Heat pumps are undoubtedly one of the best inventions in the field of heating systems. It literally makes it possible to extract virtually free energy directly from the air, as well as from the ground or water. If you use a pool heat pump, the cost of heating water can be significantly reduced.
We will tell you how to choose the optimal model for using “green” energy to generate water-heating heat. The article presented for review describes in detail the principle of operation of the system. Here you will learn how to install the unit and how to properly operate it in a domestic environment.
Pool maintenance costs
As an example, consider a pool with a 3x7m mirror and the costs of its operation, depending on its type and heating source, taking into account current energy tariffs:
| Pool type | Number of operating hours* | Heat loss, W*hour/m2 | Pool mirror area, m2 | Total heat loss, kW |
| Outdoor pool without cover (water temperature +20℃) | 2880 | 450 | 21 | 27216 |
| Outdoor swimming pool with cover (water temperature +20℃) | 3600 | 100 | 21 | 7560 |
| Indoor pool (water temperature +20℃, room temperature +23℃) | 8760 | 90 | 21 | 16556 |
- *120 days (summer 90 days, 15 days spring, 15 days autumn) x 24 = 2880 hours
- *150 days (summer 90 days, 30 days spring, 30 days autumn) x 24 = 3600 hours
- *365 days x 24 = 8760 hours
Having the cost of 1 kW of thermal energy and the total heat loss, you can easily get the total cost of maintaining the pool in terms of heating (without taking into account other funds and maintenance). Consider an indoor pool (water temperature +20℃, room temperature +23℃) - 16556 kW of heat per year.
| Thermal energy source | Energy carrier | Price of 1 kW of heat | Total heat loss, kW | Total costs for maintaining the pool, UAH |
| Heat pump (Electric heating tariff) | air/electricity | 0.25 UAH/kW | 16556 | 4139 |
| Heat pump (Electric heating tariff) | ground-water / electricity | 0.225 UAH/kW | 16556 | 3725 |
| Heat pump (standard tariff) | air/electricity | 0.48 UAH/kW | 16556 | 7946 |
| Heat pump (standard tariff) | ground-water / electricity | 0.42 UAH/kW | 16556 | 6953 |
| A gas boiler | natural gas | 1.02 UAH/kW | 16556 | 16887 |
| Solid fuel boiler |
| 0.59 UAH/kW | 16556 | 9768 |
| 1.27 UAH/kW | 16556 | 21026 | |
| coal | 1.39 UAH/kW | 16556 | 23012 | |
| Electric boiler (tariff “Electric heating”) | electricity | 0.90 UAH/kW | 16556 | 14900 |
| Electric boiler (standard tariff) | electricity | 1.69 UAH/kW | 16556 | 27979 |
| Solar collectors | Sun | — | 16556 | only electricity is needed to operate the circulation pump |
As can be seen from the table, the amount of pool maintenance can vary significantly depending on the selected heating source. Therefore, the main advice is to carefully weigh everything and choose the golden mean. A more detailed calculation of the cost of 1 kW of thermal energy is here
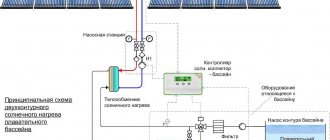
Scheme of operation of a heat pump for heating a swimming pool
The operating diagram of a heat pump for heating a pool is quite simple and includes the following elements:
- Primary heat source - air, water, soil or technological process
- Heat pump
- Heat exchanger
- Pool water circuit
- Filtration system (not shown for simplicity)
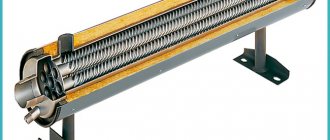
As a rule, the circuit contains a shell-and-tube type heat exchanger. Shell and tube heat exchanger is easy to maintain and durable. This type of heat exchanger is most often used to heat a swimming pool.
It is important to choose the right heat exchanger for a heat pump - Be sure to consult with specialists
Properly selected equipment and high-quality installation are the key to success when implementing a pool heating system using a heat pump.
Calculation of heating a house with a heat pump
For normal operation of the heat transfer installation, high-quality thermal insulation of the building is necessary. Therefore, before purchasing a heat pump, it is necessary to insulate the walls, floors and ceilings, and then perform a calculation of heat losses (Q).
A simplified formula for calculating the amount of heat (W) leaving the house through the building envelope (walls, windows, floor, ceiling) looks like this:
Q = S x (difference between indoor and outdoor air temperatures)/ Rt.
