Wet grass underfoot, foggy windows, droplets on the walls of a damp basement - all this is the result of condensation of water vapor from the atmospheric air. Everyone has encountered this, but not everyone was interested in how to determine the dew point. Most often, this task has to be solved by architects, builders and designers, and people far from this area are hardly familiar with this concept.
How to determine dew point
The nature of the appearance of dew
Water condensation on various surfaces occurs as follows.
Atmospheric air is always more or less saturated with water vapor. As the temperature drops, water changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state. This occurs when the surrounding air comes into contact with cooler surfaces and heat loss occurs. This leads to the formation of water droplets. Morning dew is easily explained by the laws of physics
The temperature at which water vapor from the air changes its state of aggregation to liquid is called the dew point.
The higher the content of water vapor in the air (or other gas mixture), the higher the condensation temperature of water, or dew point. For example, at 100% relative humidity, the dew point is exactly the same as the air temperature. Conversely, the lower the relative humidity, the lower the dew point. This means that for condensation to form, the air must be cooled more.
Comfortable dew point values for humans
| Dew point, °C | Human perception | Relative humidity (at 32°С), % |
| more than 26 | extremely high perception, deadly for asthma patients | 65 and above |
| 24-26 | extremely uncomfortable condition | 62 |
| 21-23 | very humid and uncomfortable | 52-60 |
| 18-20 | unpleasant for most people | 44-52 |
| 16-17 | comfortable for most, but feels at the upper limit of humidity | 37-46 |
| 13-15 | comfortable | 38-41 |
| 10-12 | very comfortable | 31-37 |
| less than 10 | a little dry for some | 30 |
What is dew point
The dew point is the temperature at which condensation begins to form.
This term refers to the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor to the limit. When cooled below the critical point, drops or fog form on objects.
This phenomenon is based on the fact that the maximum steam production of a cubic meter of air varies depending on its temperature.
Examples (data given in grams):
- -5°C – 3.25.
- 0°C – 4.85.
- +10°C – 9.41.
- +22°С – 19.44.
- +28°С – 27.26.
The relative humidity value shows what the current set amount of water vapor is in relation to the maximum possible amount. For example, if this parameter is 34.5% at a temperature of +28°C, then the water vapor content in the air will be 27.26*0.345=9.4047 g/m3. From the above statement it follows that when the air is cooled to +10°C, the relative humidity will reach approximately 100%, i.e. this temperature is the dew point under given conditions. If the air cools further, too much water vapor is produced, some of which condenses.
Absolute air humidity
The main characteristics of humid air are:
- density of water vapor in the air;
- relative humidity.
Air is a composite gas and contains many different gases, including water vapor. To estimate its amount in the air, it is necessary to determine what mass water vapor has in a certain allocated volume - this value is characterized by density. The density of water vapor in the air is called absolute humidity
.
We recommend reading: Water-type heating convector built into the floor
Definition. Absolute air humidity
- the amount of moisture contained in one cubic meter of air.
Absolute humidity symbol
:
(as is the usual designation for density).
Absolute Humidity Units
:
(in SI) or (for the convenience of measuring small amounts of water vapor in the air).
Formula for calculating absolute humidity
:
Designations:
mass of steam (water) in air, kg (in SI) or g; the volume of air in which the indicated mass of steam is contained, .
On the one hand, absolute air humidity is an understandable and convenient value, since it gives an idea of the specific water content in the air by mass; on the other hand, this value is inconvenient from the point of view of the susceptibility of humidity by living organisms. It turns out that, for example, a person does not feel the mass content of water in the air, but rather its content relative to the maximum possible value.
Scope of application of the concept
The transition of moisture into a liquid state significantly changes the living and working conditions of people and affects the functioning of structures and mechanisms. Therefore, in many areas, special attention must be paid to the location of vapor deposition.
Construction
The shell of most buildings is vapor permeable. The exception is metal workshops and garages. The relative humidity indoors is higher than outdoors, and water vapor penetrates the walls under partial pressure.
Buildings have vapor permeability, which depends on the type of building material.
If there are areas in their thickness with a saturation temperature or lower, condensation occurs, causing these effects:
- Reduced thermal resistance of the structure.
- Reducing the service life of building materials. When it gets colder, the water turns to ice and expands, causing internal damage.
- Development of mold and fungal colonies (when the surface is wet).
Building materials have different vapor permeability. The lowest is in heavy reinforced concrete (buildings with floors) - 0.03 mg/m*h*Pa, the highest in aerated concrete blocks - 0.23 (at a density of 400 kg/cubic m).
Agriculture
When the air temperature drops, moisture condenses on the shoots and leaves of plants. If repeated frequently, this leads to disease. Thus, knowledge of the condensation point allows you to plan preventive and therapeutic measures.
Moisture condenses on the leaves of plants.
On the other hand, in arid regions, condensation of atmospheric moisture can partially replace the irrigation system. Breeders are working to develop varieties that can absorb water in this way. Knowing the critical point will then help determine the required irrigation capacity if the weather forecast does not predict rain in the near future.
Conservation measures for some plants, such as grapes, are also planned taking this parameter into account. If it is high, it means there is a lot of moisture in the air and frost damage, including radiation damage, will be moderate.
If the dew point is low, cover the shoots or water the area.
