Due to the long winter period, in most regions of the Russian Federation, in industrial and residential construction, pouring the foundation in winter is practiced. For individual developers who prefer to do all the work themselves to save budget, these technologies do not bring tangible benefits. The costs of ensuring the minimum possible strength gain of cement stone are increasing sharply.
How concrete gains strength
Concrete is an artificial stone. It consists of crushed stone, sand, cement, water and special additives. Crushed stone and sand provide strength, while cement and water form the “glue” that forms the monolith. Special additives make it possible to give concrete the necessary characteristics: rapid strength gain, the ability to lay in winter, frost resistance, and so on.
Concrete gains strength gradually; this process consists of two stages.
Grasping
– this is a loss of mobility of the solution. Its speed depends on the air temperature. For example, if it is +5 °C outside, the concrete will set in 15–20 hours, but the reference, or design, temperature is considered to be +20 °C. With it, setting occurs 1–3 hours after mixing the concrete mixture, that is, mixing all components with water. Before setting begins, you need to have time to place the mixture in the formwork, compact and level it.
Strengthening, or hardening
is the process of achieving a given strength by a concrete mixture. The optimal conditions for its collection are a temperature of +20 °C and a humidity level of 80%. The estimated period of “hardening” to brand strength at normal temperature and without additional measures is 28 days. Then the strength gain of concrete slows down, but does not stop growing throughout its entire service life.
Brand strength is an important characteristic of concrete. It is designated by the letter “M” and numbers from 50 to 1000 - the higher the index, the stronger the concrete. Physical and mechanical characteristics are determined by the selection of the composition of the concrete mixture, its water-cement ratio, as well as the quality of the components used: fillers, cement, water and additives.
The influence of temperature on the characteristics of concrete
Everyone knows that the solution hardens faster if the weather is warm, but the heat can have a detrimental effect on freshly poured concrete.
At temperatures ranging from 5 to 15 degrees above zero, the composition sets naturally, while the concrete releases heat into its environment. But on hot days this does not happen.
In such conditions, the concrete frame begins its formation with an even increased volume of material. When the temperature is lost, the surface gradually settles, and the formed crystalline structure creates obstacles to this process. Ultimately, due to the tension created inside, the foundation becomes covered with cracks in the fourth to twelfth hour from the moment the pouring is completed.
In order for the foundation to maintain its integrity at twenty-five degrees Celsius and above, it is necessary to use quick-hardening Portland cement to prepare the concrete, pouring it with water five to six hours after the end of concreting and shading it with available materials.
Slowing down of hydration is achieved by introducing plasticizing and modifying additives. Appearing cracks indicate that it is necessary to re-compact.
Why increase the water resistance of concrete?
The higher the water resistance of concrete, the less susceptible it is to water pressure, as well as the effects of chemically aggressive substances in the soil and groundwater: acids, alkalis, salts, and so on. The water permeability of concrete is negatively affected by excess mixing water, undercompaction of the concrete mixture and lack of maintenance of freshly laid concrete.
Water that has not entered into the hydration of cement (the so-called transformation of a plastic mass into a monolith) forms pores in the concrete after evaporation. Some of them are not closed and form end-to-end channels. Moisture penetrates through them into the foundation, which expands when freezing, which contributes to the further destruction of concrete.
To reduce the amount of mixing water while maintaining the mobility of the concrete mixture, plasticizers are used. They reduce the water-cement ratio, reduce the pore volume in concrete and increase its density. It should be taken into account that it is necessary to select the composition of a specific concrete mixture in laboratories, taking into account the features and characteristics of the materials used: cement, coarse and fine aggregates and various additives.
During installation, special attention is paid to compacting the concrete. The concrete mixture must completely fill the required space without creating voids. This is especially important with dense reinforcement of the structure. For these purposes, special devices are used - deep and surface vibrators.
The use of additives to increase frost resistance
Frost-resistant additives, which prevent water crystallization, make it possible to carry out winter concreting without the use of energy-intensive heating processes.
Today in the construction industry various types of additives are used to improve the quality of concrete and its hardening.
To ensure the desired effect it is necessary:
- study the manufacturer's instructions;
- analyze the compatibility of components with the materials used.
Independent use of additives does not cause difficulties for private developers.
How to care for concrete after pouring
In concrete with a low water-cement ratio, it is necessary to retain water, which is needed for the hydration process. If this is neglected, the quality of the final product will noticeably decrease. The standard concrete care regimen involves moistening the freshly laid foundation every 3-4 hours for the first 3-5 days after pouring, depending on the ambient temperature. Also, the concreting area is covered with damp burlap or film, and special film-forming compounds are used.
Features of pouring the foundation depending on the type
The pile foundation is poured in winter using technology that involves heating and insulating the concrete.
