visiting the bathhouse. After all, in bitterly cold weather the temperature inside is almost equal to the outside temperature.
Additionally, the water supply system for the bathhouse, used year-round, is equipped with a pressure sensor (pressure gauge), as well as a check valve. They are installed at the entrance of the water supply pipe to the room before distribution.
To solder polypropylene pipes, you need a special welding machine; before arranging the water supply for the bathhouse, you should purchase corners, fittings and couplings.
Which heat exchanger to choose for a sauna stove
When choosing a heat exchanger design, the advantages and disadvantages of each type are taken into account. The selection of a suitable device is influenced by the intended purpose and the required performance:
- A sauna stove with a built-in heat exchanger is used for simultaneous heating and hot water supply. Long-burning furnaces operating in gas generation mode cannot provide the necessary heat transfer when installing a hanging tank. The reason for this is that flue gases have a lower heating temperature. If you plan to install a long-burning stove, there is no alternative to a built-in coil or plate structure. Efficient heating in a bathhouse is only possible from a stove with a built-in heat exchanger.
A sauna stove with a samovar-type water heater is distinguished by high hot water output, but for heating, the tank placed on the chimney is not very suitable in terms of technical characteristics.
When choosing what to install, a built-in heat exchanger or a samovar type, take into account the features of their operation. For simultaneous heating and provision of hot water, a coil, plate heat sink or water jacket is better suited. Exclusively for hot water supply, it is better to install a samovar-type water heating tank.
How to install a heat exchanger in a furnace
Built-in heat exchanger - installed at the factory, drum type - installed on the chimney pipe. The tanks are made of different internal diameters, therefore, installation does not require much effort and is carried out simultaneously with the removal of the chimney pipe. Factory containers are supplied with a capacity from 20 to 80 liters.
The difficulty lies in connecting the batteries from the stove. On the body there are special outlets for supply and return of coolant, to which the heating system pipes are connected.
Work is carried out in compliance with the following recommendations:
- Pipes for connection to the heat exchanger. The coolant temperature often exceeds 85-100°C. Plastic, with such heating, can be deformed, so it is not used. For the heat exchanger, you need to use steel pipes; copper will do.
- Connecting batteries - with natural circulation, the length of the pipe from the furnace body should not exceed 10 m.
- Installation of circulation equipment - heating systems with forced circulation are installed for large heated rooms, often used in industrial baths.
- Diameter of the heat exchanger pipe - manufacturers clearly indicate in the technical documentation the size and thread pitch, which facilitates the selection of pipes for installation. The diameter of the pipeline in the heating system can be increased, if necessary, but not decreased.
Flaws
Despite many advantages, the installation of a heating element on a chimney pipe also has disadvantages . One of them, the most important, is a sharp decrease in the smoke temperature at the installation site of the heat exchanger. This can lead to deterioration of traction and the formation of condensation, increased soot deposition inside the pipe.
In addition, when connecting a heating system, for example, a garage, you need to calculate the volume of coolant to avoid boiling water and bursting pipes . Welds must be completely sealed.
Any heat exchanger design significantly increases the efficiency of the furnace . For trouble-free operation of the system, it is necessary to carry out a visual inspection of all its elements at least twice a year , and, if necessary, timely repairs, descaling, replacement of gaskets and other necessary maintenance work. In this case, water heating and heating systems will operate flawlessly for a long time.
Heat exchanger manufacturing
Tip for making a heat exchanger
You can make a heat exchanger from sheet steel, pipes bent in the form of a coil or horseshoe, an old cast-iron radiator, and even a heated towel rail.
Sheet steel heat exchanger
In the case of using sheet steel (thickness more than 2.5 mm), cutting is carried out, preliminary “grabbing” of the joined elements by welding, checking the geometry, and then final welding. The tank can be made either rectangular or cylindrical; in the latter case, you will need a metal bending machine.
Example of a heat exchanger for a brick sauna stove
Heat exchanger for brick oven
You should not use galvanized steel, because... At temperatures above 200 degrees, zinc begins to evaporate.
Nozzles are welded to the heat exchanger at the top and bottom to connect the coolant circulation pipes. It is desirable that the pipes have threads at their free ends, this will simplify installation.
A heat exchanger in the form of a register can be used in a brick kiln. It is made from copper or steel pipes, collecting them into a single “skeleton” through which water will circulate.