S – area of the enclosing structure in m2;
Rt – thermal resistance of the material of the enclosing structure (taken from the SNiP tables on building heating engineering).
By alternately calculating the heat loss of walls, windows, floors and ceilings, they are summed up and the number of kilowatts lost by the house in 1 hour during the coldest period of the year is obtained. The heat pump power must be no less than the total heat loss. If, in addition to heating, the installation will heat water for domestic needs, then its power will be increased by 20%.
When choosing an air-to-air or air-to-water heat pump, you should focus on the thermal power that it develops in the low temperature region, since it is significantly lower than the power when operating in the warm season.
As an example, we give the parameters of the NIBE FIGHER F2300-14 air-water installation. Operating in a temperature range from +7 to + 45C, it produces about 18 kW, and at an air temperature of -15C only 10.7 kW.
Pool heat loss
To select the power of the heat source, it is necessary to calculate the heat loss of the pool. Of course, such a calculation should be made by a heating engineer, but for a general idea of the order of numbers, we present an empirical table of pool heat loss. With its help, you can easily determine the required power of the heat source:
| Pool type | Heat loss from 1 m2 of pool at different water temperatures, W*hour/m2 | ||
| 20 °C | 24 °C | 28 °C | |
| Indoor swimming pool (room temperature 23 °C) | 90 | 165 | 265 |
| Indoor swimming pool (room temperature 25 °C) | 65 | 140 | 240 |
| Indoor swimming pool (room temperature 28 °C) | 50 | 100 | 195 |
| Outdoor swimming pool with cover | 100 | 150 | 200 |
| Outdoor pool without cover (wind-protected position) | 200 | 400 | 600 |
| Outdoor pool without cover (position exposed to wind) | 450 | 800 | 1000 |
It should be noted that the initial heating of the pool may take several days, so do not worry if the initial heating of the pool takes a long time.
Heat source options for heating a pool
Let's consider the main heat sources for heating the pool and compare their technical and economic indicators:
| Thermal energy source | Energy carrier | pros | Minuses |
| Heat pump (Electric heating tariff) | air/electricity |
| |
| Heat pump (Electric heating tariff) | ground-water / electricity |
|
|
| Heat pump (standard tariff) | air/electricity |
| |
| Heat pump (standard tariff) | ground-water / electricity |
|
|
| A gas boiler | natural gas |
|
|
| Solid fuel boiler | oak firewood |
| |
| wood pellets |
| ||
| coal |
| ||
| Electric boiler (tariff “Electric heating”) | electricity |
| |
| Electric boiler (standard tariff) | electricity |
| |
| Solar collectors | Sun |
|
Solar collectors are beneficial for open-type swimming pools when the pool is used in the summer and off-season. In combination with a backup source of thermal energy, it is an excellent solution for ensuring a comfortable water temperature in the pool.
Electric boiler - very high operating costs do not allow us to recommend this type of heating for a pool.
A gas boiler is a compromise solution, but operating costs are still high, therefore, taking into account other disadvantages, it is not recommended for heating a pool.
Biomass boiler (wood, pellets) - this option is not as economical as it is more difficult to maintain, therefore, the person who equipped the pool is unlikely to want to spend his precious time on constant maintenance of the boiler. Based on the above, it is not recommended for heating a swimming pool.
A heat pump is an excellent solution for heating a pool. Autonomy – You can start the heat pump from your smartphone and upon your arrival the heat pump will raise the temperature in the pool to a more comfortable one. There is no need to clean or check anything, everything works automatically, plus it’s much cheaper than heating with gas, wood or electricity. Can be used to heat both indoor and outdoor swimming pools. For outdoor pools, we recommend a combination of solar collectors and a heat pump, since during the main operating time - in the summer - only solar collectors will work. Therefore, maintaining the pool will be practically free on sunny days, and when there is no sun, the heat pump will provide protection and you will always be able to plunge into the warm water of your pool in the morning, afternoon and evening.
Operating Requirements
During tank operation, the filter unit gradually becomes clogged.
To maintain efficiency and productivity at a high level, cleaning work must be carried out regularly. Particular attention should be paid to the equipment of sand filters. During operation, scale is released, which reduces throughput
This can lead to congestion.
Note: Flushing occurs every ten days. If the tank is used intensively, the frequency of filter cleaning can be easily changed.