The pile type of foundation is well suited for land plots with soft, loose soil. Such a foundation consists of piles that are immersed in the ground and connected to each other by reinforced concrete beams or a slab. With this arrangement of the foundation, it is necessary to transfer its loads to harder soil rocks. The depth to which the piles are laid depends on the geological features of the site. The best option for installing piles would be soil that freezes to a great depth.
The advantage of metal screw piles is that this type of foundation can be laid in the cold season. The advantage of winter installation is the integrity of the grass cover on the construction site, which will delight the owners with its appearance in the spring. The piles are made of steel, which withstands cold well.
To properly install a pile-screw foundation in winter, you need to perform the following steps:
- make markings and start screwing the piles, having previously made small pits (if you make them to the depth of soil freezing, then screwing will be no different from summer);
- if the ground is very frozen and cannot be drilled, you will have to preheat it with a fire;
- add anti-frost additives to the concrete (the cost of these materials is significant, but you need little concrete for such a foundation, so a small amount of additive will be required).
Let's look at how easy it is to lay a screw foundation in winter:
- Open up the top frozen layer of soil.
- Screw the piles into soft soil.
Unlike a strip foundation, a screw foundation has the following number of advantages:
- time savings associated with the quick installation of screw piles (1-2 days of work);
- cost savings compared to strip laying in winter;
- the ability to use screw piles with large differences in height and in the presence of “difficult soils”.
It is also possible to build a strip foundation in winter using frost-resistant additives, but experts recommend constructing it in winter from ready-made concrete blocks, where the mortar is poured only into the connecting seams.
There is a solution for winter laying, depending on what type of foundation you want to build for your house.
What are penetrating additives
To increase the water resistance grade of concrete, mineral materials of penetrating or penetrating action are often used. They are added to the mixture during preparation or applied to a prepared surface, that is, cleaned of dirt and cement laitance, as well as a water-saturated surface using a plaster sprayer or brush.
Active chemical additives in the material react with the components of the concrete mixture. As a result, insoluble compounds or crystals are formed. They create a continuous barrier that prevents the flow of water. Depending on the type of concrete being processed, the degree of its waterproofness can be increased by two or three levels.
What happens if the temperature regime is not maintained?
If you are in doubt at what temperature is best to pour the concrete mixture, consult with experienced builders. If existing requirements for concreting at certain times of the year are not met, negative changes may occur to the concrete base of the building:
- cracks will appear. As a rule, they are formed at temperatures exceeding twenty degrees Celsius, unless the uniformity of moisture drying and the process of hardening are controlled. As a rule, the poured base is covered with a film and periodically moistened;
- Microcracks form inside the foundation. At what temperature in spring and at what autumn does this happen? If the air does not warm up above three degrees Celsius, the water begins to transform into ice, increasing its volume. Then it dries, leaving behind microscopic cracks that contribute to the destruction of the concrete base;
- displacements are observed. When frozen sand or gravel is used to mix a concrete mass, pieces of ice get into the mass, forming void areas. Under the influence of the maximum load, the foundation base shifts;
- tension increases. The reinforcement frame of the future foundation, welded at a negative temperature, will expand in volume in warm weather and create increased stress on the structure, leading to emergency situations.
What to look for when concreting a foundation
In order to competently carry out construction work and reduce further costs of repair and operation of the foundation to a minimum, you must adhere to a few simple rules:
- The foundation design should not allow cracks to form under any load.
- The entire volume of concrete must be poured without technological and “cold” joints, that is, in one technological cycle.
- If the work involves the formation of technological seams, they must be sealed using swelling cords, sealants or waterstops.
- Working reinforcement must be installed in strict accordance with the design; the thickness of the protective layer of concrete must be at least 15 mm.
- It is necessary to compact the laid concrete with vibrators or use self-compacting concrete.
- Newly laid concrete needs to be maintained.
Are there any advantages to winter concrete work?
In general, working with concrete in harsh conditions of low temperatures entails additional difficulties, but it is impossible to stop construction for six months every time autumn comes, and besides, winter work also has significant advantages:
- Winter discounts on building materials and the decline in demand for labor make it possible to save money.
- In winter, foundations can be concreted on weak or brittle soil.
- Frozen access roads make it possible to easily deliver heavy equipment and materials to a construction site.
What time of year is best to pour the foundation?
Difficult weather conditions negatively affect the strength gain of concrete.
Abundance of precipitation
at the stage of setting the concrete mixture can lead to its saturation with excess moisture. This leads to an increase in the water-cement ratio and a decrease in the strength of concrete.
Frost
turn mixing water into ice, which disrupts the hydration process of cement. When water freezes, it expands and internal stresses arise in the freshly laid concrete, which leads to damage to the foundation.
