Energy prices have been getting higher and higher lately, and effectively insulating a home is one of the main challenges that homeowners have to solve. One of the latest materials that appeared on the market several years ago is polyurethane foam. This is a coating that is applied in a continuous layer to any (almost) surface. Insulation with polyurethane foam is the most effective.
House insulated with polyurethane foam
Types of polyurethane and their features of application to coatings
Before you understand the types of insulating materials, you need to understand what polyurethane foam is. This is a composition formed from two components: diisicyanate plus polyol. They are mixed in strictly equal proportions. If there is an excess in the amount of one or another of the two compositions, the technical characteristics that should manifest themselves during the operation of the insulation will suffer.
Application of polyurethane foam on plywood Source odstroy.ru
The components are mixed by placing them in a special high-pressure chamber. Both substances individually are considered toxic, but when they are combined, a completely harmless mixture appears. That is why the material can be used in residential conditions without unnecessary worry. During this process, carbon dioxide is formed, which is actually responsible for the ability to retain heat.
There are several types of polyurethane foam composition:
- Open cell. This is a lightweight type of material, and in appearance it can be confused with mineral wool. The raw material is hygroscopic, but costs more than mineral wool. If you use this type of raw material, you will additionally have to take care of the steam and waterproofing of the layer on all sides. The open-cell version is successfully used for insulating internal partitions and ceilings. For outdoor conditions, it is better to refuse to use this type of polyurethane foam.
- Closed cell. An ideal option for insulating a house from the outside; it is applied to any surface except polyethylene and is not hygroscopic. Additionally, it is divided into several varieties: medium density (28-32 kg/m3), medium density to eliminate cavities, high density (40-80 kg/m3).
Open-cell polyurethane foam for insulation Source stroiliderinfo.ru
What is polyurethane foam
A new type of insulation for Russia, polyurethane foam, is rapidly expanding its niche in the construction market. Poor knowledge of the characteristics of the material, aggressive advertising by manufacturers and anti-advertising of competitors have led to the fact that this material is full of myths and conjectures, among which not only ordinary consumers, but also professional builders are lost.
This is what foamed two-component polyurethane looks like.
The problems start with terminology. By polyurethane foam insulation, many understand foam rubber, familiar to everyone from childhood. But this is a soft and very elastic type of polyurethane foam, which can be used to insulate entrance doors in a building, but not structural elements. Real insulation is in liquid form.
But even here, consumers and experts make inaccuracies, considering simple polyurethane foam to be the same as polyurethane foam insulation. At first glance, they are right: both materials are made of polyurethane foam. But there is still a significant difference. PPU insulation consists of two components: “A” - polyol and “B” - polyisocyanate. When mixed, they enter into a polymer synthesis reaction with the release of carbon dioxide. The result is a foamed material with a rigid structure and closed cells. Polyurethane foam can be purchased in barrels or pre-filled cylinders.
Polyurethane foam consists of one component, which, when exposed to air, comes into contact with water vapor (which is why there is a recommendation to wet the surface before applying foam) and polymerizes with oxygen, creating open cells of frozen foam. Hence the completely different physical and technical indicators. To make it clear what we are talking about, we present a table with the main characteristics of the materials.
Table 1. Main indicators of polyurethane foam and polyurethane foam.
| Types of polyurethane foam / Indicators | PPU | Polyurethane foam |
| Thermal conductivity, W/(m×°K) | 0,022-0,035 | 0,025-0,045 |
| Number of closed cells, % | More than 90.0 | Less than 50.0 |
| Change in foam volume compared to the beginning of the expansion process | 1 in 40 | 1 to 70-90 |
| Vapor permeability, mg/(m*h*Pa) | 0,02-0,05 | 0,07-0,17 |
| Density, kg/m3 | 20,0-80,0 | 8,0-18,0 |
| Moisture absorption,% | 1,0-3,0 | 10,0-60,0 |
| Compressive strength, kgf/cm2 | 1,53-10,19 | About 1.02 |
| Bending strength, kgf/cm2 | 3,3-19,37 | About 17.0 |
One type of polyurethane foam is polyurethane foam.
The next myth is that the insulation is new, little studied. Therefore, it is better to give preference to a well-tested, albeit not the best, heat insulator.
Indeed, in Russia this type of insulation began to be used only in the mid-90s of the last century. It is finding its niche with difficulty, since consumers still prefer traditional insulation materials: expanded clay, glass wool and basalt fiber wool.
The late appearance of PPU in the CIS countries does not at all mean that it appeared in the countries of Europe and North America at the same time. There it has been known since the late 30s of the 20th century (invented by the German chemist Otto von Bayer). Today, the lion's share of the insulation market in the USA and Europe is occupied by two-component polyurethane foam.
Pros and cons of using
The PU foam material has both advantages and disadvantages. To many, these characteristics may seem significant, so we do not recommend ignoring this section. Let's start with the positive qualities:
- PPU insulation can be considered the most effective;
- seamless continuous connection that leaves no chance for the cold;
- sprayed even on surfaces with complex shapes (log walls);
- low level of hygroscopicity (of course, if it is not an open-cell structure);
- ideal adhesion to various materials and surfaces;
- long-term operation (as mentioned above, it can last 25 years if it is a closed-cell material);
- the service is checked in the first year (if no problems with the surface occurred during this period, then they will not arise the rest of the time);
- the application process does not take much time and at the same moment is carried out efficiently, without omissions;
- It is not subject to combustion, as it has self-extinguishing properties.
Applying a thin layer of polyurethane foam Source etalonteplo.ru
There are also several disadvantages that should also not be overlooked. These include:
- too overpriced. This insulation will cost the owner twice as much as mineral wool including installation;
- the need to use high-quality equipment for application. The final result depends on this;
- insulation is difficult to do with your own hands due to the need to have special equipment;
- is susceptible to ultraviolet radiation, since under its influence the structure of the dried foam darkens and collapses.
One can still argue about the last drawback. The fact is that if the thickness of the polyurethane foam is sufficient, then the sun's rays will not completely destroy it. A two- or three-layer application of polyurethane foam can be left even outdoors without applying a final finish.
Application of several layers of polyurethane foam on metal profile walls Source 9dach.ru
Parameters of sprayed insulation
It’s worth saying right away that, as with any other insulation, it is preferable to insulate the walls of buildings from the outside. If you insulate from the inside, the outer wall will freeze. How many defrosting/freezing cycles it will withstand depends on the material, but rarely will such a house last more than 10 years.
When insulating the outside with polyurethane foam, a final exterior finish is required - the surface has a very unattractive appearance. But there are no problems with freezing of the walls, the building will last a long time.
There are no problems with the roof at all. Roofing materials are designed to withstand repeated freezing, so roof insulation with polyurethane foam can be done from the inside, spraying it directly onto the “underside” of the roofing material or onto the sheathing.
