When choosing how to heat and hot water a home, people pay particular attention to cost and practicality, as this will affect regular monthly expenses for many years. Of course, each solution has its pros and cons. The advantages of pyrolysis furnaces compared to traditional solid fuel boilers include a low negative impact on the environment, reduced fuel consumption and reduced maintenance costs.
You can make a pyrolysis oven yourself without much expense
The operating principle of a pyrolysis furnace, drawings and its advantages
A pyrolysis or gas generator furnace belongs to the class of long-burning heat generators. To understand the principle of its operation, it is necessary to become familiar with an important feature of organic fuel: when exposed to high temperatures and limited access to oxygen, the long hydrocarbon molecules of which it consists break down into shorter ones, and the resulting substances have a gaseous state of aggregation.
This process is called pyrolysis (gas generation is the Russian equivalent), and the volatile cocktail released is called wood gas. All substances included in its composition - hydrogen, methane, nitrogen, carbon monoxide, etc. - are flammable. In a conventional stove, only a small part of this mixture burns (blue flashes can often be seen in the fireplace), and the rest flies down the chimney.
Pyrolysis furnace options
Pyrolysis heat generators are designed somewhat differently. Their working part is divided into two chambers: in one (gasification chamber) solid fuel is charred at a temperature of approximately 1100 degrees, in the second (afterburning chamber) the wood gas released in the process is burned. Air is supplied to both zones forcibly and strictly dosed. The one that enters the first chamber is called primary, the second - secondary.
The solid residue present in the 1st chamber upon completion of pyrolysis is charcoal (coke). It can be removed, then the heat generator will play the role of a charcoal kiln. But usually coal is also burned, that is, a pyrolysis furnace “squeezes” all the heat it can out of organic fuel.
Simplified diagram of a pyrolysis furnace
To increase efficiency, a special element is installed in the upper part of the furnace of a pyrolysis furnace, called a catalyst, afterburner, turbulator or divider (each manufacturer chooses the name to suit his taste). It is a ceramic part interspersed with oxides of various metals. The best effect is demonstrated by catalysts with the addition of platinum. The role of this element is as follows:
- being a good reflector, it returns thermal radiation into the smoldering mass of fuel and thereby increases the volume of pyrolysis gas released;
- thanks to the special shape of the catalyst, the pyrolysis gas passing through it is cut into several streams, swirls and mixes well with air, which together ensures more complete combustion;
- This element, due to its high temperature, causes ignition of the pyrolysis gas, being essentially a burner of a pyrolysis furnace.
Today, pyrolysis furnaces and boilers are used quite widely. They heat residential buildings, industrial premises and other buildings with constant occupancy. This popularity is explained by the following advantages of this type of heaters:
- Since all fuel components are burned, the installation has a high efficiency - up to 85% (some manufacturers even claim 93%).
- As a result of the complete oxidation of organic molecules, the exhaust of a pyrolysis furnace for the most part contains only carbon dioxide and steam - no heavy hydrocarbon radicals, carbon monoxide and other under-oxidized substances. For this quality, units of this type are sometimes called smokeless. They do not harm the environment and need to be cleaned relatively rarely.
- The supply of pyrolysis gas to the afterburning chamber can be easily adjusted, so in terms of ease of control and inertia, this furnace can be compared with a gas heater: the power can be quickly changed from 5 to 100%. For the same reason, it is much easier to automate than other solid fuel heat generators.
- The fuel for pyrolysis furnaces can be not only wood, but also all kinds of garbage, including old car tires. There are also models that run on liquid fuel, such as used machine oil.
- Heat can be removed using water (the furnace is equipped with a heat exchanger and turns into a boiler) without deteriorating the characteristics of the furnace.
- On one refueling, the unit operates much longer than a conventional metal stove (up to 24 hours).
In addition to the disadvantages characteristic of all solid fuel appliances (the need to store and periodically add firewood, large sizes, etc.), pyrolysis furnaces also have specific ones:
- the fuel is required to be as dry as possible (at a humidity of more than 12%, pyrolysis does not proceed well);
- Condensation forms abundantly in the chimney, which is due to the low exhaust temperature.
The fans and electronic control unit require power to operate.
Negative effects of reduced loads
In addition, during calculations, one should take into account the negative impact on the entire fuel system of working with a reduced load.
- With excess power, increased moisture condensation occurs on heat exchangers and chimney surfaces, in slow modes. Consequently, the installation must be selected in such a way that the vast majority of the time, combustion takes place with the most efficient performance and coolant temperature, up to 80 - 90 ° C. Using such a unit irregularly or for periodic heating at the dacha will not be at all rational.