Special means are used to remove such deposits. Cleaning is carried out several times a year. Backwashing is in progress.
In this case, a lime dissolving agent is added. When the product enters the device, the flushing is switched off. This ensures that the product completely dissolves the lime.
This takes on average several hours. This is followed by a thorough cleaning. The filter is used to purify water. Therefore you should not save.
When choosing a device, it is necessary to take into account all its advantages and disadvantages, as well as the amount of purified water. This will allow you to choose the right option for your pool.
The following video will show you how to create a billiard filter with your own hands:
Page 4
Many village residents appreciated the opportunity to swim in the pool, which is located directly in the yard. Swimming radiates the entire body and brings tangible health benefits.
In order for water processes to bring the greatest benefits, it is important to keep the water in such an artificial pond clean. Unfortunately, tap water contains many pollutants, the penetration of which into the body has a negative impact on human health.
The sand filter is well suited for small tank volumes. The stores are filled with similar products, but the prices are not the lowest. You can approach this issue from a different angle - make a sand filter with your own hands.
Characteristics of heat pumps
The main indicator by which the efficiency of a heat pump is assessed is the heat conversion coefficient, abbreviated as CPT (in the English abbreviation COP). It has nothing to do with the efficiency that is familiar to us - the efficiency factor. KPT (COP) shows how many kilowatts of energy the pump pumps per kilowatt of electricity it receives. Depending on the operating conditions, the CFC of a heat pump can range from 3 to 5, which, without further discussion, confirms the economic benefits of its use.
The most stable performance indicators are demonstrated by soil and water installations, since the temperature of water and soil does not fall below zero degrees. Units that collect heat from the air depend on its temperature. When the thermometer reaches sub-zero levels, their productivity decreases by an average of 40-50%.
The second operating parameter is power in kilowatts. It is selected based on the amount of heat loss of the building.
If you liked the article, please share it
Previously on the topic:
Share
How to install a heat pump in your home
- It is possible to place modern heat pumps in the basements of residential buildings. This is especially true for geothermal equipment with the connection of an inclined cluster circuit. In this case, the well for the collector may be located directly under the house, in the basement.
- Requirements for installing a heat pump in an apartment building. A backup heat source must be installed. In the winter season, the defrosting module will stop for 3-4 seconds. At this point, you will need to compensate for the lack of heat.
- The pump is installed in any room large enough to accommodate a storage tank and provide easy access to all system components for maintenance.
To start heating your home with a heat pump, you need to invest money. Subsequently, the costs will be fully recouped. The time required to reach “zero” is 3-8 years.
Which heating is better for a home - gas or heat pump?
Energy-saving technologies for the home are slowly but surely replacing traditional types of heating. The only thing that holds back the widespread implementation of installations is the need for a significant initial investment of money.
Most manufacturers have been working for a long time to reduce the cost of technology, therefore, the prospects for using heat pumps in heat supply systems for private homes are quite optimistic. You can soon expect an increase in sales by 10-15%.
Heat pumps are not limited solely to domestic use. It is possible to use heat pumps in heating multi-storey buildings, as well as industrial facilities. If you compare the efficiency of using gas boilers and heat pumps, you can clearly see what prospects exist for each type of equipment.
Disadvantages of heat pumps
The main disadvantage, especially noticeable when used in apartment buildings, is the dependence of heat pumps on temperature fluctuations. And if geothermal models are more or less resistant to changing weather conditions, then air stations sharply reduce productivity if the temperature drops to -15°C.
Installation of heat pumps with an earth circuit costs an additional 30-40% of the total cost. The work requires the use of specialized machinery and equipment. The price for modern models can reach 1200-1400 thousand rubles.
In comparison, purchasing and installing a gas boiler will cost only 200 thousand rubles. The efficiency of gas equipment does not depend on external factors, and installation takes 1-2 days at most.
Advantages of heat pumps
Cost-effectiveness is the main advantage of heat pumps. Financial costs during the heating season are almost three times less compared to natural gas. No permissions are required to connect. An exception is for geothermal equipment; you will have to formalize the right to drill wells. The operation of heat pumps is absolutely safe and environmentally friendly.
The main heating of the house using a heat pump has significant advantages over the operation of gas boilers, but due to the high cost of equipment using low-potential energy, they are inferior to them in popularity.
Calculation of power and temperature of a warm water floor
Step-by-step instruction
To avoid installation errors and breakdowns during operation, it is important to study the instructions for the pool pumping equipment
How to install correctly?