Insulation of walls inside structures
By choosing cellulose insulation Ecowool and insulating wooden structures with it, you can avoid a conflict of materials, since the fibrous structure of wood and similar ecowool will “breathe” evenly, regulating air humidity naturally - drawing in moisture and releasing it in one algorithm. In such a tandem there will be no sharp temperature limit, and therefore no prerequisites for the structures to get wet. For a frame house, filling the walls with ecowool along the width of the studs using the wet-glue method or by injection, under the pressure of fluffed ecowool in the cavity - that is, insulating the inner layer is a reliable protection of wooden structures from getting wet caused by the dew point. Unfortunately, this effect is difficult to achieve with insulation materials that do not absorb moisture - polyurethane foam, polypropylene foam, or cannot remove it. Mineral wool, having excellent declared properties, loses them when wet, and it is quite difficult to dry it.
Another point negates the insulation of cavities with roll and sheet insulation: the presence of seams. Even super-high-quality installation does not guarantee that there will be no cold bridges in the joints - cracks that deliver cold air to warm internal surfaces or warm and humid air to external ones. This is where an unplanned dew point may appear, nullifying all insulation efforts.
Where should the dew point be?
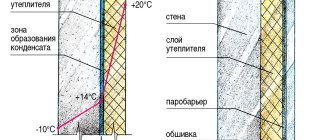
The ideal location for the dew point in a wall is the insulation on the outside of the wall. The thickness of the insulation on the wall should be such that during the coldest period of time, condensation does not flow into the wall itself, and if it does flow, it does not remain there for a long time.
Dew point isolated
The destructive effect of dew point in the body of a load-bearing wall can be seen in the following article.
Walls based on porous materials, such as foam blocks and sandwich blocks, brick and similar materials, require a higher layer of thermal insulation, since they absorb and accumulate moisture. Therefore, even a short-term (a few days) dew point in a porous wall can have a detrimental effect on the internal integrity. Thus, so-called warm masonry materials can only be effective in certain regions where winters are less frosty.
However, if it is predicted that the dew point will periodically move deeper into the wall of the house, or if this is likely, this fact should be taken into account when choosing masonry materials. In such cases, high-density masonry materials that can withstand several freeze-thaw cycles without damage are well suited. With a high frost resistance coefficient. Such frost-resistant materials include brick and foam concrete.
Frost resistance indices of the most commonly used wall materials
What types of bird feeders can be made?
Even the most beautiful bird feeder bought in a store cannot replace one made by yourself, especially if children are involved in the manufacturing process.
From improvised means and inexpensive materials, you can build a variety of models that differ in certain design features:
- hanging structures with easy access to grain feed;
- tray feeders with a practical canopy to protect the tray;
- full-fledged feeding houses with roof slopes and perches;
- bunker crafts and peelers with original and non-standard designs.
To fill feeders of any type, you can use a variety of food, grains and bread, nuts and seeds, not forgetting the taste preferences of birds living in a given region.
How to calculate the dew point in a wall with insulation
It is impossible to accurately calculate one place in the wall where condensation will form. Because the dew point depends on several parameters and is a variable value. You can only calculate a certain distance in the thickness of the wall where liquid will form under different temperature changes outside the house.
For example, if the indoor temperature is stable and the temperature outside becomes colder, the dew point will move along the thickness of the wall, closer to the room.
This formula can be used to calculate the dew point as accurately as possible for both homogeneous and multi-layer walls.
Calculating the dew point for any multi-layer wall is quite simple; the following data is required:
- Dew point at relative humidity in your area (table below)
- External temperature
- individual thickness of each wall layer
- internal temperature
- Thermal conductivity coefficient of the material from which the walls of the house are made
To determine in which part of the designed wall the dew point and condensation will be located, you need to know two values.
- The dew point temperature in our region, as well as the humidity and temperature inside the building of interest to us. We can see this in the table above. Let's call this indicator Tp (dew point).2
- The air temperature that will occur at the boundary of two layers of the wall at the values of interest to us. Let's call this number Tc (the point between the layers).
If the difference between the above values is positive, the dew point is inside the insulation, if the value is negative, the dew point will accumulate liquid inside the wall or house.
In other words, if the temperature at the interface between the insulation and the wall is higher with a positive sign than the dew point temperature from the table, condensation will form in the insulation.
Let's take the following conditions as an example:
The dew point temperature in a region with 60% humidity and a room temperature of 21ᵒC according to the table will be 12.9ᵒC. The air temperature at the interface between the thermal insulation and the wall is 15 ᵒC.
The difference between these values is 15 ᵒC – 12.9 ᵒC = +2.1
If the difference between the above values is positive, as in our case, the dew point is in the insulation, if the value is negative, the dew point will collect liquid inside the wall or house.
In our case, the temperature of liquid vapor release occurs before the saturated air reaches the main wall. And condensation will settle in the insulation, and not in the load-bearing wall of the house or inside the house.
This raises the question: if we take the dew point temperature at a given humidity level from a given table, how do we calculate the temperature between the layers of the wall?
The temperature at the boundary between two wall layers is relatively easy to calculate using the following formula:
Tc (temperature between wall layers) = (t2 – t1)x (S1x0.01/k) / (S1x0.01/k), where:
t2 – internal air temperature
t1 – external temperature
S1 – wall material thickness
k – thermal coefficient of the wall material
Simple example:
Let's take as an example a region where the dew point is 12.9 ᵒC in a region with 60% humidity, the indoor temperature is 21 ᵒC, and the outdoor temperature is 12 ᵒC below zero.