Sprayed thermal insulation can be applied to any surface, and the roof can be insulated from the inside
Whether to insulate the house from the outside or from the inside, we figured it out. Now a little about the layer thickness. Insulation with polyurethane foam is usually made of large thickness. This is not due to the fact that small is not enough. Usually, just according to thermal characteristics, an insulation thickness of 2-3 cm is required, but they make it at least 5 cm. This is so that under any conditions the dew point ends up in the thickness of the thermal insulation, and not in the wall material. Since polyurethane foam is non-hygroscopic, it cannot get wet, condensation simply does not occur, and excess moisture is removed naturally due to the vapor permeability of the material.
Features of the device kit for carrying insulation
Application of polyurethane foam to the surface requires the use of special equipment. Before purchasing it, you must make sure that all components are available. These include:
- cylinders for forming foam with liquid inside (2 pieces);
- a spray gun from which foam will be released;
- hoses connecting the gun and cylinders;
- interchangeable nozzles for guns of various modifications;
- component keys necessary for assembling equipment;
- technical lubricant.
Since coating polyurethane foam surfaces is considered a difficult task, and special equipment is expensive, special services have to be involved in the process. If there is an appropriate sprayer unit on the farm, the main thing is to connect it correctly.
Gun variant used for polyurethane foam Source onlinetrade.ru
Manufacturers and prices
Experts call the following companies the best producers of polyurethane foam:
BASF Polyurethanes GmbH. The German company is a leader in the production of polyurethanes. The product line also includes polyurethane foam. In Russia, together with OJSC Nizhnekamskneftekhim, they created the Elastokam enterprise to produce components for polyurethane foam.
Yantai Wanhua Polyurethanes Co., Ltd. Chinese manufacturer with a high-quality line of polyurethane foams.
SYNTHESIA INTERNACIONAL SLU The Spanish chemical company SYNTHESIA INTERNACIONAL SLU has been producing polyurethane foam since 2008. The products have found their buyers in many countries around the world, including Russia.
The price from all manufacturers is about $650 per 1 m3.
Safety precautions when spraying polyurethane foam on the facade
When applying insulation to walls, be sure to follow the rules below.
Before starting work, you must ensure that you have special clothing. Any work uniform or special disposable suit will do.
Respirators and protective gloves must be present, because if the composition gets on exposed skin, there is a danger of burns.
Protective suit for spraying polyurethane foam Source remontik.org
Application area
Liquid two-component polyurethane foam serves as an excellent insulation material for any structural elements of frame, brick, block and panel buildings, since its low weight does not create serious mechanical loads on house structures, including lightweight ones.
Good adhesion of polyurethane foam with all building materials allows you to spray insulation on vertical and inclined surfaces: facades, roofing, walls inside the house, ceiling. Excellent thermal insulation properties coupled with fairly high moisture resistance make this type of insulation attractive for thermal insulation of country houses, attics, balconies, floors (along joists). Low level of moisture absorption - foundation.
Attention: the use of the material under compressive loads reduces the thermal insulation effect to zero, and therefore polyurethane foam is not sprayed under the screed and “wet facade”.
Polyurethane foam insulation is also used in other industries. It is used to insulate freezers and is sprayed onto pipes of heating systems. Recently, in industrial construction they have begun to use ready-made sheet material for sandwich panels, when liquid polyurethane foam is poured into molds at the factory.
Technology for insulating the façade of a house with polyurethane foam
The facade of the house is insulated using standard instructions, which are described step by step below:
- We assemble the equipment, then open the valves and wait for the mixture to flow through the hoses to the sprayer.
- We pull the trigger and point the gun at the wall that needs to be insulated. We distribute the composition evenly over the entire area of the partition.
- We apply polyurethane foam strictly starting from the bottom; if there is a sheathing, then first we fill the voids under it.
- We place the gun so that it is at a distance of no more than 25 cm from the facade of the building.
- We move the gun evenly, without sudden jerks. This way there is every chance of getting a perfectly even coating.
- After finishing work on one side of the house, we move to the other, while turning off the spraying and changing the nozzle (since it hardens very quickly when the supply of material is stopped).
- We adjust the spray intensity if we need to make a thinner layer, then we adjust the equipment so that the jet is as fine as possible.
- If the layer thickness is insufficient, wait until the material hardens and apply a second layer on top of it.
- When applying the second and subsequent layers, we monitor the intensity, since the foam can greatly increase in size and go beyond the lathing, and this is unacceptable, since problems with the decorative finishing of the facade may then arise.
Please note that when laying the second and subsequent layers, it is important to maintain the evenness of the coating. Moreover, re-application of foam should be carried out from places where there are polyurethane foam joints.
At this stage, the insulation process has not yet been completed; in order for the heat-insulating material to reliably serve for more than a dozen years, it is secured by reinforcement. How to do this, read in the next section.
Insulation of the external wall of a building using polyurethane foam insulation Source uteplenie-penop.ucoz.ru
Sputtering process
If you have entered into an agreement with a company, a minibus arrives at the appointed time. It contains spraying equipment. To operate a high-pressure apparatus, a voltage of 380 V is required. If you only have 220 V, you usually start a generator that produces the required voltage. A low-pressure apparatus can operate from a 220 V network, but, as discussed below, the quality of thermal insulation will be significantly worse.
Typically, only hoses are pulled into or around the house to supply the foam components to the gun. It's comfortable. Workers who spray thermal insulation are dressed in protective suits, wearing a respirator, gloves and goggles. A respirator is necessary, since before hardening the components of the foam are toxic, and everything else is to protect the skin from ingress of polyurethane foam, which then cannot be removed.
The foam is applied from bottom to top, in small portions. Fill everything in without skipping, trying to prevent the formation of shells. As the foam expands, make sure that the layer thickness is no less than the required one. After the foam hardens, the excess can be cut off, but the deficiency cannot be made up for.
Facade reinforcement technology with step-by-step guidance
When all the work on insulating the facade of the house is completed, you can begin finishing, but first you need to carry out reinforcement so that the finishing layer fits well on the insulation. The whole procedure will consist of a small step-by-step algorithm:
- Wait until the applied layers of polyurethane dry well, then cut off any excess waves and bumps, and then sand the surface. To do this, use a special attachment for an angle grinder or coarse sandpaper.
- Cut the reinforcing mesh into fragments so that the length of each is equal to the height of the insulated wall.
- Apply the adhesive composition to the surface of the insulation so that it does not extend beyond the dimensions of one piece of mesh. Remove any remaining adhesive using a notched trowel. This is necessary so that small grooves remain on the wall.
- Apply a piece of reinforcing mesh and embed it in the glue, then smooth the composition using a flat spatula. It is important that the entire part is well soaked, this will encourage adhesion.
- After completing the reinforcement of the facade, coat the entire surface with glue again so that its thickness is at least 2 mm.
