The lower crowns in a wooden frame are one of the most vulnerable places. No matter how hard the owners try to protect a wooden frame (be it a house or a bathhouse), it is not immune from deterioration. Wood is an excellent building material, but its service life is limited.
The situation when the house is in good condition, but the base is very rotten, is quite common. The owner of a wooden building should think about the possibility of repairing the lower logs already at the construction stage.
When is it necessary to replace the lower crowns?
If a wooden frame house requires major repairs after 50-60 years of operation, then its lower crowns (basement part) may fail much earlier. Accelerated destruction of wood occurs for the following reasons:
- Rotting as a result of frequent and prolonged direct contact with sedimentary and flood moisture, the release of groundwater, the accumulation of penetrating moisture and condensation.
- Damage by microorganisms (fungi, mold, bacteria), insects (ants, bark beetles, etc.) and various rodent pests.
- Destruction under excessive loads.
- Mechanical damage of various types.
The following factors contribute to the appearance of these destructions:
- Absence or poor quality waterproofing between the foundation and the plinth, as well as on the outside of the lower part of the wall.
- An improperly organized drainage system, which causes the accumulation of sedimentary and flood water, as well as moisture formed when snow melts.
- Lack of foundation ventilation (vents or vents).
- Violations during construction - use of low-quality wood, incorrect choice of log diameter, use of undried wood, insufficient antiseptic treatment and anti-rot impregnation of wooden elements, incorrect calculation of loads, violation of the rules for laying the lower crowns.
Important. The lower crowns, made of high-quality, durable material and impregnated with a protective composition, with proper waterproofing, have the same service life as the entire wooden frame of the house.
Stage 4. Waterproofing the base
Waterproofing strip foundation
Waterproofing strip foundation with roofing felt
Treat the surface of the foundation with molten bitumen and lay a layer of roofing material on top. After the bitumen has completely dried, repeat the procedure. As a result, you will have reliable two-layer waterproofing.
Waterproofing with mastic
Additional insulation with roofing felt
Preparatory work
A properly carried out preparatory stage creates the basis for high-quality repairs. It includes the following activities:
- Visual inspection. It must be carried out periodically so as not to start a destructive process. The above-ground part of the foundation, the filling element and the 3-4 lower crowns of the frame are inspected with special care. An obvious reason for repair is the appearance of visible defects - cracks in the wood, deformation of individual logs (including bulging in one direction or another), discoloration, traces of insects and pests. A pronounced sign may be the presence of a specific smell of rotten wood.
- Checking the internal condition of the wood. Superficial signs do not always indicate the need for major repairs - sometimes they just need to be cleaned off the logs and covered with a protective layer. Things are much worse if the process goes deeper into the material. The first sign of this is established by the dull sound heard when the logs are tapped with a hammer. To create a more accurate picture, you need to use a chisel and carefully remove the top layer of the tree to assess the condition of the core.
- Assessing the scope of work and drawing up a repair plan. At this stage, the types of defects and the distribution of damage are identified - local, i.e. on a small area of logs; damage to individual logs; destruction of almost the entire basement area (on one wall or along the entire perimeter of the house). Accordingly, repairs can have the following types: replacement of a small section of a log; replacement of one log with or without lifting the entire frame; complete replacement of the entire basement part of the frame.
Complete replacement of the lower crowns
Major repairs in the form of a complete replacement of the lower crowns include raising the frame, removing rotten logs and installing new crowns. The work is carried out in the following order: preparatory activities, replacement of the lower crowns and beams.
Preparatory activities:
- maximum lightening of the entire structure (removal of furniture and plumbing, removal of doors and windows, dismantling of the floor and roofing);
- dismantling stoves and fireplaces if they do not have their own independent foundation;
- separation of the chimney from the ceiling and roof, if the stove is not dismantled;
- disconnecting floor joists if they are embedded in the lower crowns to be replaced;
- shutting down all communications.
To secure the crowns along the entire perimeter of the house, boards with a thickness of at least 3 cm are nailed vertically at a distance of 45-60 cm from each other. You can fasten adjacent crowns using metal staples. Fastening is provided on both sides of the wall (outside and inside).
To lift the log house at a distance of 60-80 cm from the corner of the building, an opening 35-45 cm wide is made in the foundation and part of the logs is cut out to form a niche for installing a jack. The following lifting technology can be used:
- With one jack. Each corner is raised in turn.
- Using 2 jacks. First, one wall is raised completely, and after it is fixed, the opposite one.
- On 4 jacks. The entire frame rises at once. This method eliminates damage to the frame, but requires coordination of the operation of the devices.