The pump is installed below the water level in the bowl, since even a powerful self-priming device will work under increased load when installed above the line. This threatens to shorten the life of the engine.
The system is mounted on a flat, solid base with low vibration levels. The optimal distance from the pool bowl is 3 m.
It is important to ensure that the equipment is protected from precipitation, moisture, frost, flooding, as well as access to the installation for regular maintenance. How to connect the pump unit:
How to connect the pump unit:
- Connect the filter housing to the water inlet pipe of the motor, align the coupling.
- Install the suction pipe with a slope to prevent air pockets.
- Connect the motor prefiltration unit to the filter.
- Install the valve with pipe connections.
- Make sure that the outlet on the valve is directed towards the pool and the inlet is connected to the outlet on the engine.
- Check the correct connection of all components, the tightness of the pipes and the tightness of the fasteners.
- Connect to the electrical network.
- Fill the system with water and start.
The power source for the pump should be located at a distance of 3.5 m from the pool bowl. Connection is only allowed to a grounded outlet.
How to serve?
Regular maintenance extends the life of devices and prevents breakdowns. To do this you need:
- check and clean the prefilter;
- clean the filter by backwashing;
- inspect equipment for sealing of hoses and connections;
- Wipe off dust on the engine and other components.
All maintenance work should only be carried out when the pump is disconnected from the power supply.
For outdoor pools, another maintenance step is to assemble the pump and store it during the cold season. The parts and components are dismantled, drained, dried, and sent to a warm room. Storing the pump at sub-zero temperatures will shorten its service life.
Maintenance
Replacing parts and repairing a pumping station requires experience and skills
It is important to take into account that independent intervention in the work can cause breakdowns and complete failure of the device.
The following factors lead to breakdowns:
- Incorrect operating mode.
- Mechanical damage.
- Voltage failures in the electrical network.
A typical malfunction is water leakage from the system. Causes:
- defects in seals and gaskets;
- damage to the impeller;
- depressurization of the outlet hose.
The problem is solved by finding the cause of the malfunction and replacing spare parts. It is recommended to purchase any components and parts for the device from the same manufacturer that produces the pump.
If the device is under warranty, you should contact a service center for repairs.
Famous brands and approximate prices
The market for heat pump equipment in Russia has been formed. The leading positions here are occupied by foreign companies, such as: Nibe (Sweden), Mitsubishi Electric (Japan), Danfoss (Denmark), Vaillant (Germany), Viessmann (Germany), Mammoth (USA) and others. In terms of price-quality ratio, Russian-made products (Henk and SunDue trademarks) are not inferior to famous brands.
The estimated price (for 2021) of an imported ground-water heat pump with a power of 10 kW, designed to heat a house with an area of 100 m2 (without installation) is 500,000 rubles. For work on drilling wells, installing pipes and commissioning, you will have to pay an average of 80,000 rubles, not including additional materials.
Domestic equipment is cheaper. The price of a Russian heat pump with similar parameters is about 360,000 rubles. Its purchase with turnkey installation will cost about 430,000 rubles. The estimated price of a 10 kilowatt air-to-water heat pump is from RUB 270,000. The average cost of this unit with turnkey installation is 320,000 rubles.
Reviews from real owners of this type of equipment are overwhelmingly positive. They note the reliable operation of geothermal heat pumps and low operating costs (maintenance, electricity).
The fears of those who are still thinking about purchasing an air-to-water heat pump based on the practice of using this technology are not justified. These units consistently produce heat down to an outside temperature of -25C.
Principle of operation
All the space around us is energy - we just need to be able to use it. For a heat pump, the ambient temperature must be greater than 1C°. Here it should be said that even the ground in winter under snow or at some depth retains heat. The operation of a geothermal or any other heat pump is based on transporting heat from its source using a coolant to the heating circuit of the house.
Scheme of the device operation point by point:
- a heat carrier (water, soil, air) fills the pipeline located under the ground and heats it;
- then the coolant is transported to the heat exchanger (evaporator) with subsequent heat transfer to the internal circuit;
- in the external circuit there is a refrigerant - a liquid with a low boiling point under low pressure. For example, freon, water with alcohol, glycol mixture. Inside the evaporator, this substance is heated and becomes a gas;
- The refrigerant gas is sent to the compressor, compressed under high pressure and heated;
- hot gas enters the condenser and there its thermal energy passes to the coolant of the home heating system;
- The cycle ends with the transformation of the refrigerant into liquid, and due to heat loss, it returns back to the system.