Then, after the prepared surface has completely dried, you can begin finishing the facade.
Application of polyurethane foam to the basement of the house Source remontnik.ru
Areas of application, spraying and the best manufacturers of polyurethane foam thermal insulation
What are they insulating?
Insulation of PPU pipes
Innovative polyurethane foam insulation, which proudly demonstrates good technical characteristics, is used for thermal insulation of the following objects:
- Industrial buildings (hangars, warehouses, service stations, prefabricated buildings, car washes, cowsheds, etc.);
- Private houses and commercial buildings;
- Refrigeration equipment;
- Technological containers;
- Pipeline communications.
The substance is universal because it insulates:
- roofs and roofs;
- ceilings and floors;
- walls, partitions and facades;
- basements and plinths;
- building foundations.
Sprayed thermal insulation has won the trust of tens of thousands of people, as evidenced by laudatory reviews. It is impeccable for any object and has excellent technical characteristics. In addition, the technology for applying it is simple; the main thing is to acquire a special unit.
Of course, this specialized equipment costs “good money” and no one will buy it for one-time use. There is only one conclusion - order the service from a reliable company. All you have to do is watch the progress of events.
Sputtering technology
The work is carried out as follows:
- the first substance is poured into the container and mixed well using a mixer;
- the second component is prepared in another container (if there is sediment, it is heated to +70°, stirred and filtered);
- in the third container the prepared ingredients are mixed;
- the substance is poured into special equipment from which it is sprayed onto the surface.
PPU installation diagram
Foam spray equipment
It is advisable that the work be performed by an experienced craftsman. As the great Dunno said, “every business needs to be learned.” This expression is also acceptable here. At first glance, there is nothing complicated about the work. But only a specialist will be able to make a surface that is even and uniform in thickness.
Famous manufacturers
Today, spray-on insulation materials from:
- “Polinora” (there is more detail about it in this article);
- "Ecotermix";
- Foam Kit;
- Heatloc Soy.
Of course, there are other well-known manufacturers that produce PU foam insulation, but products from these “KITS” are in greatest demand (or better “promoted” by marketers). A “fur coat” donated to the building will certainly not allow Winter to steal precious warmth from your home!
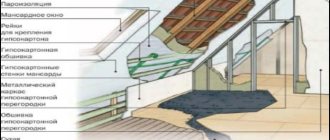
How to insulate an attic with polyurethane foam
The attic is insulated with foamed polyurethane foam from the inside. Therefore, it is immediately important to take care of free access of fresh air into the room, since vapors when sprayed have a toxic effect on the body. Then everything is done in stages.
First stage: preparatory
Perhaps the simplest step is preparing the room for insulation work. It includes clearing the attic of unnecessary items that could accidentally be stained with foam. Furniture is removed, and all non-removable objects are covered with plastic film.
Be sure to cover glass surfaces and doors: with cloth or paste over them with newspapers. If possible, the entire process should be carried out in an empty but well-ventilated area. Sealed windows will have to be opened to provide ventilation.
Dismantling of the attic room before insulation Source par-torg.com
Stage two: dismantling
It is important to dismantle the old covering from the ceiling and remove deteriorated insulation. If the premises have not yet been inhabited, then no preparation will be required. The chipboard and slats that make up the attic structure are checked for integrity; if they are damaged, they need to be replaced.
This step also involves removing dust and debris, removing cobwebs in the corners, and then coating the surface with a primer to increase the chances of adhesion.
Preparing the attic before insulation Source remontnik.ru
Disadvantages of sprayed polyurethane thermal insulation
Despite a number of advantages of thermal insulation, discovered by the scientist Bayer Otto, there are also disadvantages (where would we be without them):
- exposure to the negative effects of ultraviolet rays, which worsen its technical characteristics;
- the possibility of deformation of an insulated surface made of fragile materials, since the foam, expanding, creates pressure (any installer of windows or doors will confirm);
- a special unit is required to apply polyurethane foam;
- relatively high price compared to other insulation materials;
- the hard type is characterized by low vapor permeability, which has a very negative effect on the atmosphere in the room (this is why it is most often used as waterproofing, for example, in the treatment of plinths and foundations).
Experts recommend calling a specialist before purchasing material to inspect the surface that requires insulation. If the building structure is strong and the price of the thermal insulation material is not scary, feel free to contact specialized companies. And to protect the material from the harmful effects of UV rays and increase the vapor permeability coefficient, you can buy special additives. I'm not even talking about the exterior decoration of the building.
Features and beneficial properties of polyurethane
When choosing attic insulation using polyurethane foam, you need to know what properties the declared material has. All detailed data will be presented in the table.
| Characteristic | Indicators |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.03 W (m*K) |
| Weight of the insulating layer | 30-70 kg/cub.m |
| Waterproof | Full (for closed cell material) |
| Fire safety | Level G-2 |
| Adhesion | High (for any surfaces) |
| Adjusting layer thickness | Possible during operation |
| Additional functions | Noise insulation |
| Drying time | 1 hour |
| Treatment against rodents and insects | Not required |
| Lifetime | 40-50 years |
Insulated PPU timber
Let’s talk separately about a new product that has gained enormous popularity in Europe today. It consists of two lamellas, between which a layer of polyurethane foam is poured. Foaming, polyurethane foam glues the boards together, creating an imitation of real laminated veneer lumber.
Practice shows that a structure assembled from two lamellas and fasteners in the form of polyurethane foam is no different in appearance from a wall made of laminated veneer lumber, but in terms of characteristics, it is many times superior to it. Insulated PPU timber is three times lighter, cheaper and warmer than solid wood. The internal filling of the wall made of polyurethane foam enhances the thermal insulation properties of the timber, and the house does not require additional insulation, which saves money on heating.
Having familiarized yourself with the advantages and disadvantages of polyurethane foam, having considered the types and technology of applying the material, it will be easier for you to make the right choice in terms of insulating your home and soundproofing it. Make the right choice, and your home will delight you with warmth and comfort for many years!
Polyurethane foam: types, properties, application
Why you need to buy linen insulation for your home
Features that must be observed by workers when applying insulation
When performing work on applying polyurethane foam to walls, the operator must ensure:
- the optimal temperature of the surface on which polyurethane foam is applied is 10 degrees;
- preheating of insulation components to the indicators provided for in the specifications for a specific type of material;
- strict mixing of components in a 1: 1 ratio;
- 100% intensive mixing of the components until a homogeneous liquid consistency is formed;
- uniform spraying and compliance with the thickness of the insulating layer.
On a note! PPU is difficult to dismantle if applied incorrectly. There is a big risk that a piece of foam will fall behind the part of the plaster that covers the wall.
It should be noted that the quality and duration of service after applying a layer of polyurethane foam depends strictly on how correct the material manufacturing technology was. In other words, if the manufacturer approached the process negligently, then you should not expect reliable operation from the thermal insulation composition. This flaw cannot be determined by eye by the appearance of the material. All you have to do is trust the seller.