After raising the corner of the log house to a height sufficient to remove one log, a support is placed under the first crown, which cannot be replaced, mounted on 2 posts. This way the frame is fixed at all lifting points, and the jack is removed.
Unusable logs are knocked off the nigels and removed outside. Then new logs are installed. They are immediately held together with nigels. A jack is again placed under the lower crown, which is used to compact the new logs.
Before completing the work, the foundation is repaired if necessary, the waterproofing between the base and the base is restored, and a new filling element is installed. After this, using jacks, the frame is slowly lowered to its original place, secured with pins.
After the log house is completely lowered, all the cracks between the logs are caulked with moss, tow or jute. The thermal and waterproofing of the base is restored.
Repair of columnar foundation
For various reasons, the columnar foundation of the bathhouse may begin to settle. The culprits for this may be both the hydrological changes in the lower layers of the soil, which thus reduce its basic load-bearing capacity, and the serious construction work that is taking place nearby. Moreover, the foundation can settle not only at a newly built bathhouse, but also at already established buildings.
Sometimes it happens that the foundation piles begin to “grow upward” and warp the entire bathhouse. This doesn't happen all that often. In this case, the piles, together with the top layer of frozen soil, simply rise upward, but practically do not settle in the spring. Even when they try to tie such piles on top with a concrete grillage or channels, they still grow. But the method of quality repair in this case will depend on how much concrete was poured under the piles in an attempt to save the situation.
If the columnar foundation begins to settle
The subsidence itself usually begins at the base of the so-called bed stone of a columnar foundation. Its first sign is cracks in the space and holes around the pillar itself. Moreover, cracks can increase over time. Although the subsidence itself, of course, can be temporary - until the bed of the base finds a more stable position for itself. Or the subsidence will continue, and the destruction will increase: the joints and seams on the log bathhouses will widen, the caulking will begin to fall out, and the cracks on the lower crowns will become wider. Therefore, the subsidence of the foundation must be stopped in time.
To do this, beacons are placed on the cracks - plaster tapes. If they soon break, then directly with the columnar foundation you need to dig a hole inclined at an angle of 35°, with a depth to the plane of the base of that same bedded stone. You need to insert an asbestos-cement pipe 20 cm in diameter into this hole and pour cement mortar into it until it is completely saturated. As soon as the poured solution stops decreasing within two hours (absorbing into the soil), filling can be stopped. But after a day or two, everything needs to be repeated - and so on three times. After which you need to put the beacons on the cracks again, and strengthen the wooden plank at the beginning of the base and the edge of the upper part of the blind area.
If subsidence continues, the bar will begin to lower. Then you need to add the solution again. But even in this case, subsidence may continue. Then a ring-shaped ditch of 20x35 cm is dug around the pillar, wooden boards are laid at the bottom and, like formwork, along the edges. A metal mesh is installed to the pins that are installed between the stones and bricks - this is done as reinforcement. For it, you can safely use different scraps of metal rods.
After this, concrete with fairly fine fillers in the form of gravel or crushed stone is poured into the equipped formwork. This creates a reinforced concrete ring around the foundation pillar, which should strengthen its load-bearing capacity, distribute the load of the settled corner of the bathhouse horizontally and, thus, stop the subsidence that has begun. If such a ring also had to be made at an adjacent or opposite angle, then it is better to place a reinforced concrete, metal or wooden beam under the rings themselves - it will triple the load-bearing capacity of the entire columnar foundation of the bathhouse.
If the pillars themselves begin to tilt
Indeed, good, high-quality baths can stand for decades on a solid columnar foundation, and suddenly begin to tilt. This often happens on damp soils - no matter how wide the concrete slab is under the pillars, they themselves may begin to lose their stable vertical position. But this can be fixed.
Replacement of columnar foundation supports.
To do this, you will have to hang up the bathhouse, dig up the pillars, forcefully level them, add concrete, bury them and repeat the procedure a year later - but no one will give a guarantee for such work. Therefore, today more and more experienced builders resort to this option:
- The bathhouse is lifted and installed on temporary supports. Moreover, nothing needs to be taken out of it; neither doors nor windows need to be dismantled. Perhaps only a few floorboards will need to be opened for a while.
- The tilted pillars are dismantled.
- A trench is opened under the bathhouse and a sand cushion is compacted.
- A well-reinforced tape 20 cm thick is poured.
- Pillars are placed on the finished tape.
- To support the floor joists, steel beams - I-beams - are mounted.