Now we need to calculate for these conditions what the temperature will be between a standard 38 cm thick one-and-a-half brick wall and a 10 cm thick external foam insulation. Subtract the dew point temperature from the table.
To do this, we will use the formula given above.
Tc (temperature between wall layers) = (t2 – t1)x (S1x0.01/k1) / (S2x0.01/k2)
According to the convention:
t2 = +21ᵒC (indoor air temperature)
t1 = -13 ᵒC (outside air temperature)
S1 = 38 cm (wall thickness)
K1 = 0.6 (thermal resistance coefficient of brick)
S2 = 10 cm (foam insulation thickness)
K2 = 0.04 (foam thermal resistance coefficient)
Calculation of the temperature between the brick wall and the foam insulation, under the climatic conditions we have chosen, will look like this:
( +21 – (-13ᵒC))x(38×0.01/0.6) / (10×0.01/0.04) = 9.52
According to our calculations, the temperature between a 10 cm thick foam core and a 38 cm thick brick wall, when the outside temperature is -13 degrees Celsius and the temperature inside the house is +21 degrees Celsius, is 9.52 degrees Celsius.
Therefore, if we subtract 12.9 degrees Celsius from the temperature between the insulation and the wall, which is 9.52 degrees Celsius, we get 9.52-12.9 = -3.38.
The calculated dew point is in the wall.
As you can see, the dew point is negative, i.e. the brick wall will reach a state of condensation and moisture will accumulate in it.
The above dew point calculation is more accurate with an error of up to 0.5 degrees Celsius, unlike some online calculators and other devices that do not take into account different material structures.
Formula for calculation
The following formula will help you calculate the dew point yourself and accurately:
This formula can be used to calculate relative humidity from a known dew point
Here Tr means the temperature of the point itself, b and a show equal (constant) values, ln is the natural logarithm, T is the indoor temperature, Rh is the relative humidity value.
As can be seen from the formula, the value directly depends on the values of two parameters:
- humidity indicator;
- actual temperature readings.
At high relative humidity, the parameter becomes higher and closer to the actual temperature level. To calculate this variable value, there is a table with a small step of parameters. From it you can find the required value by measuring the relative humidity and actual temperature.
We recommend reading: Filter for heating (boiler, system): installation, types
Table 1. Determination of the indicator using the ratio of influencing parameters on which the dew point depends
From the table we calculate that at a temperature of, for example, 19 degrees and a humidity of 50%, the condensation parameter will be 8.3 degrees.
From this video it becomes clear how thick the insulation should be for the most comfortable conditions:
Precise definition
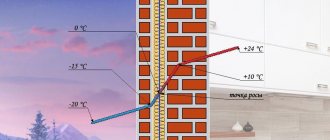
Water vapor most often condenses on the walls themselves or inside their structure if they are not insulated or built properly. Without insulation, the value will be close to the temperature of the inside of the wall, and in some cases, the wall in the middle of the house. When the temperature inside the enclosing structures is below this value, condensation will occur during a cold snap at negative temperatures outside.
There are several places where the indicator may be located on non-insulated structures:
- inside the structure, close to its outer part, the wall will remain dry;
- inside the wall, but close to the inside, the wall becomes wet with temperature changes;
- the side of the wall that is located in the building will constantly be covered with condensation.
Experts do not recommend insulating rooms from the inside, explaining that when using this method of thermal insulation, the parameter will be located under the heat-insulating layer in the middle of the room . As a result, a large accumulation of moisture will occur .
- condensation can accumulate in the center of the wall and, during cold weather, move towards the placement of heat-insulating components;
- the place where moisture accumulates can be the boundary of the enclosing structure and the insulating layer, which becomes damp and forms mold in the middle of the rooms;
- in the middle of the heat-insulating layer itself (it will gradually become saturated with moisture and begin to mold and rot from the inside).
The dew point is formed by three components: atmospheric pressure, air temperature and humidity.
Polystyrene foam, mineral wool or other type of insulation must be placed on the outside of the building , which will allow the value to be placed in the insulating layer (with this arrangement the walls inside will remain dry). For a clearer understanding of the parameter, there are graphs for its placement on the walls of houses with insulation, as well as on buildings that do not have an insulating layer. To make this calculation yourself, you can determine the dew point in the wall with a calculator.
Dew point calculation online calculator
There are many programs on the Internet that can be used to calculate the approximate position of the dew point on the wall. The program calculates the dew point based on a number of criteria that must be entered manually. It includes information about the material from which the wall will be built, the number and thickness of layers of the wall, air temperature inside and outside the building and humidity. The online calculator is easy to use for calculations. Along with digital calculations, you can see charts and graphs of dew point movement depending on changes in air temperature. However, the calculation results of many calculators vary, and the accuracy of the calculations is unknown.
Online dew point calculator
If you don't take into account the dew point
In the construction industry, ignoring the rules can lead to undesirable consequences. Metal, brick, concrete, wood and other materials will have a shorter lifespan. The formation of condensation in the area of polymer-density materials when installed as thermal insulation is unacceptable and leads to the following problems
- Structures fail prematurely, leading to premature failure.