High air temperature, low humidity and wind
increase the rate of water evaporation from freshly laid concrete. This leads to disruption of the process of cement hydration and destruction of concrete in the surface layer, the appearance of shrinkage cracks.
Based on this, and also taking into account that the process of concrete gaining strength lasts 28 days, the optimal time for pouring the foundation is the period from late spring to early summer.
In addition to the advantage of comfortable conditions for carrying out work, there will be enough time ahead to eliminate possible defects, arrange waterproofing and additional protection. As a result, a foundation built in the spring will not be afraid of autumn temperature changes and winter frosts.
Concreting techniques in winter conditions
The main condition for the correct pouring of concrete at subzero temperatures is the preservation of heat sufficient to ensure strength gain. Popular methods of laying mortars in winter:
- Preheating of the mixture being prepared;
- Installation of reliable thermal insulation and maintenance of the solution;
- Electric heating of concrete poured into formwork;
- Addition of special additives that reduce the freezing point of water and accelerate hardening.
Thus, it is possible to concrete outdoors in winter without loss of strength indicators, but for this you need to adhere to the chosen methods. In terms of costs, the use of heat guns is the most unprofitable option; the cheapest method is the addition of additives. Electric heating and thermal insulation are intermediate options.
Temperature increase during kneading
To pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures, the components are heated. The fillers are heated to 55-60⁰С, and water is supplied to the solution at 90⁰С. Cement is heated to room temperature before adding, otherwise it loses its bonding properties. Before laying, the temperature of the solution should not be lower than 35⁰C.
When mixing, you need to use a concrete mixer, into which heated water is supplied first, then fillers, and only then cement. When pouring such a mixture, the thermal energy of the monolith is enough to gain critical strength, taking into account the fact that additional heat is released during cement hydration.
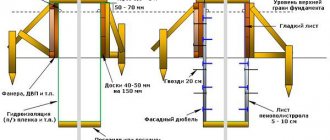
Heating and insulating the solution
At very low temperatures, the heated mixture requires additional insulation or heating. It is more economically feasible to insulate using inexpensive heat-insulating materials that do not require additional energy sources. The concrete surface is covered with hay or straw, old rags, peat, film or heat-insulating blankets are used. Sometimes so-called “warmhouses” are set up, similar to greenhouses.
If you concrete at temperatures below -5⁰С, additional heating will be required. The following technologies are used for this:
- Heating with heat guns or stoves under greenhouses. This is a costly method that requires constant additional moisture. Suitable for areas without electricity.
- The use of thermomats powered by electricity. They are laid out on the surface of the poured concrete and connected to a power source. Requires a large amount of electricity. Infrared emitters are installed above the poured surface or around the formwork; the intensity and direction of heating is regulated by reflectors. Suitable for vertical and inaccessible structures.
- To warm up a concrete area, special cables or electrodes are used through which electric current is passed. The technique is convenient to use, but requires large amounts of electricity. Installing an electrode system is more expensive because the resistance of the solution, which itself is a conductor, increases as it dries.
Introduction of additives
Improving the characteristics of the solution with special additives is the most convenient and economical method of filling the solution in winter. By using it in conjunction with heating, you can speed up work and improve the quality of concrete. There are two main types of additives for pouring concrete mortar in winter:
- Compositions that reduce the freezing point of water. The solution hardens for quite a long time, but the water does not crystallize, so the quality of the concrete does not suffer. To speed up the reaction, thermal insulation is required. For this purpose, calcium or sodium salts and potash are used, which prevent water crystallization.
- Additives that increase the rate of hardening of the solution. They reduce the time necessary for concrete to gain critical strength, so the water in the heated mixture does not have time to crystallize. Calcium nitrite-nitrate, the same potash, calcium salts mixed with urea are used.
The amount of additives depends on the temperature range in which the concrete structure will be poured. From -5 to -10⁰С, up to 5-8% by weight of cement is added. With a decrease in temperature to -15⁰C, the concentration is increased to 10% by weight of the added cement, and at -25⁰C, at least 15% of additives must be added.
How to pour a foundation in winter
If it is still necessary to concrete the foundation in winter, several technological methods are used.
Antifreeze additives and hardening accelerators
– they allow work to be carried out at sub-zero temperatures without loss of speed and quality.
Heating concrete with an electric cable
– it is attached to the reinforcement frame and connected to the network, and then remains in the body of the concrete.
Warming up concrete with heat mats
– unlike cables, mats are installed on the surface of a heated structure and can be used repeatedly.
Arrangement of the greenhouse
− this is a structure similar to a greenhouse, which is assembled above the work site. Heat guns are installed inside to maintain positive temperatures, so in the “warmhouse” you can safely carry out foundation construction work: knitting the reinforcement frame, concreting, installing waterproofing and installing waterstops.