The same principle is used for refrigerators, so home heat pumps can be used like air conditioners to cool a room. Simply put, a heat pump is a refrigerator with reverse action: instead of cold, heat is generated.
Do-it-yourself heat pumps can be designed based on three principles - energy source, coolant and their combination. The source of energy can be water (pond, river), soil, air. All types of pumps are based on the same operating principle.
Classification
There are three groups of devices:
- water-water;
- ground-water (geothermal heat pumps);
- use water and air.
Thermal collector "ground-water"
A do-it-yourself heat pump is the most common and effective way to produce energy. At a depth of several meters, the soil has one constant temperature and is little susceptible to weather conditions. A special environmentally friendly liquid, popularly called “brine,” is used on the external circuit of such a geothermal pump.
The outer circuit of the geothermal pump is created from plastic pipes. They are dug into the ground vertically or horizontally. In the first case, one kilowatt may require a fairly significant area of work - 25–50 m2. The area cannot be used for planting work - only planting annual flowering plants is allowed here.
A vertical energy collector requires several wells of 50–150 m. This device is more efficient; heat is transferred by special deep probes.
"Water-water"
At great depths, the water temperature is constant and stable. A source of low-potential energy can be an open reservoir, groundwater (well, borehole), or wastewater. There are no fundamental differences in the design for heating of this type with different coolants.
The water-to-water device is the least labor-intensive: it is enough to equip the pipes with the heat carrier with a load and place them in water, if it is a body of water. For groundwater, a more complex design will be required and it may be necessary to construct a well to discharge the water passing through the heat exchanger.
"Air-water"
This pump is slightly inferior to the first two and in cold weather its power decreases. But it is more universal: it does not require digging the ground or creating wells. You only need to install the necessary equipment, for example, on the roof of the house. This does not require complex installation work.
The main advantage is the ability to reuse the heat leaving the room. In winter, it is recommended to have another heat source, since the power of such a heater can be significantly reduced.
Counterflow devices
With the help of such products you can swim in a small home pool. Such pumps are divided into two types:
- Mounted. They are suitable for small seasonal pools. There is a pump, nozzles, lighting, handrails, automation and control system. The design is quite easy to install. This does not require serious effort.
- Built-in models. They are equipped with a suction element that extracts water when it is located below or above the required level. This is a more expensive and complex design, unlike the previous version. Such designs are suitable for stationary pools.
The counterflow area should be approximately 12-14 cm above the water level. If this fact is not taken into account, its operation will be extremely ineffective.
In principle, choosing a pump for your pool does not have to be a difficult task. You don’t have to bother and buy a version that contains all the delights of this mechanic. If you show some imagination, you can create an excellent system of circulation, heating, and the like in your pond.
Characteristics
Most thrifty owners want to save money on heating and water supply for a private home. A heat pump is suitable for such purposes.
It is quite possible to build it yourself, while saving a lot of money - a factory-made device is very expensive.
Properties and device
The device has an external and internal circuit along which the coolant moves. Components of a standard device: a heat pump, a device for intake and a device for heat distribution. The circuit from the inside consists of a mains-powered compressor, an evaporator, a throttle valve, and a condenser. The device also uses fans, a pipe system, and geothermal probes.
- does not emit any harmful substances, absolutely environmentally friendly;
- there are no costs for the purchase and delivery of fuel (electricity is spent only on moving freon);
- no need for additional communications;
- absolutely fire- and explosion-proof;
- full heating in winter and air conditioning in summer;
- A self-built heat pump is an autonomous design that requires minimal control effort.
How does a heat pump work?
The simplest example that clearly explains the principle of operation of heat pumps is a household refrigerator. We all know that food is cooled in its freezer due to the circulation of refrigerant. Taking internal heat, the refrigerator throws it out. Therefore, the freezer compartment is cold, and the rear grill of the device is always hot.
The principle of operation of a heat pump is the opposite. Taking heat from the environment, it transfers it into the house. Figuratively speaking, the “freezer compartment” of this device is located outside, and the hot grate is in the house.