Heat exchanger - register
Video - Construction of a sauna stove with a heat exchanger
Ready-made internal type heat exchangers usually consist of a housing to which elongated leads are connected. The tank is hung on the front or any other wall of the furnace, and waste streams are discharged through holes in the wall. Fixation is carried out with spacer sleeves and clamping nuts.
Heat exchanger "Ermak"
Heat exchanger "Ermak"
When making a heat exchanger, it is important to know that pipes with a diameter of more than one inch must be connected to it, otherwise the movement of water to the “consumer” and back will be difficult. The best pipes for the manufacture of a heat exchanger and circuit are copper or stainless steel
Moreover, bending a copper tube will be much easier than a steel one, and the thermal conductivity of the former is 7.5 times higher
The best pipes for making a heat exchanger and circuit are copper or stainless steel. Moreover, it will be much easier to bend a copper tube than a steel one, and the thermal conductivity of the former is 7.5 times higher.
Description of heaters
If in the past the most popular were classic heaters, which only allowed heating the steam room, today universal stoves with heat exchangers are in demand on the market. Such installations allow you to simultaneously heat the steam room and solve the problem of heating water. Thanks to their use, the comfort of bathing procedures increases and the costs of purchasing appropriate thermal equipment are reduced.
Stoves with a water heat exchanger will be a convenient solution when the steam room and washing room are located separately in the bathhouse. Universal heaters are easy to use, they are extremely convenient, quickly heat the room, completely solving the problem with warm water. The choice of stoves with heat exchangers available today allows you to purchase or make them yourself for both a small steam room and a spacious public bathhouse. Advantages of stoves with a thermal circuit:
- long service life;
- compactness of heaters;
- efficiency and high speed of heating the room;
- possibility of making it yourself.
How to properly make ventilation in a bathhouse with your own hands
Difference by type
There are several types of heat exchangers for equipping sauna stoves. They are distributed:
- by design;
- by location.
Depending on the design features, there are:
- coil. which is a fairly simple option. Both ends of the heat exchanger are removed from the tank to take in cold water and release heated water;
- connection of two metal containers. cylinder and parallelepiped. When heated, water from such a heat exchanger flows through pipes to its destination.
The second version of the heater is considered the most common, because with its help not only the water becomes hot, but also all the rooms of the bathhouse are heated. This saves fuel and, accordingly, money.
The location also determines two types of heat exchangers:
- mounted that is, located on the chimney;
- built into the furnace design.
A wall-mounted device receives the necessary heat not from the stove itself, but from the chimney by heating the emitted gases. Due to the significant capacity of the box, the liquid quickly heats up in the tank and remains hot throughout the entire heating time of the bath. As a drawback, it is worth noting the massive appearance of the device. Sometimes, when installing a chimney, a heat exchanger of the so-called samovar type is first installed. and then the chimney pipe.
It is imperative to ensure that the heat exchanger is filled with water, since in a dry state it can overheat and lose its sealing properties.
When assembling a system for water circulation, you should stop using plastic pipes in the steam room. The high temperature of such a room affects the plastic, as a result of which this material begins to release substances that are harmful to human health.
The heat exchanger built into the furnace design has the form of a sealed flat tank with a capacity of up to 5 liters. Two pipes with threads cut at their ends are welded into this tank. They are connected to water pipes leading to a large volume remote tank (up to 100 l)
In the furnace, the heat exchanger has a place between the convector casing and the firebox. In this case, the device does not come into contact with fire at all.
It is necessary to fill the system with water just before starting to fire the stove, since a heated dry heat exchanger under the influence of cold water loses its tightness and simply begins to leak. In order to prevent the appearance of air pockets in the system, water must be pumped from below using a pump.
Heat exchangers for stoves of these types deserve great attention because of the opportunity to save on fuel, because for their normal functioning they require heat accumulated from the combustion of wood. Thus, a built-in type device is heated by thermal energy used to heat the steam room and stones
The heat exchanger is located on the chimney. It is powered by heat, which simply goes out into the pipe. Its efficiency and heating rate are much higher due to the larger capacity of the device. In this case, the tank into which hot water is drained can be removed a significant distance from the stove.
How to equip a good water source?
An important question is where to get water for the bath. Of course, the ideal source for it is a limestone well, called an artesian well. But the price that workers charge for drilling it discourages many bathhouse attendants from even going into the steamy water at all.
