One of the most important concepts in construction is dew point. At the stage of wall insulation, this allows you to correctly select the type and thickness of the heat-insulating material and create an optimal microclimate inside the building. There are several ways to determine the dew point. However, you also need to know what to do with the results obtained.
Nature of dew
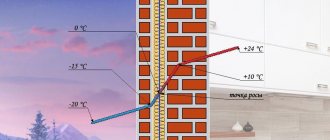
The nature of dew on the grass, as well as the appearance of moisture on windows, is the same even in buildings. Dew condenses from water vapor in the air when cooled to the dew point temperature.
How to look for a point - just imagine the simplified structure of the air. At normal pressure, the molecules are located at a relatively large distance from each other. Between them there is an empty space where several water molecules fit - that is, water
When air cools, it contracts, like any cooling body. The molecules move closer to each other and the distance decreases. The microcosm becomes crowded, so water is forced out of the volume. So, water molecules combine to form large drops - dew. Sometimes the drops are small - then fog forms. The dew point temperature is the level at which water flows out of the air - condensation occurs.
Nature of dew
Thus, at a given temperature, the maximum volume of dissolved vapor can be calculated. It turns out that for a certain temperature there is a maximum volume of dissolved vapor. Less remains in dry air, so condensation is impossible in such conditions. There is no more vapor than the maximum, because the excess is already beginning to fall into drip moisture. This process helps you understand how to draw up a project and properly organize insulation work in a specific room.
Air can be easily compared to an ordinary sponge: while the water is inside it, it is not visible, but when pressed with a certain force, you can see a different volume of liquid released.
At + 20 degrees, one cubic meter of air in a standard apartment with a normal microclimate contains approximately 15 g of water. No condensation is released because at a given temperature the air dissolves no more than 17.3 g of steam. But in the case of cooling the room, for example, to + 10 degrees, the maximum water content at the condensation point is 9.4 g of water. It turns out that 5.6 g of liquid will not fit in a cube. They will collect condensation on objects and materials.
Why does the foundation need to be insulated from the outside?
Many people think that it is easier to insulate the base from the inside, and in doing so they make a grave mistake. They insulate the basement from low temperatures, but at the same time do not save the material from which the foundation is made from the destructive effects of water and cold: when freezing, microcracks form in the foundation that has absorbed moisture, which gradually expand, and sooner or later the foundation begins to crumble and loses strength and reliability.
Insulating the foundation from the outside allows you not only to protect the lower part of the house from moisture, but also to protect the foundation walls themselves from freezing. At the same time, the dew point shifts towards the insulation, which is much more resistant to the harmful effects of moisture and low temperatures than concrete.
The essence of the term
The dew point in walls without insulation is located a little closer to the outside. The steam condenses, making the wall damp. In winter, when it is converted into water at the condensation interface, moisture accumulates only on the outer part.
If the walls were designed without insulation, the point in them is located a little closer to the outside. The steam condenses and moistens the wall surface. In winter, moisture accumulates at the joints only from the outside. And with warming, the moisture settled there should begin to evaporate. Here you need to take care to ensure a balance between the volume of incoming steam and its evaporation. The balance can be shifted further away from the room. To do this, choose one of two methods:
- reduce vapor permeability in the wall, reducing the volume of vapor;
- improve the ability of the external part to evaporate at the condensation interface.
Location
For single-layer walls, the vapor permeation resistance will be the same at any measurement location. The same applies to temperature. Condensation boundaries for proper design within it. This allows you to maintain a balance in removing moisture from any room except those where the humidity level is too high.
For walls with thermal insulation made from insulation materials with different vapor permeability and resistance values. The temperature is distributed unevenly. At the junction of layers there are differences. To achieve balance, it is necessary to ensure that the resistance to steam permeability decreases from the inside to the outside. Otherwise, the balance will shift and moisture will begin to accumulate in the wall.
Dire consequences
Did you insulate the walls inside when it was impossible? My sincere congratulations - you are a truly Russian person who first acts and then thinks. Do you hope it will pass? No! Unfortunately, you will now have to face the following problems:
- wet walls;
- wet thermal insulation material;
- musty aroma;
- dampness;
- mold;
- fungus;
- rot;
- peeling of facing raw materials;
- destruction of structures - elements in a wooden house fall apart very quickly;
As you can see, the consequences are very serious. Therefore, when insulating walls, you cannot neglect the advice of specialists and turn on the “Russian” option. True, if you don’t want the saturated steam to turn into water, which will happily settle on all kinds of surfaces in your home.