- The type of fuel used has no less influence in the calculations. The caloric content of which, like its humidity, significantly affects the power received and creates a certain delta of up to 25 -30%.
- When using coal, especially heat-loaded surfaces of the secondary afterburning chamber must be protected by a lining, usually fireclay brick.
- Cast iron should be used as the main material due to its resistance to fading and deformation. But, as you know, working with it in artisanal conditions is almost impossible, so making a stove of such parameters with your own hands is out of the question.
- For home craftsmen, the main material is structural steel, preferably having heat-resistant characteristics, otherwise the lack of heat resistance will have to be compensated by the thickness of the walls.
Types of pyrolysis furnaces
Units operating according to the described principle can be divided into two categories: with full and partial gas generation.
Furnaces with a full gas generation cycle
This is exactly the device that was described in the first section. Its manufacture in a home workshop is a rather complex and expensive process. Due to the high temperature in the firebox, it has to be made from heat-resistant alloy steel, which is not cheap.
Furnace with a full gas generation cycle
But the main difficulty is different: the rate of wood gas release is constantly changing, and to monitor this process you need cunning and expensive electronics, which, depending on the conditions inside the stove, regulate the supply of primary and secondary air. Thus, the user can independently manufacture only the steel body of the furnace; everything else - the air supply system, controller, catalyst-afterburner - will have to be purchased.
Furnaces with partial gas generation and diagrams
A wide variety of versions of such units are constantly being developed by both reputable companies and craftsmen.
Butakov stove
The products of the former are published under brands with euphonious names like “Professor Butakov”, Breneran, Bullerjan, etc., the latter designate their creations more prosaically – “Bubafonya stove”, “Slobozhanka”, “Rocket stove” or simply “oil stove from cylinder for the garage."
Slobozhanka stove
Among them there are designs with both separate and combined afterburning. Such an installation cannot be called a full-fledged pyrolysis unit, but it still contains some structural elements for afterburning wood gas. At the same time, the developers completely abandon forced air supply, so that the stoves become energy independent. We will learn how to make one of them ourselves.
Pyrolysis
Not everyone is familiar with the concept of “pyrolysis”. This process is the thermal decomposition of organic matter (when there is not enough oxygen) into pyrolysis gases and solid residues. At high temperatures, the pyrolysis gas mixes with oxygen, as a result of which both the gas itself and the organic matter, in our case the fuel, are completely burned.
If the solid residues are removed after the first stage, the process of making coal will actually be ensured. However, we are interested in the process as a whole, considering it as a heating system.
Design, device and principle of operation of a homemade pyrolysis oven
A simplified version of a gas generator device differs from a full-fledged one in the following features:
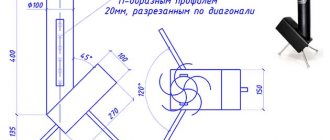
- The afterburning chamber is located not from below, but from above, so wood gas enters it by gravity. This is implemented as follows: the upper quarter of the internal space of the furnace is separated by a perforated horizontal partition, which does not reach the front wall by 20-25% of the length of the firebox. Thus, most of the flue and pyrolysis gases will be deflected forward and we get a front-burning stove that is quite easy to control. The lower quarter of the internal space will play the role of an ash pan - it is separated from the firebox by a grate.
- Primary air enters the firebox due to natural draft. For this purpose, there is a hole in the wall of the furnace with an adjustable damper - a blower.
- Air is not supplied separately to the afterburning chamber - it is taken from the firebox.
- The draft is limited by a damper installed in the chimney, which has a cutout of a certain area. When the stove is lit, this damper opens completely.
An important feature of stoves with this design is the relatively low temperature in the firebox - if wood fuel is used, it is only 550–650 degrees. Thanks to this, the requirements for the furnace material are significantly reduced - even the firebox can be made from structural steel - without alloying additives - with a thickness of only 4 mm. True, in this case the stove cannot be heated with coal, since it will quickly burn out (coal burns at a temperature of 800–900 degrees).
Flaws
However, despite all the advantages, these long-burning stoves also have their drawbacks, which can be listed in the following points:
- The cost of a pyrolysis combustion boiler is quite high, which, however, can be manufactured on your own if you buy all the necessary components for its assembly, while significantly reducing costs.
- Using only dried wood for heating, otherwise the useful effect of this unit is greatly reduced and the chimney quickly becomes clogged.
- Forced traction using an electrical power source.