Application conditions and surface preparation
Even with good adhesion, which is characteristic of polyurethane foam insulation, surface preparation will not be superfluous. First of all, you need to remove everything that is crumbling - and first of all the old paint. Grease stains must also be removed and neutralized. They shouldn't exist.
Polyurethane foam is applied to dry, grease-free surfaces
Everything that should not be covered with foam should be covered with polyethylene secured with tape. It must be secured carefully, without gaps - it is difficult to remove the foam.
When insulating a roof with polyurethane foam, there are two ways to apply thermal insulation. The first is to make a permanent continuous sheathing onto which foam is poured. The second is to make a temporary frame consisting of two parallel planes.
If the outer walls of a building are insulated with polyurethane foam, a finishing finish is assumed. And after cleaning the surface, you need to make sure that you can strengthen it with something - it won’t work with foam. To do this, most often, wooden or metal strips are placed on the walls, to which the exterior trim is then attached. This completes the preparation. But applying polyurethane foam is only possible on a completely dry surface, at temperatures above +10°C. There are no other conditions.
Insulation of facades with mineral wool
Mineral wool is classified as an environmentally friendly material that does not emit harmful substances. In addition to thermal insulation properties, it also has sound insulation properties. According to GOST, mineral wool comes in three types: fiberglass, slag and rock. Each of them has its own characteristics. Glass wool contains glass threads that can irritate human mucous membranes, so you only need to work with this material in special clothing. Slag wool is not suitable for insulating baths and steam rooms because it absorbs moisture. Stone wool is suitable for installation on any surface.
Before you start insulating the facade, you need to clean it of dirt and fittings, dismantle all the slopes and pipes in order to have access to the walls. Mineral wool is produced in rolls. They can be cut into squares to make it easier to attach to walls. Then make markings on the walls, this will help to install the insulation evenly. The next element is the base profile. This is a steel holder that is attached to the wall, it supports the insulation and regulates the gap between the wall and the mineral wool. After this you need to prepare the glue. It retains its properties for two hours, so it is important to work quickly. Apply glue to the entire surface of the mineral wool blocks. Then the insulation needs to be glued to the facade, starting from the base profile, gradually rising higher. Lay out the mineral wool in a checkerboard pattern. After this, secure the slabs with facade dowels, apply a base layer of plaster on top, install a fiberglass mesh and cover it with a primer layer.
Insulation of walls by spraying 5
Insulation of frame house walls with polyurethane foam
Wall insulation
According to statistical data, the amount of heat loss through building envelopes varies within
15-30%. The understandable desire to provide comfortable living conditions inside residential premises leads to an increase in energy costs for heating the building. And if previously insulation of buildings was achieved by increasing the thickness of the walls, then with the advent of modern heat-insulating materials with low thermal conductivity, lightweight and easy to install, the need for massive enclosing structures has disappeared. The importance of effective thermal insulation, especially relevant for unstable Russian winters, with sudden temperature changes - from abnormally low to thaws, can hardly be overestimated. 1 cubic meter of high-quality thermal insulation allows you to save about 1.4 - 1.6 tons of fuel equivalent per year.
The use of energy-saving technologies in construction is popular today in all developed countries of the world. Modern thermal insulating multilayer enclosing structures are also one of them. Walls made of any building material: wood, brick or concrete panels are exposed to aggressive weather conditions. In addition, any soil on which the building stands is more or less saturated with water (surface or ground). Thanks to the porous structure of the most common materials in construction, this water can rise up to 4 meters above ground level through the pores and capillaries in brick, concrete or wood. All this has a detrimental effect on the wall material, promotes the formation of cracks in them and
other deformations, and constantly high humidity leads to the appearance of mold. Heat is easily lost through the resulting cracks, increasing heating costs. The most effective way to protect building facades is their thermal and waterproofing.
The larger the area of external surfaces, the higher the heat loss, and since the main area of the external surfaces of the house is its walls, only the right approach to their insulation will minimize these losses. The choice of insulation is influenced not only by the material from which the house is built or the parameters of the insulation itself, but also by the method of its installation: external or internal.
Wall without insulation
In this case, the temperature zero is inside the wall structure. The presence of moisture in the wall causes it to turn into ice at the freezing point, which destroys the wall. The wall is exposed to temperature changes. The thickness of the wall here is clearly insufficient for thermal comfort inside. Heat loss through wall structures can reach up to 80%. Therefore, despite the heaters operating at full power, it is cold inside the room.
Insulation of walls from the inside
With internal thermal insulation of a wall, the temperature zero shifts to the internal boundary between the wall and the thermal insulation. If there is even a minimal gap between them, a condensation zone appears here; moisture from the room, inevitably entering there, freezes and, expanding at the same time, leads to peeling of the heat-protective coating. Therefore, the conclusion is: the use of water-permeable insulation for internal thermal insulation is unacceptable. In addition, condensed and accumulated moisture during the winter period cannot be removed even in summer, which leads to progressive dampening of the walls and associated consequences.
The wall in this case is located in a zone of negative temperatures, which sharply reduces the thermal inertia of the enclosing structure, which clearly does not contribute to improving the microclimate in the room. Reduction of heat loss is far from optimal.
Insulation of walls outside
The temperature zero in this case is located inside the outer heat-insulating layer. The possibility of condensation formation is eliminated, so the wall remains dry. Destruction of the heat-insulating layer here can only occur if it is vapor permeable. Only with this method of thermal insulation are wall structures not subject to temperature changes and perform their function as efficiently as possible, being a kind of compensator for temperature changes inside the room. Heat loss is significantly reduced. Insulation of walls outside
the price is posted on our website in the form of a price list.
The main advantages of external thermal insulation of building wall structures are thus:
- equalization of temperature fluctuations in the wall mass, which eliminates the appearance of cracks in it resulting from uneven temperature effects, which is especially typical for large-panel external walls;
- protection of walls from the destructive effects of alternating freezing and thawing, which are a consequence of an unstable climate;
- shift of the “dew point” into the heat-insulating layer located outside the wall, which prevents moisture condensation on its inner surface;
- no need to install a special vapor barrier, which is mandatory in the case of internal thermal insulation;
- more favorable and comfortable indoor microclimate;
- the opportunity in the future to change the design of the building by improving the design of the facades;
- there is no selection of usable area.
Insulating a house from the outside In some cases, external thermal insulation is not possible for a number of reasons, for example, the external design of the building has historical or architectural value, or the building has a complex architectural topography, etc. There is a solution for such cases. You just need to choose the most suitable thermal insulation material that can mitigate the problems that arise. Only insulation with a very low thermal conductivity coefficient will not take up much usable space. In addition, to reduce the likelihood of condensation and mold, it is recommended to perform internal insulation with low vapor permeable insulation that does not allow water vapor to penetrate into the zone of possible condensation. External thermal insulation requires the installation of scaffolding on the outside of the building.