- The surface of the material swells;
- Condensation is necessary on surfaces with temperatures below the dew point;
- Large areas of finishing material peel off;
- Harmful fungi and mold develop on walls, causing illness;
Psychrometer
A more convenient and accurate device for measuring relative humidity is a psychrometer (from the ancient Greek ψυχρός - “cold”) (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Psychrometer (Source)
A psychrometer consists of two thermometers, which are fixed on a common scale. One of the thermometers is called a wet thermometer because it is wrapped in cambric fabric, which is immersed in a reservoir of water located on the back of the device. Water evaporates from the wet fabric, which leads to cooling of the thermometer, the process of reducing its temperature continues until the stage is reached until the steam near the wet fabric reaches saturation and the thermometer begins to show the dew point temperature. Thus, the wet bulb thermometer shows a temperature less than or equal to the actual ambient temperature. The second thermometer is called a dry thermometer and shows the real temperature.
On the body of the device, as a rule, there is also a so-called psychrometric table (Table 2). Using this table, you can determine the relative humidity of the surrounding air from the temperature value shown by the dry bulb thermometer and from the temperature difference between the dry and wet bulb bulbs.
However, even without such a table at hand, you can approximately determine the amount of humidity using the following principle. If the readings of both thermometers are close to each other, then the evaporation of water from the humid one is almost completely compensated by condensation, i.e., the air humidity is high. If, on the contrary, the difference in thermometer readings is large, then evaporation from the wet fabric prevails over condensation and the air is dry and humidity is low.
How to move the dew point in a wall
If, after performing all the calculations, you are not satisfied with the position of the dew point, you should consider moving it. This can be done as follows:
- improve the microclimate in the room - install forced ventilation, additionally heat the air.
- increase the insulation layer on the outside;
- remove the thermal insulation layer from the inside and move it to the outside;
- Use a material with high water vapor permeability;
The appropriate option should be chosen depending on the climatic conditions of the area, the design features of the house, financial capabilities and the building materials used.
Ignoring such a phenomenon as condensation in a wall “oven” can be very expensive. The minimum is an unpleasant smell in the room and constant dampness. The maximum is large colonies of mold, damaging the interior decoration of the walls, destroying the insulation and the health of the residents. Therefore, calculating the dew point is very important if you want to build reliable and dry walls in your home.
Why do windows cry?
There are specific recommendations for the microclimate in a residential area. This is humidity -40-50% and temperature +18-23C . Maintaining these parameters minimizes the possibility of condensation forming on the glass surface.
Its appearance is also associated with human life (it also releases moisture!). That is, there should be as many people in the room as sanitary standards allow.
High humidity can also be associated with improper air exchange. Here, too, there are standards: at least 3 “cubes” per “square” of area in one hour.
For kitchens, these requirements are even stricter: from 6 to 9 “cubes” per hour, depending on the type of stove ( 9 cubic m/hour for a gas stove ). Therefore, everything depends on the quality of ventilation.
There is a contradictory situation; The house was completely renovated, the old windows were replaced with double-glazed windows, and mold began to appear in the rooms. What is this connected with?
The fact is that during a complete reconstruction, the heating is changed, modern boilers are installed instead of old gas water heaters, and the windows are insulated. By and large, there are fewer opportunities for natural ventilation.
If previously moisture from the room could escape through loose window slits, through the hood of an old gas water heater, now there is no such possibility.
The operational characteristics of a double-glazed window (the “K” coefficient, in particular) are important, but secondary.
About the dew point in plastic windows
When it comes to the dew point for plastic windows, many people imagine a certain, secret place. In reality, as we have already seen, it is impossible to see the dew point. Let's repeat: the dew point is the temperature at which water vapor in the air becomes saturated and condenses after cooling to it. There are special tables that allow you to calculate the dew point for a certain relative humidity and a certain temperature. One such table is shown below.
Dew point for relative humidity
Note. Let's assume that the air humidity is 50% and the temperature is +21 degrees. Under these conditions, the dew point is +10.2. What does it mean? If the surface temperature in the apartment drops to +10.2 degrees, condensation will form on it. As a rule, the coldest surfaces in an apartment are plastic windows, so this is where excess moisture most often gets in.
People often encounter condensation on double-glazed windows. Based on what was said above, condensation can be dealt with in two ways - increasing the temperature of the windows and reducing the humidity in the apartment. A comfortable level of humidity can be achieved by ensuring normal air exchange. Any excess moisture - from laundry, a boiling pan, etc. – Any excess moisture – from washing, pots, etc. – must go away and not accumulate in the room. First of all, the apartment should be regularly ventilated. The frequency of ventilation is determined individually, but we recommend doing this for at least 10 minutes twice a day. Also, do not forget to use special ventilation valves.
Ways to eliminate condensation on entrance doors
The way to get rid of condensation is to ensure the influx of dry fresh air from outside and the outflow of vapors from the enclosed space. It is possible to install a “warm curtain”, which will heat the door with heated air. The surface temperature of the door leaf will increase and the dew point will shift. Insulating the door leaf will not eradicate condensation problems. Condensing moisture settles due to the large temperature difference between the outside and the room. In this case, it is recommended to install an unheated vestibule at the entrance. It would not be amiss to equip a canopy over the entrance to protect the door from direct exposure to the sun's rays and precipitation. It is recommended to open the metal sheet of the front door with special powder polymers. It is better to fill all hollow elements in a metal door with foam in order to eliminate the appearance of cold bridges.