Calculation of parameters
When designing a furnace, they strive to solve the main problem - to provide the required power. It will depend on the amount of fuel, so you need to correctly calculate the volume of the firebox. This can be done using a simplified method.
We set the required power
Suppose, based on the results of the heat loss calculation, it turns out that 10 kW of heat is required to heat the room at the lowest outside temperature.
We determine the required furnace power in normal (flame) combustion mode
It is known that in the gas generation mode the furnace power is 10-30% of that which develops in the flame combustion mode. Consequently, to obtain 10 kW with gas generation, the unit, when burning with a flame, must develop a power of W = 10 / 0.3 = 33.3 kW (we assume a 30 percent power ratio).
We choose the least energy-intensive fuel of all types that are supposed to be used
Here, for example, is data on the calorific value of some types of wood:
- beech: 15.5 MJ/kg;
- birch: 16.5 MJ/kg;
- aspen: 18.2 MJ/kg;
- oak: 20 MJ/kg.
Of all the listed species, beech gives the least heat, so we will focus on it.
We determine the volume of fuel reserve that can provide the required power
It should be taken into account that a portion of firewood burns in flame mode in approximately 4500 s. Therefore, during this time it should provide the following amount of heat: Q = 33.3*1000*4500 = 149.85 MJ.
Let's calculate the required mass of fuel, taking into account that it burns only 80% completely, and the efficiency of a homemade stove is approximately 50%:
M = 149.85 / (15.5*0.8*0.5) = 24.17 kg.
Knowing that the density of dry beech is 620 kg/m3, let’s convert the resulting mass value into volume: V = 24.17 / 620 = 0.039 m3 = 39 liters.
Determining the volume of the firebox
It should be taken into account that the furnace load factor is on average 0.63. Thus, it should have a volume: Vt = 39/0.63 = 61.9 l.
Therefore, the required volume of the firebox can be taken as 62 liters. Its length should be taken equal to 0.5 m - so that sufficiently long logs can be laid. Other sizes are optional. For example, the width can be 300 mm, then the height should be 413 mm (0.3 * 0.413 * 0.5 = 0.062 m3).
Advantages
Let us highlight the main advantages that a pyrolysis oven has:
- High efficiency – up to 85%. When compared with conventional ovens, this is a very good indicator.
- Fast fuel heating. Achieving a comfortable room temperature in a short period of time.
- Environmental friendliness. Combustion products contain harmful substances in extremely small dosages. Therefore, such stoves are called smokeless: there is no soot, a clean chimney.
- Economical operation. It is ensured by prolonged and complete combustion of fuel.
- Wide range of thermal power. The furnace is capable of operating in the range from 5 to 100%.
- Various fuels can be used, in addition to the recommended types: car tires, garbage, raw firewood and others.
- No need for constant monitoring. Fuel is loaded once a day, and ash can be unloaded much less frequently.
- You can do it yourself. It is enough to draw up the correct diagram, make a drawing according to which you can implement the task.
Powerful pyrolysis boiler
Required materials and tools
To create a furnace with partial gas generation you will need the following:
- Sheet steel 3–4 mm thick.
- Equal-flange steel angle 50x4 mm.
- Pipe with a diameter of 50–60 mm.
- Steel reinforcement with a diameter of 8 mm - the grate and damper axles will be made from this material.
- A pipe made of steel or cast iron with a diameter of 110 - 120 mm for the manufacture of a chimney.
- About 15 bricks.
You should not use high-carbon steel, for example, grade Steel 45. Due to the high temperature, it can become stronger, losing its ductility (this phenomenon is called hardening). An acceptable option is steel grades from St3 to Steel 20.
You will also need tools and consumables for them:
- Electric welding machine and electrodes in the amount of 5 packages.
- Drill with a set of metal drills.
- Grinder with a working part diameter of 230 mm and 10 cutting wheels for it. Cleaning wheels may also be needed.
In addition to the above, you will need a hammer and a marking tool: tape measure or ruler, pencil.
Assembly
It is necessary to assemble the structure with your own hands according to the drawings and at the site of operation. After laying the foundation, the internal walls and ash compartment are installed. Structural elements are assembled using welding.
Pyrolysis oven in nature
The heat exchanger, chambers, and grates are being assembled. External stiffeners and walls and a top plate are installed. Water tanks are being installed. Sand is poured between the walls (it is pre-calcined to get rid of organic components), which will accumulate heat and prevent overheating of the structure.