There are also sand wells - but they are often too sandy and require serious filters. This point is also alarming - if the territory itself is radon-bearing, which cannot be checked by eye, then the water from it will contain a large amount of radioactive soil gas radon. That is why the best option is an ordinary well, for which you can find water using a frame.
Once water is found, test drilling can be done and a well can be dug. It is only important to purchase the “correct” rings - with a tongue-and-groove system that are attached to each other. This will prevent possible horizontal displacement of the rings. It would be good if the rings were additionally tied together with special metal brackets. And so that the upstream veins cannot get inside, when laying between the rings, it is advisable to make a seam from a special rubber tape such as RubberElast. In extreme cases, a cable - foam, jute or linen - is suitable. But you can’t lubricate it with bitumen - it’s harmful, liquid glass is a waste, and only the quick-hardening mixture Plitonit Aquabarrier is suitable.
At the bottom of such a well you need to make a bottom filter - from crushed stone, stones and geotextiles.
The resulting space around the well should be filled not with earth, but with sand - it will drain water from the walls and thereby reduce frost heaving. It wouldn't hurt to insulate the well - at least with the same extruded foam, which doesn't produce crumbs. And the top of the well must be covered - with a steel or plastic lid - so that leaves do not fall into it and then the entire water supply system of the bathhouse does not become clogged, and there is no need to replace a burnt-out pumping station.
The water itself will be taken from the well by the outlet pipe - it is important to make its entrance completely sealed. But not with bitumen mastic - it will pollute the water and cause a tarnished color to appear on it. Waterproofing needs to be done in multiple layers - with silicone, cement mortar, liquid glass and Kiilto fiber rubber.
Here's how it's done: a layer of silicone is placed on the hole in the ring and plastered with a mixture of waterproof and frost-resistant tile adhesive. When it dries, a layer of fiber rubber is applied - it is usually used for waterproofing showers. Once it dries, apply another, thicker layer. And after that, plastering again with a mixture of tile adhesive and liquid glass. The next day, all this is coated with blue clay and polystyrene foam is laid, followed by loam. And all these manipulations are carried out both from the inside and from the outside.
Types of heat exchangers for sauna stoves
Structurally, the heat exchanger can be a coil or a tank with a maximum volume of 5 liters and two pipes for connecting a water tank/radiator.
According to the mounting method, heat exchangers are divided into two types:
- internal. Such products are fixed on one of the side walls of the furnace or mounted on its bottom. It is also possible to install a water jacket, which literally encircles the fuel chamber from the inside or is located in the space between the stove casing and the walls of the firebox;
Heat exchanger for furnace
- external.
Heat exchangers of this type are fixed to the chimney or attached to the wall of the furnace. External heat exchanger on pipe
Internal type heat exchangers have the best heat saving indicators. The water in them will heat up until the stove cools down completely down to its last brick or stone.
The fastest heating of water is provided by internal heat exchangers and external ones installed on the chimney. At the same time, the first products often imply the need to make design changes/additions to the sauna stove, while the second cannot be called a decoration for the steam room (a wide tank does not fit well into the interior).
Example of an internal steel heat exchanger in a brick kiln
If we compare products in terms of ease of installation, the palm is occupied by heat exchangers that are hung on the outer walls of the furnace. Such products have a long service life and do not spoil the appearance of the stove, but the water in them takes longer to heat up and cools much faster.
Classification and purpose of heat exchangers
There are several types of heat exchanger devices, classified according to their location :
- In the body of the furnace;
- Near her body;
- Near the chimney pipe.
All bath heat exchangers perform identical functions - by contacting the fiery surface of the firebox or chimney, they heat water in a large container using the principle of convection. Their use allows you to place the water tank in the room adjacent to the steam room.
Tin pipe
Tin as a material for smelting a heat exchanger is very practical and reliable. Essentially, a chimney with a heat exchanger for a bath will look like a pipe wrapped around a smaller metal or copper tube. During the heating process from the tube, the air passing by will also warm up.
It will be enough to weld the spiral tube. Soldering can also be done with tin, previously degreased with orthophosphate acid. In this case, the heat exchanger will be secured especially securely, because it is not without reason that tin samovars are considered the standard of reliability among analog products.