As for the value of thermal conductivity, it is determined by a number of factors: the density of the material, the size, type and location of pores and, most importantly, humidity. The values of thermal conductivity in our country and abroad differ due to the discrepancy between the current standards (GOST and ISO), which require different test conditions.
It is clear that the accumulating heat capacity of the outer wall mass cannot be used in this case (with internal thermal insulation). But we will get an advantage in another way:
- savings in energy resources previously spent on heating external walls are obvious;
- There is practically no heat loss; when you turn on even a small low-power heater, a comfortable temperature is quickly established in the room.
Cold bridges can be eliminated by applying insulation with partial overlap of the floor slabs. The junction points can be easily decorated in the future.
An important condition for the effectiveness of internal thermal insulation is the high adhesion of the insulation to the wall material; the material must not only adhere very tightly to the enclosing structure, but become one with it, a durable monolithic structure. Only in this case, in the complete absence of even minimal gaps and cracks, moisture from living quarters will never be able to get to the dew point. In this case, the dryness of the enclosing structures will be guaranteed, and seasonal temperature changes in conditions of complete absence of moisture access will not have a destructive effect on the wall material.
And such thermal insulation material exists. Possessing the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient among the entire extensive range of thermal insulation materials, rigid spray polyurethane foam occupies a minimum of interior space. The thickness of the polyurethane foam layer ranges from 20-35 mm.
Polyurethane foam is the only thermal insulation material that can be used indoors. Insulation of frame walls or insulation of brick walls with polyurethane foam will be carried out using spraying technology using special professional high-pressure equipment. For internal insulation, only non-combustible materials with an absolute guarantee of environmental safety and low density can be used. Low-density polyurethane foam is the best choice in this case.
Outstanding adhesive characteristics, allowing polyurethane foam coating to be applied with equal efficiency on surfaces of any shape from almost any existing building materials, at any angle of inclination to the horizon, makes it possible to spray the coating even on the ceiling, which is a necessary condition for insulating cold bridges. The resulting coating adheres tightly to surfaces with any relief, taking on their shape.
Foamed polyurethane, being in a liquid state for some time, fills even the slightest cracks and leaks. After curing, the sprayed coating becomes a single rigid structure with the wall, isolating it from destructive moisture. More than 15 years of experience in using this technology for internal insulation of walls of buildings and structures only confirms its effectiveness and further prospects for use.
Internal thermal insulation with sprayed polyurethane foam
After polymerization of the sprayed polyurethane foam layer, the protective layer on the side of the room is finished with plaster, wood panels, plasterboard or facing bricks at the discretion of the owner. When using internal thermal insulation, the temperature of the inner surface of the walls increases by an average of 2 - 4 degrees, which has a beneficial effect on the general microclimate in residential premises.
As we have already noted, such a solution to the issue is recommended only in exceptional cases when it is not possible to carry out external insulation.
Insulation of frame walls or insulation of brick walls occurs from 100 to 150 kilowatt-hours of thermal energy lost through one square meter of an ordinary non-insulated wall per year, which corresponds to 10-15 cubic meters of gas. These figures can be reduced by 90% using spray-on foam for external thermal insulation.
External thermal insulation with sprayed polyurethane foam, decorated with plaster
Rigid polyurethane foam is sprayed directly onto dust-free wall surfaces without prior priming. The primer is applied to a layer of cured polyurethane foam to ensure better adhesion to the decorative plaster finish. One of the advantages in this case is the absence of the need for special fastening with pins or using plaster mesh, which is typical for traditional types of thermal insulation.
Insulation of a double masonry external wall using spray-on polyurethane foam
One of the thermal insulation systems that has become widespread in regions with extreme weather conditions is the use of sprayed polyurethane foam between two layers of external masonry. In this case, after spraying polyurethane foam onto the internal masonry, the wall is covered with external masonry. To ensure good adhesion between the insulated surface and the heat-insulating material (PPU), it is necessary that the surface is dry and dust-free. An external wall of rendered masonry, quarry stone or brickwork is not just an outer shell, but also has a protective function in relation to the insulating layer. An important condition for this method of thermal insulation is the air gap between the heat-protective layer of polyurethane foam and the outer wall, which is necessary to eliminate excess moisture or infiltrated rainwater.
Possessing a high degree of adhesion to a wide variety of materials, polyurethane foam has established itself as an excellent thermal insulator for walls made of ceramic or silicate bricks, wooden beams, gas or foam concrete blocks.
One of the varieties of polyurethane foam is rigid sprayed polyurethane foam “PENOGLAS™”. This material consists of more than 90% closed gas-filled pores; therefore, it has high thermal and waterproofing characteristics and is an excellent material for insulating the facades of country houses. An important condition for the use of such a polyurethane foam heat insulator is the presence of forced ventilation in the house, since polyurethane foam, having excellent protective qualities, nevertheless cannot “breathe”. There are low-density polyurethane foams with a large-porous structure, which are most suitable for insulating vapor-permeable wall structures inside a building. Such PU foams have 50% closed and 50% open pores, which is what determines their “breathing” properties.
High-density polyurethane foam (60 kg/m3), which simultaneously has waterproofing properties, can provide reliable protection of walls from precipitation and, in some cases, from groundwater.
External insulation of the walls of a house with polyurethane foam does not look quite aesthetically pleasing. The final coating for thermal insulation using sprayed polyurethane foam is especially necessary in cases where the aesthetic component is very important. The fact is that polyurethane foam, when applied, repeats the texture of the surface, i.e. when applied, for example, to brickwork, even with a layer of only 50 mm, the contours of the masonry are clearly visible. With a greater thickness of the layer of sprayed polyurethane foam, its own roughness is layered onto existing irregularities.
Of course, the polyurethane thermal insulation coating must be protected from the outside with a finishing finish. In addition to the factor of visual appeal, it is not recommended to leave an open layer of polyurethane foam without coating due to the loss of PU foam of its quality characteristics under the influence of prolonged exposure to solar radiation. An unprotected polyurethane foam coating first acquires a characteristic yellow color, then turns brown and ultimately collapses. The protective layer applied to the polyurethane foam coating should not transmit UV rays.
The most economical finishing method is to paint it. The most common materials used for this purpose are acrylic or silicate facade paints (service life up to 3 years), enamels based on silicone resins or epoxy polymer enamels (service life about 30 years), paints and varnishes of the “liquid plastic” series (service life service life more than 10 years), as well as polyurea (durability more than 50 years).
Since the service life of the polyurethane foam coating itself is more than 20 years, the use of less durable materials for finishing is irrational.