Finding the right place
When performing calculations, the thickness of the insulation is not taken into account the speed of air movement, pressure, or density. They only talk about approximate values, and this is actually not critical for the process of calculating the thickness of the insulation.
To determine the dew point, it is easier to use tables of approximate values; there is no need to try to independently invent something that has long been invented and systematized. Also, you should not trust various programs on dubious sites on the Internet. Sometimes they produce values completely randomly.
House without insulation
If the house is not insulated at all, then the location of the desired location corresponds to the weather conditions. When the climate in a given area is stable, without sudden changes in temperature, humidity forms outside the building. It's practically perfect. But during cold weather, the situation changes - the wall becomes the place where condensation is released, because the point moves to the inside. The current situation provokes constant humidity in the autumn and winter.
External insulation
With the correct calculation of the volume and good quality of the material for insulation purposes, the point ends up inside or slightly moves to the border with the wall. This is the only way the walls remain dry, regardless of humidity, temperature and changes in these indicators. The external part must be reliably protected from negative environmental conditions.
Insulation from outside
Internal
If the weather in a given area is changeable, with large temperature fluctuations day and night, then insulation inside is not the most suitable option. Against the background of stable weather, condensation accumulates between the center of the wall and the heat insulator, and when the temperature drops, it sharply shifts to their junction. Because of this, the walls will be partially wet.
With increasing temperature differences inside and outside, the condensate boundary shifts into the insulation material, so the walls will constantly remain damp. Internal insulation is carried out even in a humid climate, if it is possible to maintain a constant, equal temperature in the house.
Options for location of problem areas
Sometimes it can be difficult to decide how necessary thermal insulation work is. Before you start insulating the walls, you should use a special non-contact thermometer to find the surface temperature located at a distance of approximately 60 cm from the floor plane.
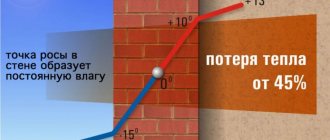
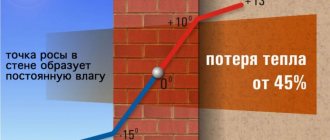
Now we need to compare the table value of condensation and the surface temperature. If the difference is more than 4 degrees, we can safely say that there is high humidity in the room, and the dew point is inside.
Example: air temperature is stable at 25°C and humidity at 45%. In this case, condensation forms in an area with a temperature of 12.2°C. When humidity increases to 65%, the dew point shifts to a warmer area, where 18°C.
Why is it so important to know the location of the condensation point? Because it determines which layer of the wall “pie” is exposed to the destructive effects of moisture. The worst option is when the insulation gets wet
Under such conditions, most thermal insulation materials lose their properties. They become deformed, allow cold air to pass through, rot, and lose their elasticity. Mineral wool is especially susceptible to these processes.
The dew point tends to shift, but most often there are three zones of its location:
- Closer to the outer surface of the wall. This option occurs if the wall is not insulated. The appearance of a problem area is also possible if the external insulation is of insufficient thickness.
- Closer to the inner surface of the wall. In the absence of insulation, condensation easily forms in this place during cold weather. Internal insulation shifts the area of condensation formation to the area between the wall surface and the insulation. With external insulation, this phenomenon rarely occurs if all calculations were performed correctly.
- In the thickness of the insulation. For external thermal insulation this is the best option. With internal insulation, there is a high risk of mold appearing in the room and, as a result, disruption of the microclimate.
- increase the layer of insulation on the outside;
- use material with high vapor permeability;
- dismantle the layer of internal insulation, moving it outside;
- adjust the microclimate in the room - install forced ventilation, additionally heat the air.
The appropriate option is chosen based on the climatic conditions of the region of residence, the design features of the house, financial capabilities and the building materials used.
Ignoring such a phenomenon as moisture condensation in the wall “pie” can be very expensive. At a minimum, this is an unpleasant smell in the room, constant dampness. As a maximum - large colonies of mold fungi, spoiling the interior decoration of the walls, destroying the insulation and harming the health of household members
Therefore, calculating the dew point is important if you want to build reliable and dry walls for your home
And the position of the dew point in the wall depends on:
thickness and material of all layers of the wall,
indoor temperature,
outside temperature,
indoor humidity,
humidity outside the room.
Further we will rely on these two concepts: the dew point and the position of the dew point in the wall.
Let's look at what happens to the position of the dew point:
in a wall that is not insulated at all;
in a wall insulated from the outside;
in a wall insulated from the inside.
Immediately, for each option, we will consider the consequences of such a location of the dew point.