Making containers for warm water
There are several options for containers - from expensive stainless steel to cheap store-bought plastic ones. We will not consider these options; we will focus on the most successful, from our point of view, metal made from sheet iron
Its advantages are not only its relatively low cost (although this is important), but also the ability to make a tank that is ideally suited in terms of linear parameters to each room of the bathhouse. As for appearance, there is a large selection of durable paints; surfaces can be painted in any color or covered with self-adhesive decorative polyethylene film
Simple water tank with lid
Table. Calculation of tank volume
| Stage | Description | Scheme |
| Find the volume of your tank | Multiply length (l), width (w) and height (h) | |
| Calculate filled volume (d) | For rectangular tanks, the filled volume is the same length and width, but less height. The new height is the filling height of the tank. | Tank fullness D |
Table. Making a tank
Step, No. Description of work Step 1. Prepare materials. You will need sheet iron with a thickness of at least 0.5 mm. We suggest making a rectangular tank, length 80 centimeters, height 40 centimeters, width 20 centimeters. The tank holds 64 liters of water, but you need to fill no more than 60 liters. You need to weld three metal pipes with threads into the tank; they are sold in stores. It is better to take the nominal diameter of the pipes at least 3/4 inch. This is the most commonly used diameter of pipelines and ensures normal natural circulation of water. To fully install the heat exchanger, you will need to have additional plumbing fixtures and fittings; we will talk about this below when considering installation issues. Step 2. Mark the tank on a metal sheet. You will need two plates 80x60 cm, two 40x20 cm and one 80x20 cm. We specially made the tank rectangular. The fact is that the distance between the inlet and outlet pipes should be increased as much as possible. This will allow warm water not to immediately mix with cold water; a significant difference in their temperatures will be achieved, which has a decisive influence on the speed of water flow in the pipelines. And not only the efficiency, but also the safety of using the heat exchanger largely depends on this criterion. Step 3. Cut the blanks to size. You need to use a grinder; when working with this tool, strictly follow the safety rules - it is very dangerous. Try to keep the cut as even as possible. Check the quality of cutting of each edge on a flat surface, eliminate large flaws. Step 4
Assemble all the parts of the tank in pairs, making them absolutely identical. Pay special attention to the corners, they should only be rectangular. Step 5. Place the front part of the tank on a flat surface, and weld the side of the tank in several places with a short seam. Do the same operation on the other side
Check their position; they will definitely move as the seam cools. Step 6. Place the second large part on the welded sidewalls, check its position, and adjust the sidewalls if necessary. Grab the elements. Make sure that the gap between the individual parts does not exceed 2–3 millimeters, otherwise during welding you will have to put wire in them, and this is undesirable. Step 7. Place the structures upside down and grab the bottom. Check and correct its position. Step 8. If everything is fine, weld all the elements. Monitor the quality of the seam; omissions are strictly excluded. You can “cheat” a little on the thickness of the weld seam; the container does not carry significant loads, but omissions are prohibited. Step 9. Weld metal pipes into the bottom. We have already said that the input and output should be removed from each other as much as possible. It is better to place the water intake pipe for the shower not in the middle, but closer to the drain; the water intake will speed up the circulation in the tank. Step 10. Burn holes for the pipes. For the pipes, you must first burn holes in the bottom of the tank; this can be done more conveniently by electric welding. Step 11. Come up with a way to attach the tank to the wall. You can weld special brackets to the back wall or install it on a stand. If you have the desire and the material, make a removable lid. Step 12. Using a cylindrical grinder, clean all seams, pour water and check their tightness. Seal holes if necessary. Step 13. Prepare the front surfaces of the container for finishing.
Video - Making a stainless steel tank
That's it with the water tank, you can install it in any room in the bathhouse. Now let's talk in more detail about heat exchangers.
What you need to know about using the device
An equally important task is choosing a stove equipped with a similar device. When considering different models, you need to be extremely careful not to miss the smallest nuances. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the basic rules that determine the safe operation of devices:
- Fastening due to movable joints compensates for temperature deformation and changes in the dimensions of the apparatus components during their heating.
- Net power is an important indicator that must be taken into account when making all necessary calculations.
- It is desirable that the dimensions of the heat exchanger correspond to the characteristics of the furnace. Only a tenth of the total heat generated in the heating unit should be allocated to perform the functions of the device.