The most reliable coating that has become widespread in recent years is polyurea, which is characterized by increased wear resistance, exceeding even ceramic floor tiles in terms of this indicator, possessing remarkable hydro- and anti-corrosion properties, and unsurpassed resistance to precipitation.
In addition to its protective properties, a wide palette of colors and an even, uniform layer of coating allow it to be used simultaneously as a facing material. However, quality comes at a price. The cost of spraying polyurea in comparison with other materials is still quite high.
The main requirements for finishing protective coatings are resistance to external factors and, of course, decorativeness. The protective properties of enamels (hardness, elasticity, resistance to UV radiation, the ability to withstand temperature changes, etc.) are usually higher than those of oil-based and water-dispersion paints, which are inferior to enamels in their decorative properties.
Plastering, curtain wall facade systems, cladding with siding, block house (decorative lining) or facing bricks, etc. are also used as finishing for polyurethane foam coating.
Excellent results are obtained when used as a finishing finishing for curtain walls. The installation of curtain facades is carried out in two stages: first of all, the sheathing is attached to the walls on hangers so that there is a gap between the future finishing and the wall, the size of which will allow not only to apply a layer of polyurethane foam of the required thickness, but also to leave what is necessary for ventilation , removing excess moisture, a space of 2-4 cm. After spraying polyurethane foam on the external walls, the installed sheathing is covered with the selected finishing material - tiles, lining, etc.
External thermal insulation behind a curtain wall with ventilated cladding
This method is practiced both in the construction of new buildings and in the restoration and repair of existing ones. The decorative curtain wall allows for a wide choice of home design.
Plastering the facade is the most preferred type of external wall finishing with increased requirements for the decorative component of the facade finishing. This rather labor-intensive process includes several stages:
- after treating the surface using mechanical tools, trimming particularly protruding areas, Ceresit ST-85 adhesive mass is applied to the wall using shotcrete, which allows not only to minimize glue consumption, but also to enhance the adhesive properties of subsequent applied polyurethane foam layers;
- installation of nylon or metal mesh that acts as reinforcement. Fastening is also carried out using glue;
- application after the adhesive mass of the plaster has dried. Better application of cement-lime mortar is ensured by using the shotcrete method;
- painting, as the final stage of finishing, is carried out at the request of the customer.
Installation of insulation under siding can be done in two ways:
- The heat-protective layer is sprayed onto the wall, forming a continuous, seamless surface, then the supporting profiles are attached to pre-installed L-shaped aluminum inserts. The appearance of cold bridges with this method of thermal insulation is completely eliminated due to complete sealing with a monolithic layer of insulation. Considering the use of additional aluminum structures, the cost of the system increases slightly.
- First, the load-bearing profiles are attached to the walls of the building; the insulation fills only the gaps between them. The required quantity of polyurethane foam is reduced, but time and labor costs increase. The thickness of the supporting profiles should be at least 20-30 mm greater than the thickness of the sprayed polyurethane foam.
Insulating the walls of a house with polyurethane foam is a modern technology for thermal protection of buildings, which simultaneously increases the noise protection characteristics of the building.
The main advantages of thermal insulation of wall structures using polyurethane foam include the minimum thickness of the protective coating, its low weight, the absence of seams, record-breaking application times (10-20 times faster than with traditional thermal insulation), no need for fasteners due to the high degree of adhesion PPU with other materials, service life, etc. Thermal insulation work by spraying polyurethane foam does not require calculations for the additional load on the foundation, due to the low weight of such a coating, while when working with other insulation materials, such a calculation is mandatory.
In some cases, it seems advisable to use combined systems for thermal insulation of wall structures, such as polyurethane foam + expanded polystyrene or polyurethane foam + mineral wool.
Carrying out work on thermal insulation of wall structures using polyurethane foam requires the provision of certain conditions:
- availability of power supply: mains or from a generator, voltage 220 V, for significant volumes of work - voltage 380 V;
- free access to the surface on which polyurethane foam will be sprayed;
- the ability to install scaffolding and move it at a height of more than 3 meters;
- favorable weather conditions without precipitation and strong winds;
- air temperature not less than +5 degrees C.
When working in winter, spraying can only be done in heated rooms.
Using PPU spraying to protect the facades of your home, you receive not only a heat-insulating coating, but also reliable, seamless protection from moisture and air penetration. In addition to low thermal conductivity (0.019-0.025 W/m*K), polyurethane foam has the lowest water absorption among all thermal insulation materials, and low air permeability allows you to create a reliable barrier to the pressure of air masses.
The use of polyurethane foam strengthens the fastening of wall panels to each other, the strength of the walls increases by 50%, which increases their resistance to wind loads, as well as seismic resistance.
The ability to use lighter wall structures reduces construction costs. The ability of polyurethane foam to be applied to surfaces of any configuration opens up greater opportunities for architects and engineers, since it allows for thermal insulation of the most complex architectural forms: arches, columns, protrusions, etc.
Since the formation of a seamless protective coating eliminates the use of fasteners, cold bridges do not form in this case. The solidity of the coating is the key to minimizing heat losses.
House heating costs are reduced in some cases by up to 60%. Because less heating fuel is used, carbon dioxide emissions are reduced.
Your own home needs constant care. Over time, buildings deteriorate, urgently requiring repairs and comprehensive modernization. The enclosing structures of such a house often no longer meet modern standards for thermal protection. Increasing heating costs in connection with this force us to take a fresh look at the problem of energy saving and pay attention to progressive methods of thermal insulation.
Thermal insulation of the building envelope with sprayed polyurethane foam is possible both during the construction of a new house or cottage, and during the renovation of an old one. When insulating such houses, special attention should be paid to certain areas through which heat leaks occur, the so-called cold bridges. Identifying cold bridges is not an easy task and it is unlikely that you will be able to cope with it on your own. The best way out may be a television inspection of your home.
Over the past decade, standards for thermal insulation of buildings and structures have been revised and tightened, which has led to the need for additional thermal insulation during the reconstruction and repair of buildings. The use of sprayed polyurethane foam in such cases is most appropriate, since it not only creates a monolithic shell that has remarkable heat, air and moisture-proof properties, covering all cold bridges, but also strengthens the worn-out structures of the old building. Porous surfaces, such as plaster, concrete, foam blocks, wood and brick, after treatment with sprayed polyurethane foam, are significantly strengthened and, to a certain extent, acquire waterproofing properties. This effect is explained by the peculiarities of sprayed polyurethane foam technology, in which the reaction mixture of isocyanates and polyols, which is in a liquid state, is partially absorbed into the cracks and pores of building materials, where it hardens (polymerizes).
As for metal structures, here too, thanks to its outstanding properties, polyurethane foam shows impressive results. Polyurethane foam is not only a good vapor barrier, it is also practically impenetrable to air oxygen, which makes polyurethane foam coating reliable protection against corrosion. In addition, the high elasticity of the polyurethane foam layer, combined with strength, allows polyurethane foam shells not to crack under the influence of temperature changes or mechanical stress, which is usually the Achilles heel of most primers and paints and varnishes. Of course, not only metal structures, but also any other building materials coated with sprayed polyurethane foam are under reliable protection from the aggressive influences of the atmosphere.