- The bathhouse is lowered onto a new foundation and its position is adjusted so that the windows and doors open well.
The main thing in repairing the foundation of a bathhouse is its timely start. Then the bathhouse itself will serve regularly for decades.
Partial replacement of timber
If an examination of the condition of the house shows that the foundation is in good condition, as is most of the base, and only a small section of the crown is destroyed, then repairs are carried out by partially replacing the elements of the frame. In this case, only the damaged area of one or more logs is removed, and a kind of “patch” is installed.
Such work involves the following steps:
- The area to be repaired is clearly marked, for which you can use a knife, ax or chisel.
- Fixation of crowns. At a distance of 35-45 cm on both sides of the boundary markings, ties from a board 3-4 cm thick (with fixation of 2-3 crowns) or metal brackets are installed.
- Cutting along the markings of the damaged area using a chainsaw, electric saw or grinder.
- Preparing the opening. The lower surface of the upper, untouched crown is slightly flattened, and cuts 15-20 cm wide are made at the ends of the opening. The entire surface of the opening is carefully treated with an antiseptic.
- Manufacturing and installation of the insert. From logs of a size similar to the installed logs, elements 1.5-2 mm shorter than the opening are cut out. After treatment and impregnation with an anti-rot composition, the insert is firmly driven into the opening using a sledgehammer. All cracks will be caulked.
Bath size
The size of the bathhouse can be arbitrary - at your own request, depending on what is planned to be placed in it. A standard bathhouse includes a sink (washing room), a steam room and a dressing room (in the modern version, a relaxation room). For a steam room, three to four square meters are enough, for a sink a little more, about five to six. The dressing room, if without sophistication, can perform its functions with a size of 5-6 sq.m. In other words, the average size of a rather modest bathhouse will be 4x5 meters, or 3x6. With a standard log size of 6.1 m, the second option will be much more economical.
Replacing timber without raising the frame
Major renovations to a house can be done without lifting the frame. The following options are available:
- Replacement of destroyed logs. First, the rotten element is removed in parts. To do this, the log is cut into pieces 1-1.5 m long, which are taken out one by one. The technology is no different from the previous method of partial replacement. After removing the entire log, exactly the same element is carefully driven into the vacant space and fastened to the adjacent crowns with metal staples.
- Replacing a damaged wooden plinth with brickwork. The technology is based on alternately cutting and removing sections of a wooden plinth 1-1.5 m long and replacing it with brickwork 1.5-2 bricks thick. The masonry is brought directly under the remaining lower crown, and waterproofing is laid between them. Gradually moving along the entire perimeter of the house, a complete replacement of the rotten lower wooden crowns with a brick basement is ensured. Next, it is enough to insulate the masonry and plaster it.
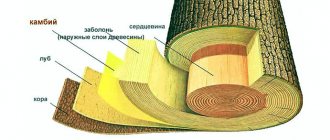
Which wood is best suited for the lower crowns of a log house?
When constructing a wooden house, the following types of wood are used:
- Spruce. This is one of the most accessible and cheapest materials. Thanks to their loose structure, spruce logs retain heat well. In addition, they have antibacterial abilities. The main disadvantages are low moisture resistance and a tendency to rot, which limits their use in lower crowns.
- Pine has a smooth trunk without knots, but in its shortcomings it is similar to spruce.
- Birch is considered a hard, durable material, but it dries out strongly, has high water permeability, a tendency to rot, and low durability.
- Larch. It has high strength, resistance to microorganisms, and is not subject to rotting. The main advantage is moisture resistance and fairly high fire resistance. Wood is a highly drying species, which requires good drying before construction. The only real drawback is the high cost.
- Oak. This wood is distinguished by its strength and durability, high hardness, and resistance to any weather conditions. In terms of resistance to rotting and moisture resistance, oak logs are comparable to larch and have a similar disadvantage.
Taking into account the economic side, wooden houses are most often built from spruce and pine. However, in the lower crowns their use threatens premature major repairs. The best option for making a plinth is larch and oak. Such materials will be more expensive than common tree species, but their very high resistance to moisture and mechanical strength will significantly increase durability.
Attention! The lower crowns of the log house bear the maximum loads, and therefore the diameter of the logs for them should be 15-20% larger than the size of the elements of the rest of the walls.
Log selection
It is best to harvest timber for the bathhouse in winter, from late November to early March, when there is no sap flow. Summer wood, compared to winter wood, dries out much more, so after shrinkage there will be more cracks and cracks in the log house. In addition, it darkens faster and is more susceptible to fungi and mold.