Filling an armored belt at sub-zero temperatures
The reinforcing belt is designed to evenly distribute the load from the upper rows of masonry to the lower ones. It seems to connect the entire structure into a single whole. which significantly increases its overall strength and durability. The armored belt is made from steel rods laid around the perimeter, which must be welded together into a single structure.
When constructing a structure from gas silicate blocks, a reinforced belt is especially important. Such blocks quickly crack at the slightest movement of the soil or during shrinkage of the base. When installing a roof on such blocks, an armored belt is also necessary, since it is impossible to attach the timber to the blocks - they can crack. To avoid deformation of the walls and the building as a whole, a welded reinforced belt is simply necessary. It is welded into a solid structure, laid on top of the masonry and filled with concrete. It is sealed with mortar on both sides so as not to disturb the thermal insulation of the walls. Concreting of the belt is allowed in the cold season only using the above methods.
Working with concrete mixture at low temperatures is allowed in cases where there is no other option, because the optimal hardening temperature of the mass is from +5 degrees to 25.
Bottom line
The optimal time for pouring the foundation in most regions of Russia, except the northern ones, is the second half of spring or early summer. During this period, the optimal weather for concreting work is established. Here are the main points to pay attention to when conducting them:
- Entrust the work of decoupling the reinforcement frame and concreting to a specialized organization. This way you will avoid mistakes, the correction of which can be very expensive.
- Use only ready-mixed concrete of appropriate strength and water resistance grades. Methods of preparing concrete on site in a metal bath and using shovels are strictly unacceptable.
- Carry out concrete work without forming cold joints.
- Increase the water resistance of concrete using special additives. For example, penetrating.
- Freshly laid concrete needs to be maintained. Cover it with damp burlap and water it every two or three hours, even at night, for 3 to 5 days. If the weather is hot, it is better to water within 7 days.
- Carry out foundation work in winter using special methods.
- If possible, check the thickness of the concrete cover using a rebar locator. It must be at least 15 mm.
- Additionally, protect foundation structures from the negative effects of soil and groundwater.
Advantages and disadvantages
We propose to understand the pros and cons of building a foundation in winter.
Benefits include:
- convenience of preparing a pit or trench in an area where the soil composition does not hold its shape well in the warm season;
- during the winter season, building a foundation in the North is a completely justified decision;
- acceptable cost of materials for which demand temporarily falls;
- availability of free time.
Unfortunately, there are also certain disadvantages. If in the summer it is possible to prepare a trench with your own hands, then in the winter season it becomes necessary to use special equipment to cope with frozen soil. The risk of purchasing low-quality building materials that suppliers were unable to get rid of during the season increases. Added concerns about how to preserve the foundation for the winter.
What is the difference between concreting in winter and summer?
The pouring process and methods of maintaining the properties of the solution in winter are more complicated. In the warm season, it is often enough to mix the components taking into account the proportions, prepare the formwork and reinforcing frame, and pour the mixture. Under normal conditions, strength gains occur in a shorter period of time:
- setting: this period lasts up to 24 hours, a thin layer of hydrosilicate is formed on the surface, at the same time the outer layers become denser;
- hardening: over the next 4 weeks, the mixture gains strength, after which further laying of building materials for the construction of walls becomes possible.
When it's frosty outside, the setting and hardening time increases. In addition, concreting in winter requires the use of special grades of cement:
- M200;
- M250;
- M300;
- M350;
- M400.
They are used under different conditions, but if the question of how to concrete in winter is being decided, then the indicated grades are the minimum acceptable for the construction of houses of a certain type.
For example, the foundation of a brick house in winter can be concreted with a mixture based on the M350 or M400 cement brand. More is possible, but not less.
In addition, in winter, before pouring the solution, auxiliary components are always added - special modifiers that improve the properties of the material. In case of mild cold weather, the covering method and insulation of the massif are sufficient. The stronger the frost, the more heating agents are used.
Monolithic slab before pouring
Dependence of design strength on the degree of exposure to cold
When concreting is carried out in cold weather, attention is paid to the critical strength. Once the set value is reached, the cold has less effect on the material. This value is 50-70% of the design strength.
Peculiarities:
- if the concrete hardened in winter before the minimum critical strength was achieved (50% of the design strength), it cannot be used;
- when the massif has already crossed the threshold corresponding to the critical strength, a slight loss of properties by the material is noted (a decrease in the actual indicator to 10%);
- achieving 70% of the design strength allows you to obtain a material with excellent characteristics.
The most common methods of concreting in winter
Some of the heating methods above are used more often than others. This is due to the high speed of achieving the desired result under given conditions in the winter months:
- heating during the mixing stage;
- application of the “thermos” method;
- use of electrical appliances.
When different methods of winter concreting are considered, it is taken into account that almost all of them require the use of anti-frost additives. The exception is those options that are based on the natural process of preserving the properties of the solution.