Any defects that arose during the operation of the building, or resulted from the dishonesty of the builders at the initial stage of construction and arrangement of the building, such as the absence of fasteners or their insufficiency, cracks, leaks, etc., are easily eliminated by spraying polyurethane foam at minimal costs.
If you need to restore an old building in need of repair, giving it heat-insulating properties in accordance with modern standards, then it is difficult to find a better solution than curtain facades, previously thermally insulated using sprayed polyurethane foam. In this case, polyurethane foam, along with excellent thermal insulation, provides strengthening of a worn or collapsing facade with complete sealing of through cracks and cracks, and also serves as additional fasteners for guides and brackets that are fixed to the facade through thermal breaks (gaskets made of thermal insulation material). At the same time, the service life of the guides and brackets themselves increases.
The physical and mechanical properties of polyurethane foam used for thermal insulation of external walls must meet certain requirements, in accordance with current standards:
- thermal conductivity coefficient – no more than 0.045 W/(m*.0С);
- compressive strength – not less than 1.0 kg/cm²;
- water absorption – no more than 300 cm3/m² in 24 hours;
- adhesion to building materials or, what is the same, the tensile strength when tearing off a polyurethane foam coating from the material of a heat-insulated structure - at least 1.0 kg/cm²;
- absence of corrosive effects on metal surfaces (fittings, embedded parts, etc.);
The main stages of work when installing thermal insulation of external walls with sprayed polyurethane foam are:
- preliminary preparation of the application surface;
- preparation of components;
- performing a technological test;
- spraying polyurethane foam;
- quality control of work performed and repair of poorly insulated areas of finished thermal insulation.
The surface on which polyurethane foam is applied must meet the requirements of SNiP 3.04.01-87 “Insulating and finishing coatings”:
- The surface should be free of traces of dirt, dust and oil stains, and dust should be removed immediately before starting work on spraying polyurethane foam.
- Metal parts of structures must be free of corrosion and grease. Degreasing metal surfaces before applying polyurethane foam is mandatory.
- Wet surfaces must be dried with compressed air, and at air temperatures below +5 degrees C, the drying air must be heated; The humidity of the base when applying sprayed polyurethane foam depends on the base material and should not exceed:
- for concrete foundations – 4%;
- cement-sand, gypsum and gypsum-sand – 5%;
- wooden – 12.0%.
- Areas not intended for application of polyurethane foam must be protected with plastic film or thick paper.
The components used to produce rigid spray polyurethane foams must also meet certain requirements:
- The chemical composition and physical properties of components “A” and “B” (isocyanates and polyols) must comply with the requirements of the technical specifications applicable to these compositions. Compliance with the guaranteed storage period is mandatory. After this period, the original components must be tested for compliance with the required specifications and, if positive, allowed to be used for half of the original warranty period.
- It is mandatory to comply with the rules for storing components and transporting them. Containers for their storage and transportation must be marked. Each batch of components must have a passport.
- Components must be prepared, tested and labeled in accordance with the specifications for that component. Components must be manufactured at specialized enterprises and supplied in special labeled containers, ready for use.
- The temperature of the components during spraying should be within 20-25 degrees C.
- Components “A” and “B” must be thoroughly mixed before use. If there is sediment in component “B”, it must be heated to a temperature of 50-65 degrees C with stirring.
For spraying polyurethane foam, domestic and foreign-made installations are used, operating according to a two-component scheme, with dosing of components (isocyanate and polyol) in a ratio of 1:1 to 1:7. The ratio of components varies depending on the requirements for the final product. The density of polyurethane foam, which is a porous cellular structure, can vary in a wide range from 30 to 300 kg/m3. However, for thermal insulation, rigid polyurethane foam with a density of 30 to 50 kg/m3 is mainly used.
Mobile and compact installations allow spraying directly on site, which is another important advantage of this method of installing thermal insulation for enclosing structures. Due to this, the reduction in costs for transportation, storage and installation work on thermal insulation brings a significant economic effect. More than 90% of polyurethane foam consists of gas; the use of modern foam generators, which make it possible to produce polyurethane foam at the site of use, is much more convenient and profitable than transporting “air” hundreds of kilometers away. From one ton of raw materials you can get 20 cubic meters of rigid polyurethane foam and spray it over an area of 500-600 m² in a layer of 3-4 cm. You should also exclude the costs of fastening and consumables, organization and security of the warehouse. As for savings, in addition to saving money, time is saved significantly. It's time to remember the saying “Time is money.” The high technology of the polyurethane foam spraying method saves up to 80% of the time when performing thermal insulation work: The time spent on loading, transporting and unloading thermal insulation materials is reduced. Agree, loading four barrels with components (1 ton of raw materials) and a spraying installation, delivering them to the construction site and unloading is much easier than 20 cubic meters of finished insulation, which can be obtained from the same ton of raw materials.
Reducing the time required to complete the work actually makes it possible to put the facility into operation several times faster. A team of two people during a work shift can spray an area on average of about 800 m², and thanks to the high rate of polymerization of the material, operation of the facility becomes possible almost immediately after the completion of thermal insulation work. Labor costs for thermal insulation of a surface of the same area using traditional thermal insulating materials are usually an order of magnitude higher.
The principle of operation of a spray installation for spraying polyurethane foam is based on mixing two liquid foaming components “A” and “B” using compressed air in the mixing chamber of the spray gun and supplying the foaming mixture to the insulated surface.
The GRACO Reactor H-XP2 installation is an electro-pneumatic high-pressure apparatus for applying polyurethane foam thermal insulation. Ideal for medium-sized objects.
Externally, the spraying technology resembles conventional surface painting with a spray gun. Curing of the coating occurs within 10-40 seconds. Spraying can be carried out in several layers to achieve the required coating thickness according to thermal engineering calculations.
Spray installations for applying polyurethane foam must provide filtration, mixing and heating of components to operating temperatures.
Foam generators must be equipped with two mixers or a recirculation system on containers with components “A” and “B”, and must also be able to work with mixtures with a viscosity of up to 2000 mPa*s.
The productivity of installations used for thermal insulation with rigid spray polyurethane foam (closed cell) should be in the range of 0.1-4 kg/min. The compressed air required for the operation of the foam generator is produced by an external compressor.
After applying the heat-protective layer, at least 24 hours must pass, after which you can begin installing the protective coating.
If, as a result of surface quality control carried out after thermal insulation work on spraying polyurethane foam, defects (cracks, delamination) were discovered, then they can be easily corrected. You just need to cut out the defective area and restore it by spraying.
The cost of attic insulation can be viewed on our website in the services section.