- It is necessary that the remote tank contains as much water as can be heated in just two hours from the moment the stove is lit.
- All seals installed at the joints of system elements must be made of materials that are resistant to high temperatures.
There are few basic requirements, but compliance with them is mandatory when installing and operating the device. This contributes to a significant increase in the durability of the device.
Description
| Specifications | |
| Country of Origin | Russia |
| Manufacturer's warranty | 1 year |
| Weight, kg) | 70 |
| Height (mm) | 760 |
| Width (mm) | 445 |
| Depth (mm) | 700 |
| Fuel | Firewood |
| Furnace material | Steel |
| Power, kWt) | 20 |
| Weight of stones (kg) | 60 |
| Steam room volume (m3) | 24 |
| Chimney size (mm) | 115 |
| Heat exchanger | No |
| Door | Without glass |
| Remote tunnel | Eat |
| Firebox depth (mm) | 550 |
| Kamenka (stove) | Open |
- Description
- Scheme of work
- Detailed description
- Documentation
- Reviews
Ermak 20 sauna stoves with a heat exchanger have a compact, rigid design, with a developed heat transfer system. Compactness allows you to save space in the steam room, rigidity eliminates the appearance of deformation of the product when heated, and a large heat transfer area ensures good power characteristics.
Calculation of heat exchanger area
A stove for a bath with a heat exchanger for heating should produce 5 kW of heat with a standard area for an ordinary family. When independently calculating the dimensions of the system elements, we proceed from the fact that 1 m2 of heat exchanger area gives about 9 kW.
It is recommended to make dimensions with a large margin, since the efficiency of the system is affected by the location and shape of the boiler, and the quality of the fuel.
When designing a system for obtaining hot water (with a remote tank), it should be taken into account that the tank itself will additionally heat the room.
The connection diagram for the heat exchanger in the bath is simple for factory-made stoves in the corresponding models. However, for people with welding skills, it is quite possible to assemble the system on their own for a brick oven. For a system with natural circulation, you will need pipes, fittings, fittings (2 taps), and a water tank.
Everything you need to make a wooden gate
The most common option is a wooden gate. It’s quite easy to make with your own hands. Its cost is low, even when using high quality boards. If you purchase less expensive coniferous boards, the gate will be even cheaper.
Wooden gate
For a wooden gate you will need:
- 10-11 boards measuring 200x14x2 cm;
- two boards measuring 200x15x5 cm;
- door handle and latch, gate awnings;
- fastening material – about 40 screws;
- antiseptic for wood processing;
- wood primer and varnish;
- cement, sand and water for making concrete mortar.
Tools you will need:
- plane, chisel, hammer, hand drill;
- screwdriver, drill, pencil, tape measure, building level and sanding material (numbers 25-16 for the first stage, and 10-9 for the final stage of processing).
Installation and connection
How to mount the heat exchanger is shown in photo No. 1:
Photo No. 1 Connecting the heat exchanger
Photo No. 2 - required slopes and dimensions
Step-by-step instruction:
- Let's determine a suitable location for the remote container. It is hung on the wall, 100-300 mm above the heat exchanger.
- The tank should not be hung directly on the wall of the bathhouse. First, we attach the guides with dowels - 2-3 wooden dies. Then, already on them, we hang the tank. The gap between the wall and the container must be at least 20 mm.
- To strengthen the structure, use special brackets, securing them under the bottom of the container. When assembling the container, do not forget to provide holes through which it will be attached.
- We will need 4 pipes: one for direct supply, the second for reverse supply, the third for filling with cold water, the fourth for the consumer. Place a check valve on the third pipe, and connect the tap and shower to the fourth.
- Using fittings, connect the remaining 2 pipes (forward and return) to the heat exchanger using good copper or steel corrugated pipe. Don't forget to seal all connections.
- We install a valve on the return line to drain the liquid. It must be installed so that it is at the lowest point.
- We attach a low tank with a heat exchanger to the wall of the furnace. How to install a heat exchanger on a sauna stove is shown in photo No. 1, and the necessary slopes are also shown there (photo No. 2). It can be built-in. Work must be carried out in compliance with safety regulations.
- Using fittings, we connect the forward and return supply pipelines.