You need to choose a tree that is not affected by rot, fungus and insects, preferably with a minimum number of knots. The trunks should be smooth and not runny, that is, the difference between the diameters of the butt and crown should be no more than 50-70 mm. The most suitable type of wood for a bathhouse is pine, although the lower crown, which is most susceptible to dampness, can be made from larch.
What tools are required to complete the work?
When carrying out repairs on your own, you will need the following tools and equipment:
- jack for raising the house (1-4 pieces);
- Bulgarian;
- gasoline or electric saw for cutting logs;
- hammer drill for forming a jack installation site on the foundation;
- electric drill for installing nigels;
- scrap;
- sledgehammer;
- hammer;
- chisel;
- axe;
- plane;
- knife;
- hacksaw;
- scissors for cutting waterproofing;
- metal brush;
- paint brush;
- roulette;
- metal ruler;
- rail to control the lifting height.
Stage 8. Caulking logs
Types of tools and methods of caulking
After shrinkage is completed, the log house is caulked. To do this, prepare the following equipment:
- hammer;
- caulk (made of wood or metal).
Attention! If you sealed the inter-crown space with tow or moss, you can skip this step, since you most likely will not need caulking. But if you find even the slightest cracks, then it is still better to carry out the procedure.
Proceed to work only after the insulation has completely dried. First, twist the material (tow or moss) into a rope, then hammer it between the crowns with a hammer and caulk.
Caulk
You can use tape jute - in this case, the material is simply fixed with nails or a mounting stapler.
Primary and secondary caulking of a log house
Video – Caulk of a log house
Is it possible to change the bottom beam yourself?
In general, the repair work in question requires a certain skill, significant time and labor costs.
The question of whether it is possible to independently replace the lower crowns of a wooden house is of a purely individual nature. If you have the necessary equipment and sufficient time, the work associated with lifting the log house can be done with your own hands.
But, if a person is in doubt, it is better to invite specialists. In order to carry out repairs correctly and efficiently, you need to take into account some nuances.
Briefly about the main thing
Knowing how to raise a bathhouse with your own hands, you can carry out a major overhaul of it, replacing the crowns and foundation without dismantling work. To implement this idea, you will need powerful jacks installed on a stable and solid foundation. The lifting is carried out gradually, in small steps, moving the mechanisms one by one to different support points and trying to prevent the box from skewing. For it to be successful, the building must first be freed from removable structures and strengthened with spacers and diagonal linings.
Ratings 0
When is the best time to do the work?
Repair of the basement of a wooden house must be carried out immediately when damage is detected. In this case, it is possible to do without major repairs and complete replacement of the lower crowns. The work itself cannot be carried out in high humidity and windy weather.
When planning the timing of repair activities, it is necessary to take into account some features of the behavior of wood. In summer, moisture moves deeper into the log, which can cause cracking when drying.
In winter, the humidity of the tree is minimal, and the moisture is frozen, which ensures uniform shrinkage. In addition, in summer, wood is more sensitive to temperature differences between night and day.
The choice of repair timing should be made taking into account the recommendations given for the construction of a wooden house:
- It is better to carry out foundation repairs in the fall, when the air temperature has not yet dropped to sub-zero values. After 2.5-3 weeks, the concrete will gain the required strength, and you can start building the log house.
- It is better to carry out work with a wooden frame in winter.
- During spring, maximum shrinkage occurs. It is better to wait out this period.
- Summer is the best option for finishing work.
Important! If the major repair of a wooden house involves raising and strengthening the foundation, as well as replacing the lower crowns of the log house, then work should begin at the end of October-November, taking into account that the completion of the log house repair will take place in December-January.
Stage 9. Roof
Construction of a roof on males with layered rafters
Rafter system
As soon as the tree shrinks, you can begin building the roof. If you do this earlier, the roof will simply collapse.
Step 1. Place wooden beams on the wall framing (we have already talked about this).
Step 2. Fix the beams and attach the rafter legs to them in 1 m increments. In the ridge part, cut the rafters at the appropriate angle for the connection.
Step 3. Nail a solid board deck to the rafters (if you plan to use rolled roofing material) or make a sheathing (if you use slate, tiles, etc.).
Step 4. Install the roofing according to the instructions for the specific material.
Step 5. Cover the ridge with galvanized sheet steel to protect it from aggressive environmental influences.
Step 6. Cover the roof gables with siding or clapboard.
How to sew up a pediment
After this, proceed to further planned work - pouring a concrete screed or building a wooden floor (in the second case, the logs are cut into the logs of the second crown and fixed), install insulation, carry out interior finishing and arrangement of the steam room according to your project.