Using rigid sprayed polyurethane foam as a thermal insulator when insulating wall structures will make your dream of a passive house come true.
Insulation of facades under siding
It is not so important what kind of siding the facade is insulated under - vinyl or metal, the main thing is to follow the sequence of steps. Siding does not protect the building from the cold, so the thicker the layer of thermal insulation, the warmer the room will be. Insulating facades from the outside helps preserve usable space inside the building.
The work order consists of cleaning the facade surface, eliminating unevenness, insulation and decorative work. To protect walls from the cold, mineral wool, polystyrene foam, expanded polystyrene, penoizol, and polyurethane foam are suitable.
Pie composition:
- primer,
- adhesive composition,
- insulation,
- reinforcing mesh,
- plaster layer,
- siding installation.
After gluing the insulation to the surface of the facade, you need to install dowels that will secure the structure. To protect the insulation from moisture, you can attach a polymer moisture-repellent film to it. Before installing the siding, wait until the plaster layer has completely dried, then begin work.
Advantages of the material
- The material is environmentally friendly and does not contain harmful substances for the human body.
- Has a high level of water absorption.
- It has protective properties that prevent the occurrence of corrosion.
- It is resistant to mechanical damage caused by impacts, high loads, etc.
- Lifetime. Due to the fact that water is not absorbed by polymer foam, its structure is not disturbed by numerous cycles of thawing and freezing.
- No seams. Sprayed thermal insulation is applied using a special gun, so after drying a seamless layer is formed, which eliminates the occurrence of temperature bridges. If they are present, significant leaks of warm or cold air from the room occur.
- Adhesion. The sprayed product adheres well to all building materials used, only they must first be cleaned of grease, dust, poorly adhering areas of the old coating and debris.
- Expenses. Allows you to reduce space heating costs by up to 50%.
Insulation of facades with penoplex
Penoplex is extruded polystyrene foam. The composition is similar to polystyrene foam, but has a uniform structure and smooth surface. Thermal conductivity is even lower than that of polystyrene foam; it does not absorb moisture. The flammability class is G4, so it is not suitable for insulating rooms with a high level of fire hazard. Due to its smoothness, polystyrene foam does not have a very high degree of adhesion.
Before insulation, the facade must be cleaned of dirt, leveled, and cracks repaired. Then prime. Mark the wall to attach the slabs of material in a checkerboard pattern and install the base profile around the perimeter of the house using dowels. Apply glue to the polystyrene foam boards around the perimeter and in the middle. After this, carefully attach the panel to the wall, starting from the corner of the building from the base profile. When the first row is ready, you need to check how smoothly the insulation boards fit to the wall and to each other; to do this, take a long level. Then you can proceed to the second row, moving from bottom to top. The next stage is fixing the slabs using façade dowels. They need to be inserted at the joints, grabbing several slabs at once. If cracks have formed somewhere, they need to be closed with an adhesive solution.
Insulation of wooden facades
Wood is a breathable material that releases and absorbs moisture. When insulating, it is important that the protective layer does not block evaporation, but, on the contrary, allows it to escape. Mineral wool and polyurethane foam are suitable for insulating wooden facades.
Mineral wool is traditionally used to protect wood from cold weather. It is easy to install, it is flexible, and even if gaps form, installation errors can be easily corrected. However, mineral wool has a high water absorption coefficient: 40% versus 2% for closed-cell polyurethane foam. This suggests that mineral wool absorbs moisture, which reduces its heat-protective properties. But it belongs to non-flammable materials, while polyurethane foam has a flammability class of G1-G4 according to GOST, depending on its type. Therefore, mineral wool is chosen for insulating baths and rooms where high temperatures are often maintained. PPU is suitable for insulating residential structures designed for a long service life - from 30 years.
Before proceeding with the installation of insulation, wooden walls must be treated with antiseptics. This will prevent mold, mildew and insects from damaging the wood. Caulk cracks and gaps in timber walls with jute and cover with sealant. Prime the wall and install sheathing on it. After this, attach a vapor barrier film, this will protect the timber from moisture. Dry all wet areas of the façade with compressed air. After this, you can begin installing the insulation. If it is mineral wool, it is important to select glue for fastening and facade dowels with a steel core. If the facade is insulated with polyurethane, you need to thoroughly heat and mix the components for closed-cell polyurethane foam. Apply the polymer to the wall in two layers, 25 millimeters each.
Technology for performing work on applying liquid insulation to walls
After the surface has been cleaned and repaired, you can proceed directly to applying thermal insulation, the technology of which involves performing the following mandatory steps:
- production of lathing, for which you can use lumber or special metal and plastic profiles;
- directly the process of spraying or pouring insulation;
- creating decorative and protective surface cladding.
The need to manufacture the sheathing is explained by the need to control the thickness of the applied insulation layer, so the size of the materials for it is selected taking this parameter into account.
In addition, the sheathing device also performs a leveling function, allowing you to eliminate surface defects.
After the lathing is made, polyurethane foam is applied to the prepared base, the spray intensity of which, and accordingly the resulting thickness, is regulated by the power of the mounting gun.
At the same time, it is important to take into account this nuance: thermal insulation is always sprayed from the bottom of the surface and is carried out along its entire width, gradually moving upward. How to choose porcelain tiles for the floor? How to cut and lay? - there is more useful information here
How to choose porcelain tiles for the floor? How to cut and lay? - there is more useful information here.
In the event that the thickness of the applied layer is insufficient, it is allowed to apply polyurethane foam in several layers.
It should be noted that the above procedure for performing work is also relevant if insulation is carried out with penoizol, which is a liquid type of polystyrene foam.
You will be interested in this article - Characteristics of polyurethane foam. Review of manufacturers.
This material is mainly used for thermal insulation of buildings and industrial facilities, as well as for filling special voids in hollow building blocks and other structures.
After the insulation has acquired its final shape and size, work is carried out to level it: it is recommended to cut off the protruding parts with a sharp knife.
Next, decorative cladding is installed or the surface is plastered, which can later be painted or wallpapered, for example, if insulation is being carried out indoors.
Table of contents
- Insulation of wooden facades
- Insulation of facades with mineral wool
- Insulation of polyurethane foam facades
- Insulation of facades with penoplex
- Insulation of facades under plaster
- Insulation of facades under siding
- Conclusion
Insulating facades from the outside will help extend the life of the building and make staying indoors comfortable. Installing insulation inside a building will lead to a movement of the dew point, which will lead to the destruction of the foundation and walls of the house and the formation of mold and mildew. All moisture that forms due to temperature changes should remain outside.
When choosing insulation, you should focus on the type of structure, materials with a low coefficient of vapor permeability and thermal conductivity. To protect structures from cold, the following are suitable:
- mineral wool,
- polyurethane foam,
- Styrofoam,
- extruded polystyrene foam.