Water supply for a bath - choosing a water source and some technical points
Proper water supply for a bathhouse is a flow of clean water under constant pressure. Moreover, the pressure is comfortable, with calculated water heating. But, if everything is clear with the latter - there are boilers for this, or in extreme cases you can use a furnace heat exchanger - then with the first everything is a little more complicated. Because the same water pressure in the bathhouse is created by a pumping station - and it is not easy to equip it, as well as to ensure a constant flow of high-quality water. But everything is possible - just follow our instructions. So, the bath water supply diagram, detailed photos and videos are on the portal stroy-banya.com!
Selection of materials
The choice of material for the heating tank only seems simple. The most common option is steel. The main advantage is low cost and ease of manufacture using conventional welding operations. However, in the conditions of a Russian bath at constant high temperature, high humidity and exposure to superheated steam, this material quickly rusts and its service life is short. In addition, water in a rusty container may take on a corresponding tint. Protection using paint coatings will not work due to the risk of fire when coming into contact with a heated oven. The painted structure can be used in a system with a heat exchanger.
Another option is cast iron. In a cast iron container, the water takes a long time to heat up, but it also takes a long time to cool, which makes it possible to retain heat even after the furnace has stopped firing. Disadvantages: heavy weight, high price and problems with corrosion.
The best option is stainless steel. Of course, it is much more expensive than ordinary steel sheet, but it does not corrode and can last for many years. The most common steel grades for the manufacture of sauna heating tanks are 8-12X18H10 (304) and 08X17 (430). Stainless steel containers are quite light, have excellent thermal conductivity, and the coefficient of deformation during sudden temperature fluctuations is negligible.
In principle, it is possible to use ready-made enameled tanks. However, such containers are good as long as the enamel protective coating is intact. When the slightest chips appear, active corrosion begins
This means that enameled tanks require increased caution during operation, which is very difficult to ensure.
The question of how to heat water in a bathhouse is decided independently, based on specific conditions. The simplest option is to install a standard tank heated by heating elements and manually deliver it to the destination point in small containers.
Tips for installing water supply for baths
In order for the system to serve for a long time and be reliable, you need to plan the construction of the bathhouse and water supply carefully, taking into account all the nuances.
Selection of materials
It is very important to choose the right pipes for supplying and distributing water. They must be durable, easy to install and withstand significant temperature changes.
Steel pipe after several years of use
Polyethylene pipes and fittings
Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene hot water pipes
Copper pipes in the bath
Installation features
The pipeline must be protected from external influences and soil pressure. To prevent pipes underground from receiving mechanical damage, the instructions recommend laying them on a sand bed or placing them in a corrugated hose of a suitable cross-section.
This will prevent them from being deformed and compressed by the layer of soil located above, and will protect against its seasonal movements.
In order to have access to a sauna throughout the year, the water supply in winter needs to be protected from freezing. And first of all, this applies to complex pumping equipment.
Warm cover for the well
Faucet for draining water to the street
Principle of operation
According to the principle of operation, water heating devices are divided into 3 types:
- a coil built into the heater;
- an external heat exchanger in the bathhouse in the form of a rectangular tank, heated directly from the furnace wall;
- external water circuit that removes heat from flue gases.
In the first case, the heat exchanger is a coil made of a steel pipe, built directly into the firebox. It is positioned in such a way that the pipe is not exposed to direct flame, that is, it is outside the highest temperature zone. It is desirable that the element stands in the way of waste products of fuel combustion, then it will not burn out and will last long enough. The built-in coil for heating the water at the outlet has connections for connecting pipes leading to a remote storage tank.
In such heat exchangers, the water warms up quite quickly, but the process cannot be called effective. After all, the heater takes heat directly from the firebox, thereby reducing the heater power. The steam room takes longer to warm up, which means more wood is consumed. Hot flue gases flew out into the chimney and continue to fly out unhindered; the efficiency of the unit remains very low (no more than 50%).
An external hanging tank made of stainless steel is another option for transferring furnace heat to water. Usually it is suspended from one of the side walls of the firebox and heated by infrared radiation from it. The method is attractive due to its ease of implementation, but is not very convenient to use. In addition to the disadvantage of direct heat extraction described above, the hanging tank also requires constant addition of cold water.