Harmless dew point location
There are exceptions that, when a dew point occurs, do not harm walls, windows and other materials at all. If, for example, condensation forms on the outside of a wall on thermal insulation, this will not affect the internal structure and microclimate.
This is the most favorable position for the dew point, since in cold weather drops of moisture will not penetrate the wall. The dew point can also be located on the inside of the wall itself if it is close to the outside surface to keep the interior of the structure dry.
In all other cases, side effects may occur. To avoid such consequences, under no circumstances should you insulate walls from the inside. Such isolation will lead to the following consequences:
- Rotting walls from the inside. In very bad cases and at very high dew points, internal wall rot can occur. This leads to the destruction of the building material itself. As a result, the wall may simply collapse.
- Moisture will begin to accumulate at the boundary between the wall insulation and its covering. As a result, mold grows right inside the wall and cannot be eliminated.
- Drops of moisture will gradually move towards the thermal insulation. If condensation previously appeared only in the center, then it will gradually move towards the thermal insulation, forming fungal compounds.
To avoid this condition, you must check this value regularly. If dangerous values occur, immediate action must be taken. However, you should know from the very beginning that thermal insulation has no place on the interior walls of the house.
Methods for determining dew point
You can easily measure the dew point yourself. There are several methods for calculating it. It is important to choose the one that is most convenient and practical. The main thing is to understand that after calculation you can only get an approximate value, since it is impossible to determine exact data for some indicators. Let's look at each method separately.
According to a special formula
This formula is one of the most accurate ways to determine dew point. The problem, however, is that you need to know the other values in order to use them to calculate the final value. The formula looks like this:
A, b – constants (17.27; 237.7);
T – air temperature;
Rh – relative air humidity.
The error of this calculation is one of the smallest - it is only 0.5 degrees Celsius. However, it is necessary to know the temperature and relative humidity, which is not always possible.
Using special calculators
Currently, there are various online services with which you can easily calculate the dew point. In these special mini-programs, all fixed data and approximate values are already entered, which are also necessary for more accurate calculations. All you have to do is enter the required values and see the result.
The information entered usually includes the material from which the value is calculated and its thickness. However, this information must be entered for both internal and external parties. The program will then output a table with the following data:
- Minimum or maximum dew point.
- Moisture content in kg per cubic meter;
Based on this data, it will be easy to understand what condition the walls of the room are in and what needs to be applied. However, there is no guarantee that such calculators will provide accurate results, so caution should be used.
In addition, in some cases the following data is required:
- Average air temperature. The approximate outdoor and indoor temperatures should be indicated. These indicators also affect the final result of the calculation.
- Type of number. The humidity level, for example, in the bathroom should be very high, while in the living room it should not exceed 70%.
- Geographical position. The climate in different regions of the country is very different. Based on this, we can conclude that the normal dew point for the subjects is not the same. It should be borne in mind that somewhere outside the humidity level will be even higher.
- Layers of material. This line indicates what is behind the main supporting material. This is important because if there is no other room behind the wall, the dew point values will be very different.
Advanced programs can even be downloaded onto devices. They have a much higher priority than traditional online calculators because they already use much more data to produce a result, which means the dew point will be determined more accurately. In addition, immediately after the final calculation, a special graph will appear on the screen, which is a schematic representation of the dew point in the wall.
Saturated steam, air humidity
We will devote today's lesson to discussing the concept of air humidity and methods for measuring it. The main phenomenon affecting air humidity will be the process of water evaporation, which we already talked about earlier, and the most important concept that we will use will be saturated and unsaturated steam.
If we distinguish different states of steam, they will be determined by the interaction in which the steam is with its liquid. If we imagine that some liquid is in a closed vessel and the process of evaporation occurs, then sooner or later this process will come to a state where evaporation at equal intervals of time will be compensated by condensation and the so-called dynamic equilibrium of the liquid with its vapor will occur (Fig. 1) .
Rice. 1. Saturated steam
Definition. Saturated steam
is steam that is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its liquid.
If the steam is not saturated, then there is no such thermodynamic equilibrium (Fig. 2). Rice.
2. Unsaturated steam Using these two concepts, we will describe such an important characteristic of air as humidity.
Definition. Air humidity
– a value indicating the content of water vapor in the air.
The question arises: why is the concept of humidity important to consider and how does water vapor get into the air? It is known that most of the Earth’s surface is occupied by water (the World Ocean), from the surface of which evaporation continuously occurs (Fig. 3). Of course, in different climatic zones the intensity of this process is different, which depends on the average daily temperature, the presence of winds, etc. These factors determine the fact that in certain places the process of water vaporization is more intense than its condensation, and in some places it is the other way around. On average, it can be argued that the vapor that forms in the air is not saturated, and its properties must be described.
Rice. 3. Evaporation of liquid (Source)
For humans, the humidity level is a very important environmental parameter, since our body reacts very actively to its changes. For example, a mechanism for regulating the functioning of the body, such as sweating, is directly related to the temperature and humidity of the environment. At high humidity, the processes of evaporation of moisture from the surface of the skin are practically compensated by the processes of its condensation and the removal of heat from the body is disrupted, which leads to disturbances in thermoregulation. At low humidity, moisture evaporation processes prevail over condensation processes and the body loses too much fluid, which can lead to dehydration.