Primitive design of a pyrolysis furnace
The chamber doors are installed. Connection is made to the circuits of the water container. The metal structure, made by hand, is ready for use.
Scheme of a pyrolysis furnace
Preparatory work
Before you start making a homemade pyrolysis furnace, rolled steel needs to be cut into blanks. This can be done in a home workshop using a grinder, however, this method cannot be called rational.
It will be faster and more profitable to pay for cutting at the metal depot where the rolled metal was purchased. There are powerful guillotine shears, gas cutters and other equipment with which the workpieces will be completed in the shortest possible time and with maximum quality. The customer will only have to clean off the burrs on the edges using a grinder.
Since the unit will turn out to be quite massive, it is best to assemble it directly at the installation site. Accordingly, before starting work, it (the place) needs to be prepared. They do it like this:
- A base of brick or other fireproof material is laid on the floor. Its length and width must be at least 600 mm greater than the corresponding dimensions of the furnace, that is, the base offset on each side must be at least 300 mm.
- In the boiler room, the base must be located in such a way that after assembling the stove, there remains a distance of at least 1 m between it and the nearest wall. This value can be reduced to 0.85 m if the wall has fireproof plaster with a thickness of 25 mm or more.
You can also offer this option for a fire-resistant coating for the wall: a steel sheet is screwed to it on ceramic linings, so that there is a gap of several centimeters between it and the wall; in this case, the lower part of the sheet should not reach the floor by 7–10 cm. The sheet heated from the stove will transfer heat to the air in the gap between it and the wall; it will rush upward due to convection, sucking in cold air from below. Thus, thanks to this simple technique we will get an additional convector.
The floor in front of the stove within a radius of 1.2 m from the center of the firebox must have fireproof protection. It consists of a steel sheet with a thickness of 1.5 mm (roofing iron can be used) and a sheet of asbestos or basalt cardboard laid under it.
Nature of installation
The installation of such a heating system requires a separate room, which must have forced ventilation. The boiler itself must be installed on a special metal or concrete platform. Also, the boiler is located no closer than 20 cm to the surface near the walls. In addition, certain means of automatic protection are needed in the form of safety valves and air supply regulators in automatic mode, since autonomous operation can occur for a long time without reloading fuel.
How to make a pyrolysis oven with your own hands: step-by-step instructions
Having prepared everything you need, you can proceed directly to the manufacture of the heat generator:
Pre-cut blanks from the corner are welded into a frame. Vertical elements (racks) should have a length of 1 m or slightly more, the length of the horizontal crossbars depends on the size of the furnace. The frame does not have to be welded - a bolted connection will do. But in this case the structure will be less durable.
Assembling the frame of a pyrolysis furnace
When manufacturing the front wall, at the cutting stage, two openings had to be made in it, one for storing fuel, the second for removing ash. The openings must be closed with doors, so hinges and hooks must be welded in appropriate places on the front wall to secure the door bolts.
Next, you need to make doors from the blanks cut out at the preparatory stage. The bolts are attached to the blanks using rivets and the hinges are welded. It is also necessary to weld 10 mm wide bars, thanks to which the doors will close more tightly.
Example of the location of the upper and lower doors
On the inside of each of the side walls, you need to weld two corners, on which the grate will subsequently be laid (it can be welded from reinforcement) and a perforated floor, separating the firebox from the afterburning chamber.
Grate
The corners should be positioned so that the afterburning chamber and the ash pan occupy ¼ of the entire height of the internal space.
Blower with slide valve
Next, you need to embed a blower with a damper into any of the side walls at the level of the top of the combustion chamber. It is made from a short piece of pipe with a diameter of 50–60 mm. Having drilled holes with a diameter of 8.5 mm in the blower, you need to insert a damper axis made of reinforcement with a diameter of 8 mm into it. On one side, the axis should protrude to a sufficient length - after bending, its shank will serve as a handle.
All that remains is to weld a steel disk to the axis, the diameter of which corresponds to the internal diameter of the blower. To prevent the damper from moving spontaneously, its handle must be equipped with a spring or threaded lock.
When cutting the blanks, a hole for the chimney had to be made in the stove lid.
Assembly of the structure
When all the walls are ready, they need to be welded sequentially to the frame. They start from the bottom, then weld the front, rear and side walls. Next, a grate with a partition is placed in the oven and a lid is welded to it. The partition separating the afterburning chamber must have holes with a total area of approximately 7% of the total area of the part. In addition, between its edge and the front wall of the stove there should be a gap of about a quarter of the length of the firebox.