Devices for extracting heat from flue gases
It should be noted that even the simplest water-to-pipe heat exchanger dramatically increases fuel combustion efficiency by up to 60%. The trick is that this device does not in any way affect the functioning of the stove itself, and does not increase the heating time of the steam room or the consumption of firewood. The main advantage of such heat exchangers is that they take away the thermal energy of combustion products, lowering their temperature.
This principle of heat exchanger operation is used by many manufacturers of metal sauna stoves, installing an open water tank directly on the chimney pipe. This option is popular due to its availability, but is not very convenient. The reason is the same addition of water as it is used or evaporates due to boiling.
Finally, the best option from all points of view is a sauna stove with a heat exchanger on the chimney in the form of a flow-through heater of small capacity (from 5 to 10 liters). A system with a remote storage tank is connected to it, as well as to the coil built into the furnace, through pipes. The volume of the remote tank is 60-120 liters, depending on the power of the heating unit. During heating, the water in the container reaches the required temperature for washing.
In addition to those listed, there are also combined models, where a sauna stove with a heat exchanger built into the firebox also has a tank on the chimney. Moreover, these elements are connected to each other by pipelines, that is, not one heater is involved in the heating circuit, but two. Accordingly, this option absorbs all the advantages and disadvantages of various modifications. Again, this stove will still require a separate storage tank since the water in the tank will boil quite quickly.
Making a heat exchanger with your own hands
To make a heat exchanger for a sauna stove with your own hands, you need to use sheet metal. the thickness of which is 2.5 mm. The upper container in the form of a cylinder is connected to the lower rectangular container using pipes. In this process, the most important thing is that the seams at the junctions of individual elements have minimal gaps. The immediate dimensions of the furnace, as well as the thickness of the pipes, must be calculated in accordance with the area of the bath.
The prepared metal blanks are attached to each other by welding and only after checking that all the parts are in place is the heat exchanger finally welded. At the end of the welding work, the quality of the seams is checked for this:
- The lower pipe of the heat exchanger is welded.
- water is poured into the system.
- a container is connected to the outlet hole.
- To check, pressurized air is supplied to the system.
- If the welding is done efficiently, there should be no leaks at the seams.
Let's talk about the rules of installation and operation
System calculation
If you decide to install the system yourself, you will have to make certain calculations. It will be difficult to absolutely accurately calculate the dimensions and volume of the system, and there is no urgent need for this.
For example, 5 kW is enough to heat a medium-sized room. This power can be provided by a heat exchanger with an area of 1 m². But the temperature in the furnace constantly fluctuates; when fully heated, 1 m² provides up to 9 kW, and when the furnace goes out, the power begins to drop rapidly and can drop by 5 to 10 times. Therefore, the area of the unit is taken with a significant margin, which makes it possible to equalize the heating of the liquid.
The configuration of the heat exchanger itself can be different; there is no consensus among experts. Some argue that stainless steel pipes are the best option, others prefer plates or manifolds consisting of 2 mating channels.
Connecting the system to the shower stall.
Tips for installation
If you decide to assemble the system yourself, then you should take into account several mandatory requirements.
- Tanks should be welded from metal with a thickness of at least 2.5 mm. The requirements for the upper, large tank are minimal; the main thing is that it does not rust or leak.
- The requirements for piping and the heat exchanger itself are somewhat higher; in the past, the most popular material for a heat exchanger was cast iron. Indeed, the material is very durable, does not corrode and holds the temperature for a long time. But cast iron also has serious disadvantages; it is heavy, which requires serious fastenings. And cast iron takes a long time to heat up.
- At this time, most experts prefer to assemble a system from stainless steel; its price is of course higher than that of cast iron or conventional steel grades that are susceptible to corrosion, but the savings here will cost more in the future. For the heat exchanger, stainless steel grades 08X17 (430) will be the most optimal; or 8-12Х18Н10 (304) they have optimal heat transfer parameters and meet all hygienic standards.
- As for the connecting pipes, naturally they should also be made of stainless steel. The drive pipe with cold water must initially, when leaving the large tank, fall slightly below the level of the heat exchanger; a drain valve is mounted at the lowest point and then rises at an angle of 2˚ to 5˚ to the entrance to the heat exchanger.
- The outlet pipe, through which hot water will flow into a large tank for a heated bath, must exit the heat exchanger, pass through the wall at an angle of at least 30˚ and connect to the tank.
The simplest samovar-type heat exchanger.
The system is designed exclusively for heating the room.