The amount of humidity is important not only for humans and other living organisms, but also for the flow of technological processes. For example, due to the known property of water to conduct electric current, its content in the air can seriously affect the correct operation of most electrical appliances.
In addition, the concept of humidity is the most important criterion for assessing weather conditions, which everyone knows from weather forecasts. It is worth noting that if we compare humidity at different times of the year in our usual climatic conditions, it is higher in summer and lower in winter, which is associated, in particular, with the intensity of evaporation processes at different temperatures.
How to use the obtained result?
As you already understand, good thermal insulation is such thermal insulation (now we are talking about external thermal insulation of the facade) in which the dew point is in the middle of the thermal insulation. This parameter depends on many factors, for example, the thermal insulation properties of the insulating material decrease with increasing water content, i.e. A material with low water absorption should be used as an insulator.
How to calculate the required insulation thickness so that the dew point is inside the insulation? The properties of the insulation and walls are important here: the thicker the insulation, the faster the cold passes. From this we can conclude that a porous material will have better thermal insulation properties, and a wall made of dense concrete will require more insulation than a wall made of cinder blocks.
Hair hygrometer
Let us now consider the principle of operation of other types of hygrometers, instruments for measuring humidity characteristics (from the Greek hygros - “wet” and metreo - “I measure”).
Hair hygrometer
(Fig. 5) is a device for measuring relative humidity, in which hair, for example human hair, acts as an active element.
Rice. 5. Hair hygrometer (Source)
The action of a hair hygrometer is based on the property of defatted hair to change its length when air humidity changes (with increasing humidity, the length of the hair increases, with decreasing it decreases), which makes it possible to measure relative humidity. The hair is stretched over a metal frame. The change in hair length is transmitted to the arrow moving along the scale. It should be remembered that a hair hygrometer does not give accurate relative humidity values, and is used primarily for domestic purposes.
Relationship between dew point and construction
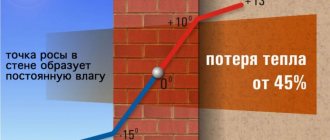
The dew point value directly depends on the relative humidity and temperature outside and inside the building. For example, if the temperature outside is 8˚C, the temperature inside the house is 22˚C, and the relative humidity is 45%, condensation will form on the outside wall.
There are other factors that influence dew point, such as regional climate conditions, insulation of the entire building envelope, quality and type of heating system, length of occupancy (permanent or temporary, as in a house or garage), and ventilation.
It is very important for builders to know the dew point in order to accurately calculate the location of condensation on the walls and determine the required insulation thickness. Knowing this, you can minimize heat loss during the cold season.
The location of the dew point may vary depending on the thickness of the wall. It depends on the thickness and type of materials of the wall itself and insulation, the temperature and humidity of the air inside and outside the building.
Each material used for the construction and decoration of walls, with the exception of metal, has its own degree of water vapor permeability. From a physical point of view, this is an indicator of the amount of water vapor that a material can pass through itself in a certain time.
Vapor permeability is one of the decisive factors when choosing thermal insulation materials, and is also important when analyzing the condition of external walls.
During periods of low temperatures, water vapor under pressure in the room will tend to escape through all layers of the outer walls. The lower the vapor permeability coefficient of the insulation, the smaller the layer that needs to be laid. Its coefficient should increase from the inside to the outside, as does thermal conductivity.
If all calculations are performed correctly, the dew point will be in the thermal insulation layer of the wall, closer to the outer surface. In this case, the water vapor will turn into condensation and will only dampen the wall. This is how water vapor accumulates in winter, and in summer it is necessary to create conditions for the evaporation of accumulated moisture.
The main condition for good insulation is the creation of conditions for the evaporation of accumulated moisture. To do this, it is necessary to make special calculations and select finishing materials.
Less suitable is the location of the dew point in the load-bearing wall of the house. This occurs if the wrong type and thickness of insulation is selected.
In the worst case, condensation is on the inside of the wall. This situation is possible if the wall is not insulated at all or if the insulation is located indoors. In the latter case, mold may form under the insulation, and the wet insulation will not retain heat at all.
Significance in other areas and countermeasures
In addition, this indicator is also taken into account by manufacturers of varnishes, paints, and protective compounds. Naturally, manufacturers and users of high-precision optics must also remember this factor so as not to harm the equipment, especially if they have to bring the devices into a warm room from the street.
In order to avoid condensation inside buildings, it is necessary to ensure good ventilation and proper moisture removal. For example, some people who want to save money may face the problem of windows constantly fogging or leaking. Poor-quality or incorrectly installed double-glazed windows can become a source of ongoing problems. So it is better to entrust such work to good professionals.
Consequences of incorrect calculations
When choosing insulation materials, it is important to remember that one of the most effective ways to protect external walls from dampness is to properly install layers of insulation.
High-quality thermal insulation will help significantly reduce heat loss and make your home more comfortable, as well as extend the life of your walls.
A thick layer that does not allow water vapor to pass through and a porous layer that allows moisture to pass out should be located on the inside of the load-bearing wall.
It is also necessary to create conditions for ventilation in the condensation zone. This way, the condensate will evaporate freely.
A properly insulated exterior wall will help reduce heat loss during the heating season from 45 to 95% and create comfort in the house.