An example of a log house with a shingle roof
An example of a log house with a shingle roof
Cornice filing
Roof overhang trim
How can you increase the service life of timber?
The service life of the lower crowns, and therefore the entire wooden house, can be achieved in the following ways:
- Application of high-quality and reliable waterproofing. Such materials include modern euroroofing felt. It is laid on top of the foundation and protects the frame well from below.
- Cover board. If there is no financial opportunity to manufacture lower crowns from larch or oak, you can increase the reliability of the base by installing boards made of these materials. It is attached on top of the foundation waterproofing and has a width of 25-30 cm and a thickness of 6-8 cm.
- Impregnation of wood with folk remedies. It is recommended to use the following substances: copper sulfate, “Finnish mixture” (slaked lime, copper sulfate, table salt, flour); natural wax; spruce resin or birch tar; bitumen; drying oil; oils
- Modern, synthetic, impregnating compounds. The following antiseptics are popular: Pinotex, Sadolin, Senezh Ognebio, Tikkurila, Belika.
You can replace the lower crowns in a wooden frame yourself in different ways. It is important to correctly assess their condition and determine the scope of work.
To prevent rapid rotting of wood, it is necessary to protect it from moisture and pests. Preventive measures will help eliminate the need for labor-intensive major repairs.
Go straight to the project search
At our dacha, the bathhouse has already been used for more than a dozen years.
The design of the bathhouse is quite traditional, a small log house. The roof is covered with slate, but for the time being, no one thought about the foundation. Over time, the lower crowns, especially the very first one - the frame crown, began to rot. As far as I understand, this problem is typical for many baths; if you heat regularly, the bottom of the wall is constantly exposed to moisture.
At first they just wanted to change the two lower crowns, but during their examination it turned out that the bathhouse did not have a foundation as such. The corners of the log house rest on large stones dug into the ground, and that’s the entire foundation.
It was decided to cast a strip of shallow depth, and make a brick plinth on top of it. The equipment included two jacks, a chainsaw and hand tools, plus a concrete mixer and a welder borrowed from friends for the time of pouring.
The old brick stove was in need of repair for a long time, and it was decided to dismantle it and, after replacing the crowns, replace it with a new metal stove. Before starting to lift the log house, the stove and chimney were dismantled. The floors and joists were also not in the best condition and were sent for firewood.
The inside of the bathhouse is lined with boards; they decided not to remove it, but to avoid cracking, raise the bathhouse slowly and evenly. The roof, by and large, is also not in the best condition, but at the moment it is not leaking, and it was decided to leave it, so to speak, until better times.
Initially, they dug under two corners of one wall; they didn’t immediately cut out pieces of logs that needed to be replaced - who knows what will come of it. Jacks were placed into the resulting holes. To prevent the jacks from denting into the ground, shields made from scraps of 50 mm boards were placed under them. They lifted it very little - about two centimeters. Then they put up temporary supports made of boards and bricks and crossed to the other side. Two supports were placed on each wall - eight in total.
Since we moved it little by little, we had to do a fair amount of running around with the jacks, five approaches on each side, that is, we raised it by about 10 cm. Maybe we could have done all this faster - two approaches and it was done, but I didn’t want to risk the skin.
On the last climb, when the wall was still on the jack, the rotten logs were sawed down and the middle part was removed. After this, props were placed under a normal log, and the jack was lowered and the corner fragments of the rotten crowns were pulled out.
To prevent the log house from standing on temporary supports for a long time, it was decided to first make corner posts - the result was small posts with a base of approximately 40 by 40 cm, and the top narrowed to 30 by 30 cm. The depth of the post is 40 cm below ground level, plus 20 cm for a sand cushion . The total depth of the trench was 60 cm. Pieces of reinforcement were placed in the columns, to which the reinforcing frame of the tape was then attached.
The column rose just a little above the ground, only 10 cm, the rest was raised with bricks. By the way, this solution did not seem to me the best, and the tape under the walls was cast higher.
The pillars were allowed to stand for four days, after which a bathhouse was placed on them. I understand that the concrete has not gained strength, but the log house doesn’t weigh much at all, and the deadlines are running out, and vacations have an unpleasant tendency to end. They cast the tape and, after letting it sit for three days, raised the base.
Waterproofing was done with roofing felt in two layers. The first is between the foundation and the brick plinth, and the second is between the brick and the first crown of the frame.
The time was spent two weeks, and almost half of the time was waiting for the concrete to gain minimum strength.