Do not forget that both the piping of the bath and the heat exchanger itself at all interface points must be equipped with special heat-resistant gaskets that provide sufficient damping clearance during thermal expansion of the metal.
Recommendations for safe operation of the system
- The pipework must absolutely not be rigidly fastened; all fastenings must be of the floating type, otherwise it will be deformed or fall off the fastenings.
- You should not get carried away with overly powerful heat exchangers; this system should take no more than 10% of the furnace power, because the main goal is to steam, and not to heat the water.
- The main tank for heating water in the bathhouse should be selected carefully; the best option is when the water in it becomes hot 2 hours after igniting the stove. If less, the water will boil and you will get excess steam. If it is more, you will waste a lot of fuel and the stove will take a long time to heat up.
- Wherever there is a threaded connection, the seals must be extremely heat-resistant, as a rule, it is an asbestos cord.
Hanging tank.
Basic criteria for choosing a heat exchanger
When choosing a wood-burning solid fuel system for heating water, you should decide on the type of heat exchanger. optimally suited in a particular case. One of the structurally simplest is the coil, which is made of a pipe bent into a ring and placed in a tank.
However, in a high-quality sauna stove, a more complex system is most often used, which consists of two containers connected by pipes. The burning fuel heats the lower tank and the heat enters the upper cylindrical tank. This design of the stove not only heats the water, but also heats the steam room and dressing room.
Features of the operation of a furnace with a heat exchanger
Most types of furnaces with a heat exchanger are filled with water or antifreeze. The operating principle of such devices is based on the natural circulation of liquid due to temperature differences. However, there are systems that are equipped with an electric pump to circulate water. At the same time, the efficiency of any furnace will depend on certain nuances.
- According to the advice of professionals, it is better to use an open water heating system in a bathhouse, in which high pressure is not pumped.
- The most effective in terms of operation are heating systems, in the arrangement of which the length of the laid pipes does not exceed 3 meters. This distance is quite enough to place the tank in the dressing room.
- Also, a lot depends on the diameter of the pipes, which should be at least 1 inch. Otherwise, the circulation of liquid in the system will be very difficult and, without the use of an additional electric pump, the sauna stove with a heat exchanger will not cope with its direct responsibilities.
Gas heating
The implementation of such a heating system has several options.
- Firstly, as I wrote above, it is possible to install a “classic” heater, in which a gas burner will be used instead of firewood.
- Secondly, you can use a standard gas boiler (the same as in residential buildings). But in this case, you will have to take care of the equipment of heating systems (installation of heating radiators, laying pipes, connecting a gas-carrying pipe to the bathhouse or a cylinder connection system).
- Thirdly, there is the possibility of installing heating from the house. In essence, this is the same option as the previous one, but with its own characteristics and disadvantages. A separate heating main is laid from the boiler used to heat the house to the bathhouse. This option is very convenient if your steam room is adjacent to the house or is very close to it.
Gas heating baths
If the distance to the bathhouse is relatively large, then in order to use this system in winter it is necessary to bury the heating main below the freezing level of the soil and insulate it well. This will prevent the possibility of defrosting and help reduce heat loss.
True, the undoubted advantage of this option is the complete elimination of the problem of maintaining a constant positive temperature in the bathhouse. In addition, you can do all the necessary work (if you have a certain skill) with your own hands.
Water heating is rightfully considered one of the most convenient and effective methods of heating. In such a situation, there are also several options for manufacturing a system, which in any case will be powered from a furnace with a water circuit.
Fortunately, today in specialized stores you can easily select stoves that are ready for installation, equipped with a heat exchanger. This greatly simplifies the task of any builder of his own bathhouse. And now directly about the options.
Water heated floors
- External heating. It is done very simply and, in fact, is arranged in the same way as a brownie. Pipes located along the walls are connected to the furnace. Depending on the area of your bathhouse, a certain number of heating radiators are connected to the pipes. Hot water passing through them heats the structure and, when cooled, returns back to the boiler.
- Water heated floor. The principle of its operation is the same as in the first option. The only difference is that the pipes are hidden in the floor, which was previously insulated (I wrote about insulating floors in a bathhouse in more detail in other articles). This design is considered non-separable (although, of course, there would be a desire to break everything), and therefore requires a very careful approach to the procedure for its manufacture. In this case, I would recommend seeking help from specialists.