If the thermal insulation is chosen incorrectly, moisture will gradually accumulate in it, reducing the thermal resistance of the wall. Therefore, in the second or maximum in the fifth heating season, heating costs will increase, if we are talking about a private house, the apartment will simply be much colder in winter.
Professional insulation is a long and expensive process. Today there are many insulating materials. Do not try to save on them, as cheap materials will become unusable after just a few heating seasons.
There are several consequences of incorrect calculations, but some of them can have a negative impact on your quality of life. The main consequences are constantly damp walls, mildew, mold, mildew and germs on the walls, which lead to many chronic diseases.
Constantly damp walls become a breeding ground for fungi and mold, and their spores are transmitted by airborne droplets and cause diseases.
Because wet rooms are difficult to heat, their comfort levels are reduced. High humidity in such walls can cause respiratory diseases.
Another unpleasant consequence of a miscalculation is the destruction of finishing materials - tiles crumble, bricks on the outer wall crumble, and the surface of the inner wall begins to swell.
Undried condensation is the main reason that the outer wall is susceptible to weathering and peeling of finishing materials.
To remedy this situation, the condition of the walls and insulation must be analyzed by a professional. With the correct calculations, you can correct all mistakes and create a comfortable and warm environment in your home.
The principles and formulas of thermal engineering calculations for the correct design of a house will be discussed in the next article, which we strongly recommend that you read.
Wallpaper
You need to immediately realize that cheap paper options are definitely not suitable. Elite wood requires adequate complementation. Of paper wallpaper, only more expensive multi-layer types are combined with wenge furniture. Suitable options:
- vinyl;
- glass wallpaper;
- non-woven.
All of them can also be used to decorate the dining area of a wenge kitchen.
Non-woven
They are made from modified cellulose, which significantly improves the appearance and consumer characteristics. They are more wear-resistant and durable. Another advantage is the possibility of repeated staining. This is especially valuable in the case of wenge, since it is difficult to immediately choose the exact shade for a wenge-colored living room.
Vinyl
They are also durable and can withstand repeated repainting. Patterned embossing on the surface, in combination with the main decor, effectively complements the interior of the living room. It can be diversified by repainting the wallpaper only partially.
Glass wallpaper
A new look in this segment of finishing materials. An environmentally friendly, durable material that is great for experimenting with color.
Stone
A wenge slide looks unusual against the background of walls made of brick or decorative stone (or their imitation). Colors vary: white, sand, cream, beige, light grey. Even black, ocher, orange, red, and graphite shades are in demand. The choice is determined by the style of the room and the preferences of the owners.
This solution adds exoticism and is especially suitable for ethnic style. Against this background, a showcase with ethnic collections or hunting paraphernalia will also look organic. However, the stone surface needs proper lighting and the addition of light accessories.
Wallpaper takes up a lot of space, even if it is covered by a display case or large cabinet
People immediately pay attention to them, so saving in any case is unwise. Using cheap options will nullify the entire effect and the living room will look pathetic
How to change the location of a point
If errors in calculations are made during the construction of a new house, this can lead to the permanent formation of mold on cold surfaces and further damage to the entire structure.
A problem in a house that has been in use for a long time can be solved by changing the main influencing factors. The following measures are provided for this:
- Organize a reliable ventilation system. If a finished building (guest house, bathhouse or cottage) is used temporarily, for example in the summer, you may notice an increase in humidity levels in all rooms. The best solution is to organize a ventilation system that provides good air exchange at any time of the year.
- Additional heating. If condensation persists on the ceiling, it means that the heating of the room is not sufficient to reduce the humidity level. The best solution is to additionally use portable heaters or household dehumidifiers.
- Make the building thermally insulated. You can move the point towards the street using façade insulation. Why is it useful to insulate walls outside? In this case, the condensation point will be between the insulator and the wall, so that even in the event of significant changes in climatic conditions, surface moisture can be prevented.
When determining the location of a point in the wall, many factors must be taken into account: climatic conditions, wind strength, sun angle, temperature, humidity conditions inside the building, floor thickness and materials.
The minimum level of humidity is specific to each type of material; the main thing is not to allow it to increase significantly. In addition, each homeowner can determine the temperature of the condensation on the surface. If thermal insulation technology is used, you can be sure of reliable protection and durability of the walls.
Thermal insulation material
To protect buildings from heat loss, high humidity and point shifts, it is insulated with thermal insulation materials. In winter, insulation helps reduce heating costs, and in summer it keeps the room cool. Each product has its own areas of application and properties. Eco-friendly and easy-to-install materials are used in construction. The required type of insulation is selected for certain conditions.
With proper insulation from the outside, the dew point will be located inside the insulation
According to their form, materials are divided into:
- roll;
- leafy;
- bulk;
- single.
By structure:
- fiber;
- cells;
- grainy.
Raw materials can be organic, inorganic and mixed.
Main characteristics of insulating materials:
- thermal conductivity;
- moisture absorption;
- porosity;
- humidity;
- density;
- vapor permeability;
- specific heat;
- strength, etc.
Penoplex
Penoplex is also called expanded polystyrene. Unlike foam polystyrene, the material has a higher density and is less subject to mechanical damage. It almost does not conduct steam due to its low vapor permeability coefficient. However, it belongs to group IV of flammability (it ignites quickly).