Afterburner injector
To connect the stove to the chimney, you need to weld an outlet with a diameter of 110–120 mm with a rotation angle of 90 degrees into the hole in the cover. Next, a horizontal section 0.8–1 m long is attached to it - the so-called hog. This is a very important element for this furnace: it delays the exit of gases from the afterburning chamber, allowing them to burn in full.
The hog (horizontal section of the chimney) is an important element for a pyrolysis furnace
At the end of the horizontal section, a damper (gate) should be installed, made according to the same principle as the blower damper. Only the diameter of the gate should be slightly smaller than the internal diameter of the pipe - approximately 90–95 mm, and in addition, a sector with a central angle of 90 degrees, that is, ¼ of the disk, is cut out of it.
This stove operates in a low-temperature mode, so caustic condensate forms abundantly in its smoke exhaust channel. If the unit is connected to an existing brick chimney, the latter should be lined with a pipe made of stainless acid-resistant steel. The same material is also used if the chimney is being built from scratch. First, a tee is attached to the hog, orienting it so that one pipe faces down and the other faces up. Several studs are welded to the lower pipe, onto which a plug will be placed - this will be a condensate receiver. To discharge condensate, you need to cut a threaded pipe into the plug and install a ball valve on it. A smoke exhaust pipe is connected to the upper branch pipe of the tee. It must be very well insulated, otherwise the draft due to the low temperature of the flue gases (only 120 degrees) will be too weak.
Note! The condensate formed during the operation of this furnace is not only corrosive, but also extremely toxic. It is very important to prevent it from entering the premises. All chimney joints must be carefully sealed with high-temperature sealant; even better, install the pipe outside, connecting it to the hog through a hole in the wall.
Boilers with top chamber placement
There are also boiler models that operate in exactly the opposite direction. Folk craftsmen designed one gasification chamber at the bottom and another at the top. These types of boilers are not yet so popular, but their advantages are already obvious:
- The system operates on natural draft using a new solution in the design of air channels.
- Eliminates the use of electricity.
- "Inverted" design.
The bottom line is that the pyrolysis gas enters the upper chamber and combines with secondary air. Discharged air enters the boiler through the lower hole, combines with oxygen, and forms a medium for the oxidation reaction. The flammable gas burns in the lower chamber and releases heat to the water. The special hardened steel of the boiler allows clear smoke to exit the chimney.
A properly installed system can function for up to 14 hours on one serving!!!
Furnace manufacturing options
The design of the stove can be complicated by turning it into a convector. To do this, it is equipped with vertical pipes with a diameter of 60 to 100 mm, 2/3 of the diameter of which must be located inside the firebox. To increase the contact area of the pipes with the high-temperature zone of the furnace, they are made curved.
Note! The diameter of the pipes is selected taking into account the viscosity, heat capacity and thermal conductivity of air. The use of thinner air ducts, even with an increased number of them, will lead to a deterioration in the performance of the convector.
The outside of the heat generator can be covered with a protective casing. Then its temperature when the furnace is operating in gas generation mode will not exceed 50–55 degrees. The air coming out of the pipes will have a temperature of 60–70 degrees.
A homemade pyrolysis furnace can be equipped with a catalyst, also made independently. A good material for it is nichrome. You can also make a ceramic catalyst using a brick or a tube of baked clay as a basis. A transition metal oxide, for example manganese, or an element from the platinum group is applied to it as follows:
- The metal salt (it should not be resistant to high temperatures) is dissolved in water, after which the ceramic base is impregnated with this solution.
- Next, the future catalyst is dried at a temperature of 160–200 degrees.
- Now the part needs to be calcined in the open air, heated to a temperature of 600–800 degrees.
The most accessible platinum salt is ammonium hexachloroplatinate; manganese nitrate can be used to make a manganese catalyst, and vanadium can be easily obtained from ammonium vanadate.
Safety
Making a pyrolysis oven with your own hands is quite possible, but it is important to make a detailed drawing and also have the skills to work with a welding machine. Since gas formation occurs unevenly, monitoring of the gas to oxygen ratio is required. For this, electronics are used that monitor the processes. One chamber generates pressure, the other creates a balance in the composition of the air-fuel mass. This is the difference between designs made at the factory and those made by hand.
Safe models of pyrolysis boilers
Note: Since the pyrolysis process is not controlled, it requires the use of an electronic system. To build a stove with your own hands, you should use high-quality materials.