Depending on the type of external heat source and the environment that collects energy, heat pumps are divided into four types:
Installations of the first type extract heat from the ground using tubular collectors or probes. A non-freezing liquid circulates in the external circuit of such a pump, transferring heat to the evaporation tank. Here, thermal energy is transferred to freon, which moves in a closed loop between the compressor and the throttle valve. The heated refrigerant enters the condenser tank, where it transfers the resulting heat to water sent to the heating system. The heat exchange cycle is repeated as long as the installation is connected to the mains.
Heat pump operation diagram
The operating principle of a water heat pump is no different from a ground heat pump. The only difference is that it is powered by water, not soil.
An air source heat pump does not require a large external collector to collect heat. It simply pumps street air through itself, extracting precious calories from it. Secondary heat exchange in this case occurs through water (warm floors) or through air (air heating system).
Assessing the economic side of the issue, it should be noted that the greatest financial investment is required for the “ground-water” installation. To install its heat-receiving probes, it is necessary to drill deep wells or remove soil over a large area to lay the collector.
A ground source heat pump cannot operate without an external pipe system or deep wells with heat receiving probes
In second place is a water heat pump, delivered to the customer on a turnkey basis. It does not require digging or drilling wells to operate. It is enough to immerse a sufficient number of flexible pipes into the reservoir through which the coolant will circulate.
The cheapest units are air-to-air and air-to-water units, since they do not require the installation of external heat energy receivers.
A feature of the installation of most heat pump systems is that they are connected not to heating radiators, but to a heated floor. This is explained by the fact that the maximum water heating is up to a temperature of +45C, which is optimal for heated floors, but insufficient for normal operation of the radiator.
A beneficial feature of this installation for the owner is the possibility of reverse mode - switching over to cooling the premises during the hot period of the year. In this case, excess heat is absorbed by the underfloor heating pipeline and removed by a pump into the ground, water or air.
A simplified block diagram of a ground heat pump installation looks like this:
In addition to the heat pump, ground circuit and heated floor, here we see two circulation pumps, shut-off valves for hot water and heating, as well as a tank accumulating hot water for domestic use.
Why do you need to purify water?
A capital, stationary reservoir is not the only solution to the problem called “lack of water on the site.” Small bowls - frame or inflatable - are quite capable of replacing such a tank. Their advantage is the ability to remove the structure when cold weather sets in. However, any container that stores water needs to be cleaned. There are several reasons for this need.
Changing the water daily is an option that is unlikely to appeal even to owners of very small pools. Such an operation for large bowls will take a lot of time, and if you also calculate the cost of one cubic meter of water, it will simply cost a pretty penny. The best option is to change the fluid monthly, but no pool can be used without filters for such a long period of time.
The water in the bowl will quickly lose transparency and become a breeding ground for microorganisms, making it dangerous for people. There is also no need to talk about the attractive appearance of such a liquid. Over time, unpleasant symptoms will appear - turbidity, insects, algae and an unpleasant odor. Frogs could become potential “residents” of such a reservoir.
To avoid exposure to all the undesirable consequences, a tandem is used - a pump and a filter. Forced circulation is an ideal solution from all points of view: in this case, there is no need to use chemicals that can affect the condition of allergy sufferers, young children and the elderly.
If the owners manage to choose the optimal pump model, as well as a suitable filter, then they can guarantee that they will have to completely change the water once every month or a month and a half. The water will remain fresh and clean during these periods of time.
Making your own heat pump
Considering the fairly high cost of this equipment, many DIYers are tempted to assemble it with their own hands, using improvised units and components. What should be said about this?
This work includes two main stages: preparing the external circuit and assembling the heat pump installation itself. You can dig trenches for laying pipes on your own. It is unrealistic to make a 50-meter well for installing a probe without special equipment. Surface installation of the collector, according to experts, is unprofitable because it does not provide enough heat for stable operation of the installation.
Now let's see if it is possible to assemble a heat pump with your own hands. This requires the practical experience of a refrigeration technician, since a beginner will not be able to fill the system with freon and pressurize it.
Manufacturing an installation based on units from an old refrigerator or air conditioner can be considered only as a demonstration option, which has no practical value due to low efficiency.
A manual for assembling a heat pump based on a compressor from an air conditioner, a stainless steel container (condenser) and a plastic barrel (evaporator) is being replicated on the Internet. Having told how to screw copper tubes onto a cylinder and mount the compressor on the wall, the author ends his story with advice, after completing the assembly, to contact a specialist who will agree to carry out commissioning and correct all the “jambs” made by the home-made man. This instruction cannot be called a serious aid for independent work.