Cotton wool gets wet, but polystyrene or EPS does not. But that doesn't change things. The result is mold and mildew on the walls. The time for the effects to appear is from one to three years.
- thermometer;
- a non-contact thermometer, which, by the way, can be replaced with a regular one;
- hygrometer.
Below is the algorithm of actions.
Step 2. Next, take a hygrometer and determine the humidity at the same point.
Step 3. In the table we gave above, find your value and then find out the cherished dew point.
Step 4. Then you should determine whether it is possible to carry out repair work in a building with similar humidity - for example, pouring a polymer floor or laying thermal insulation. To this end, take a non-contact thermometer and measure the temperature of any surface at the same point 60 centimeters away. In the absence of this device, you can take a simple thermometer, wrap it in a rag and take readings in about fifteen minutes.
Step 5. At the end, compare both numbers. If the surface is warmer than the air by more than 4? C, then the humidity is high and there is a possibility that the dew point is
If so, then thermal insulation work should be supervised by an experienced specialist who will take into account the thickness of the building material that will be used for this
Calculations
Depending on the location of the dew point - further or closer - the wall will remain dry or begin to constantly get wet. The condensate temperature corresponds to the following factors:
- humidity in the building;
- temperature in the building.
When the temperature is + 20 degrees, the humidity is approximately 60%, condensation falls on any surface with a temperature less than + 12. At a relative humidity of 100%, the point is equal to the actual air temperature. It turns out that condensation falls out everywhere.
Combined wall
At the construction stage, the insulation is built into the thickness of the wall and forms an indivisible whole with it. So, expanded polystyrene or other types of insulation, sometimes home-made, are placed inside, between the facing and rubble masonry. The use of insulation inside will provide:
- Moving the dew point to the outer surface of the wall.
- Reduced overall construction costs.
- Reducing the load on the foundation.
Search for a point
The exact location of the point depends on several factors:
- wall materials;
- outside temperature;
- room temperature;
- humidity - outside and inside.
The calculations are easy to do. Anyone who plans to insulate a house must first understand this issue. It is important to carry out the work according to the rules. The point is the temperature when steam turns into droplets, that is, condensation occurs.
The normal temperature in living rooms is + 22 degrees, closer to the floor it is usually a little lower, and near the ceiling it can reach + 27 degrees. In the central part of Russia, the minimum indicator for the environment is minus 15 degrees, short-term decreases to minus 20-25 are acceptable. In the southern regions, the maximum minus is 7, with a rare drop to minus 10-15 degrees.
Humidity in rooms is usually taken as an average value, but not a minimum - it is about 50%. But there is a certain reserve, because in winter the air is usually drier under the influence of active heating. This reduces humidity to 30-40%. Some owners actively resist this microclimate by purchasing devices to maintain healthy humidity and growing indoor plants.
In spring and autumn, steam flows through the insulation in the opposite direction - that is, from the street side. Because of this, humidity is taken as 90% for calculations.
Conditions to consider
Why can some people insulate walls from the inside, while others cannot? What kind of discrimination? The fact is that there are a number of factors that allow or prohibit interior wall cladding.
So, for example, you need to start from:
- mode of residence in the house;
- performance of the ventilation system;
- operability of the building heating system;
- the quality of insulation of all elements other than walls (ceilings, floors, windows);
- material and, accordingly, wall thickness;
- temperature conditions in the building and outside the window;
- percentage of humidity in the building and outside;
- climate and location of the house.
Based on the above factors, the following conclusion suggests itself. Insulation from the inside is quite likely if:
- mode of residence indoors – permanent;
- the ventilation system functions according to all rules;
- the heating system is manufactured correctly and functions properly;
- all structures are insulated and fully cope with the task;
- the wall to be insulated is thick;
- The region of residence is relatively warm.
In principle, before you start insulating from the inside, you should analyze all the “incoming data”, after which you can make a decision. But, as practice shows, out of 100 people who wanted to sheathe the walls from the inside, only 10 were able to complete the insulation without disastrous consequences. In the other 90 cases, the cladding must be done externally.
The importance of calculations
The air entering the street during the cold season becomes sharply supercooled and manifests itself as settling moisture. Any materials whose temperature is below the dew point become a surface. As a result, when the temperature outside decreases, the walls are constantly damp. This is a favorable environment for mold and pathogens, which then enter the air inhaled by a person and provoke dangerous diseases of the respiratory system, for example, asthma.
A building with damp walls will not last for a long time - it begins to undergo continuous destruction, which is constantly intensifying. Thus, it is important to make correct point calculations at the design stage. Then it is important to choose the right materials:
- for the construction of walls, their thickness;
- for insulation, their thickness.