A small pyrolysis oven that can be used in a garage
Oven operation and maintenance
The furnace with partial gas generation is put into operation as follows:
- A portion of quickly burning fuel is placed on the grate - thin branches, wood chips, pellets or even cardboard. Having fully opened the slide valve and the ash pan, ignite the fuel and close the firebox door.
- After the fuel turns into coals (you can monitor the combustion through the ash pit), several dry logs are placed on it. If you have a large log of wood, there is no need to split it - you can lay it as is, provided that it fits in the firebox.
- Having closed the door, the furnace is switched to gas generation mode: the slide valve is completely closed and the blower is covered, using it to regulate the furnace power. Let us remind you that there is a cutout in the damper, thanks to which the chimney is not tightly blocked.
In pyrolysis furnaces, ash is formed in very small quantities, so the owner has to remove it relatively rarely - once every 7-10 days. However, it must be taken into account that in stoves with partial gas generation, the chimney and firebox very quickly become overgrown with soot. So it has to be removed relatively often - also about once every 10 days. You should not run the unit too hard: soot and resin reduce the clearance of the smoke exhaust channel, prevent the transfer of heat to the walls of the furnace, and if the layer is sufficiently thick, it can flare up and cause a fire.
There is no need to remove soot by burning. This idea can also lead to a fire, and, in addition, if the stove is made of ordinary (structural) steel, it can suffer from high temperatures. It is better to simply scrape off the carbon deposits with a spatula, brush or a scraper specially made for this purpose.
The chimney is cleaned through the condensate receiver, after removing the plug from it.
Features of a long-burning stove
The first step is to understand what happens when wood burns. For a flame to appear, the temperature of the wood must be brought to approximately +150 degrees, using an external heating source. Usually, a piece of paper lit from an ordinary match is enough for this. After this, the process of slow charring of the material begins, which, after reaching +250 degrees, begins to decompose into simple chemical elements. The white smoke that appears when a flame is ignited includes gas and water vapor: they are emitted by heated wood. Ignition of the released gaseous components is observed when heating reaches +300 degrees: as a result of this, the thermochemical reaction is significantly accelerated.
The breakdown of organic matter into simple elements is called pyrolysis. Practice shows that during the combustion of wood, part of the energy potential inherent in it remains unused. This is reflected in a significant amount of waste remaining after the flame goes out. In pyrolysis furnaces, fuel is used much more efficiently, which is achieved by separate combustion of gases released during fuel combustion. At the same time, the rate of smoldering of the wood itself is very low, which helps to increase the operating time of the stove on one stack. The Bubafonya stove, which is a type of pyrolysis heater, guarantees almost complete combustion of all fuel.
History of technology
Heating organic materials in the absence of oxygen leads to chemical and physical changes in them. In the past, these phenomena were used to produce charcoal. The most primitive method looked like this: the wood was covered with a clay mound and heated in the relative absence of air. With the help of this technology, coal production reached its peak in the 11th-12th centuries.
The serious consequences of such forest processing are now being felt in some areas of Africa and Asia. Despite its apparent simplicity, this method is not environmentally friendly. As a result of wood pyrolysis, resins are released, which are volatile products with a high molecular weight. They condense easily at normal ambient temperatures. But despite this, the solid residue (coal) has traditionally been a valuable fuel for primitive agricultural communities, due to the following qualities:
- high carbon content compared to the original wood;
- low sulfur content.
Previously, steel production, including successful attempts to cast cannons from it, was based on the reduction of iron oxide with carbon in coal. A similar technology using charcoal, based on the processing of eucalyptus, is also practiced in modern Brazil as economically justified.
The pyrolysis oven is very economical to use
Pyrolysis has found wide industrial application in coking operations. Furnace designs and reaction conditions varied depending on demand and prices for the final products. In mid-19th century Europe, carbonization of coal was used to produce gas that was used to heat and light homes. At that time, only royal palaces could use such innovations. Household use of pyrolysis gases ceased with the development of transportation of natural hydrocarbons.
Read also: instructions for making a pyrolysis boiler yourself.
How to make a pyrolysis oven with your own hands:
During World War II, many cars and trucks were converted to wood gas generated in vehicle-mounted mobile units. Their productivity was low due to the low energy density of the gas, which, as a rule, contained large amounts of nitrogen and other non-flammable compounds.
The durability of engines using such fuel was short and was reduced primarily due to fly ash entering the cylinders along with wood gas. But despite these shortcomings, the use of such machines was justified by the shortage of fuel. After the end of the war, these installations were forgotten until the present day.
Now the problem of obtaining fuel from biomass instead of fossil fuels is again relevant.