Penoplex is recommended for external wall insulation
Penoplex of the “comfort” category is produced for insulating walls, terraces, loggias, and balconies. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 9 times less than that of mineral wool. The material requires little time to heat the room after cooling due to its low heat capacity. The operating temperature range is -70…+70℃. Penoplex of this type does not have the best sound insulation, has the lowest density and lower tensile strength compared to other materials.
Penoplex for walls is suitable only if an effective ventilation system is installed in the room to maintain comfortable humidity.
A 2 cm wide layer of polystyrene foam retains heat almost as well as 40 cm of mineral wool or 37 cm of brickwork.
Styrofoam
Polystyrene foam is a material characterized by lightness and buoyancy. It is resistant to fire, but when exposed to fire it begins to melt. The material is easy to process and is not subject to infection by fungi and mold.
Polystyrene foam is obtained from foamed polymer raw materials: polystyrene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polyurethane. It consists of small identical balls that are fastened together. High-density rigid foam is used for insulation. The panels are easy to connect using rubber or epoxy adhesive.
The temperature range is not important for polystyrene foam, but the material is subject to mechanical damage.
Slabs 5 and 10 cm thick are used as thermal insulation. But, despite the structure, the material is sound-permeable.
Polystyrene foam is one of the most common materials for home insulation.
Mineral wool
Thermal insulation material consists of compressed fibers. Glass, basalt and slag are used as raw materials. The starting material is melted and spun into fibers. Their length is 2-60 mm. The air pores of the mats fill approximately 95% of the total volume. The product is easy to produce and has a low cost.
Mineral wool has many qualities suitable for home insulation.
Due to its porosity, cotton wool allows air and steam to pass through, maintaining air exchange. At the same time, it does not burn and is resistant to moisture, has good sound insulation. But the material has 2 drawbacks:
- contains phenol;
- Flying pieces of cotton wool, falling on human skin, cause itching.
Factors influencing heat loss
Thermal processes correlate well with electrical processes: temperature difference acts as voltage, heat flow can be thought of as current - there is no need to create a special term for resistance. The concept of least resistance, called thermal bridges in heating engineering, is also completely correct.
If you consider any material in cross section, it is quite easy to determine the path of heat flow at both the micro and macro levels. As the first model, we will take a concrete wall in which, due to technological necessity, the through fastenings are made with steel rods of arbitrary cross-section. Steel conducts heat slightly better than concrete, so three main heat flows can be distinguished
- From steel bars to concrete
- Through the thickness of concrete
- Through the steel bars
Heat loss through thermal bridges in concrete
The most interesting model is the final heat flow. Because the steel core heats up faster, the temperature difference between the two materials will occur closer to the outside of the wall. Thus, the steel not only “pumps” heat out itself, but also increases the thermal conductivity of the adjacent concrete masses.
Thermal processes in porous media proceed according to a similar pattern. Almost all building materials consist of an extensive network of solid materials, between which there is a space filled with air. Therefore, a solid, dense material is the main conductor of heat, but due to its complex structure, the path along which heat moves is larger than its cross-sectional area. Therefore, the second factor determining thermal resistance is the heterogeneity of each layer and the entire building envelope.
Reducing heat loss and shifting the dew point in the thermal insulation of external walls
Condensation hygrometer
As can be seen from the formula, it includes absolute humidity, with which we are already familiar, and saturated vapor density at the same temperature. The question arises: how to determine the latter value? There are special devices for this. We will look at condensation hygrometer
(Fig. 4) is a device that is used to determine the dew point.
Definition. Dew point
– the temperature at which steam becomes saturated.
Rice. 4. Condensation hygrometer (Source)
An easily evaporating liquid, for example, ether, is poured into the container of the device, a thermometer (6) is inserted, and air is pumped through the container using a bulb (5). As a result of increased air circulation, intensive evaporation of ether begins, the temperature of the container decreases because of this and dew (droplets of condensed steam) appears on the mirror (4). At the moment dew appears on the mirror, the temperature is measured using a thermometer; this temperature is the dew point.
What to do with the obtained temperature value (dew point)? There is a special table in which data is entered - what density of saturated water vapor corresponds to each specific dew point. It is worth noting a useful fact that as the dew point increases, the value of the corresponding saturated vapor density also increases. In other words, the warmer the air, the greater the amount of moisture it can contain, and vice versa, the colder the air, the lower the maximum vapor content in it.
Useful tips
Ventilation must be ensured in such a way that the relative humidity in the home does not exceed normal values (40%-60%). This requires an air flow from outside. In houses and apartments with natural ventilation, it should enter through the cracks in the windows.
But when you replace windows with sealed vinyl windows, there is no air flow. Ventilation does not work, even if the exhaust ducts are equipped with fans. This problem can be solved by installing window or wall valves.
Also make sure there is a gap under the inner door.
Relative humidity
To describe this perception, a quantity such as relative humidity
.
Definition. Relative humidity
– a value indicating how far the steam is from saturation.
That is, the value of relative humidity, in simple words, shows the following: if the steam is far from saturation, then the humidity is low, if it is close, it is high.
Relative humidity symbol
:
.
Relative Humidity Units
: %.
Formula for calculating relative humidity
:
Designations:
water vapor density (absolute humidity), (in SI) or ; density of saturated water vapor at a given temperature, (in SI) or .