They also determine the method of insulation - inside or outside. Be sure to select a method for organizing ventilation and heating systems in order to maintain an optimal microclimate - this is 18-23 degrees Celsius and 40-50% humidity.
The point at which condensation forms is easy to calculate yourself. To do this, it is enough to take into account the climate of the region. In addition, to obtain more accurate results, you can hire specialists from a construction company. There are always people there who do these calculations professionally.
Areas of application
There are many areas that take this temperature into account. One of the areas is aviation. During aircraft operation, condensation may form on some of its parts and freeze. This leads to freezing of the engine, metal structures of the flying vehicle and its breakdown.
In forestry, fire conservationists use dew point to calculate fire hazard class.
Experts calculate the likelihood of forest fires and develop protective measures.
Most often, determining the point is necessary in construction and agriculture.
Video: Dew point - insulating the house wisely
Construction
In construction, this value is determined when insulating the facades of buildings and private buildings. If you do not take into account the indicator or calculate it incorrectly, due to settling moisture, the wall finishing material will deteriorate or pathogenic flora and mold will appear.
Agriculture
In agriculture, experts determine the likelihood of damage to crops due to weather conditions, knowing the point and atmospheric humidity.
When cultivating new plants, breeders try to create varieties that condense moisture on the vegetative parts. Such plantings can exist with little precipitation.
How to display the dew point
Usually, if a house was built a long time ago and is actively used, but the walls are damp, we can conclude that it is time to think about changing the factors that influence the dew point. It will be necessary to increase the heating to reduce humidity or reduce the temperature difference between the coatings - that is, to make external thermal insulation.
In this situation, many people are wondering why insulation is needed from the outside. The answer is simple - it’s more convenient; the ambient temperature affects the thermal insulation, not the walls. The curve of temperature changes becomes flatter, and the actual location of the point moves to the edges of the insulation.
The thicker the layer, the greater the likelihood of displacement beyond the boundaries of the wall. As a result, carefully insulated walls will last longer and help save on heating costs.
Insulation from outside
Condensation during internal insulation
If there is no additional insulation on the walls, then there are several options for shifting the condensation point. It is located in the wall - closer to the street side or to the room. If it is close to the inside, the place of condensation moves inward. Then you can see small droplets on the surface. Surfaces that are not finished with insulation often get wet.
If the material of the building frame is cold, the point is on the inside of the wall. You will need to make some calculations and take care of thermal insulation, taking into account the climate of the area.
If the materials are chosen correctly, the thickness of the insulation is correctly calculated, the point falls into the thickness of the material and never moves closer to the room. This will keep you dry all year round. The weather damages only the insulation, and the wear rate of the partitions is noticeably reduced.
Insulation from the outside is reliable protection against condensation in the apartment. If the thickness of the insulation is insufficient or its thermal conductivity is not taken into account, then the condensation point will behave as it would without insulation. Moisture actively accumulates in the rooms. If this happens, then the problem can only be solved by increasing the layer of insulating material. There are 2 ways:
- Add an additional layer of thermal insulation.
- Change the material to a new one with the correct thickness.
If the thickness is too large, the point remains inside the insulation; no negative consequences will occur in any season. But the greater the thickness, the greater the material costs.
Calculation
Consequences of incorrect calculations
When choosing materials for insulation, remember that one of the effective ways to protect external walls from moisture is to correctly arrange the layers of insulation.
High-quality thermal insulation will help to significantly reduce heat loss and maintain comfort in the house, as well as extend the life of the walls
A dense layer that will not allow steam to pass through should be placed on the inside of the load-bearing wall, and a porous layer that allows moisture to pass through should be placed on the outside.
It is also necessary to create conditions for ventilation at the condensation point. In this case, the condensate will evaporate without obstacles.
A properly insulated external wall will help reduce heat loss during the heating season from 45 to 95% and create comfort in the house
Thermal insulation material
It is better to use thermal insulation that is installed outside the building. Usually this is polystyrene foam, penoplex, stone wool. There are several types of mineral wool insulation; they have good vapor permeability. Some of the moisture remains in the insulation and flows down under its own weight. The material does not deteriorate in any way, because fiberglass or basalt-based fiber is not affected by moisture.
Additionally, you can install a waterproofing layer at the bottom of the building to prevent destruction of the foundation. Penoplex is vapor-permeable, therefore, during the installation process, an air pocket is maintained to remove moisture from the material. If all installation rules are followed, the walls will remain in perfect condition longer, and the effectiveness of thermal insulation will delight you for many years to come.
Material options