A foundation on clay causes many difficulties during construction, especially when groundwater is close to the ground. Clays saturated with water are record holders for the strength of frost heave. Foundations and all other underground structures on clay are affected by these forces, causing serious deformations, cracks, failures and destruction. Of course, mostly in cases where a clay foundation is designed with errors and without taking into account the influence of foundation soils.
What type of base to choose
As a rule, a strip foundation from different materials or a columnar base is made for a log house.
The specific type is determined based on the results of a soil study for its composition and basic properties, as well as according to the level of groundwater flow. Therefore, before planning to build a house, it is better to contact a company that provides geodetic services. The company’s specialists not only determine the characteristics of the soil, but also recommend the type of foundation, as well as materials for its manufacture.
You still need to know for yourself when it is best to use which foundation for a log house on a certain type of soil:
- The strip base, usually made of reinforced concrete, is mainly used on very wet soils or soils with high groundwater levels, such as peat or marshy soils.
A variant of a monolithic strip foundation for a wooden cottage. Such soils mainly consist of soft, fertile soil. In this case, the depth of the foundation depends on the weight of the structure; the heavier the house, the more solid the foundation must be used. And also on the presence or absence of a basement. - In addition to reinforced concrete, a strip foundation for a log house can be made from brickwork, however, this option is quite expensive and is therefore not used often.
- If the soil contains sand, clay or loam, as well as rocky inclusions, in principle, any type of foundation can be installed.
However, there are some limitations to the columnar base. If there are large fragments of rock in the ground, there is a high probability of encountering such an area when drilling a well. And since all work is carried out, as a rule, manually, it is unlikely that it will be possible to break through the rocky rock. Columnar foundation for a log building - A columnar foundation for a log house is mainly used on dry, densely structured soils that are not subject to movement, and soils with a large amount of sand.
Briefly about the main thing
It is impossible to unambiguously recommend one or another foundation on loam - which is better and which is not suitable at all - without accurate information about the characteristics of the soil at a specific construction site. Soils with a high clay content are considered the most problematic when choosing and constructing a foundation that needs to be stable and able to withstand vertical and lateral loads. But now you know what types of foundation you will have to choose from, and you will be able to demand that the contractor strictly fulfill the design requirements.
| Additionally The exhibition of houses “Low-Rise Country” expresses sincere gratitude to the specialists for their assistance in creating the material. (Royal Pile Factory) – expert in pile foundations. If you need more detailed advice, you can use the following contacts: website: kzs.ru email: tel.: 8-800-222-76-17 |
Ratings 0
Read later
Types of clay soils
Before determining the type of foundation, it is necessary to clearly understand what type of soil the construction will be carried out on.
Loams are widespread in central Russia
Depending on the amount of clay content, soils are of the following types:
- sandy loam is a loose rock containing sandy and silty components in combination with 5-10% clay;
- loam - soil in which the clay component is represented in an amount of 10-25%, and the rest is sand;
- clay is a fine-grained sedimentary rock with a high percentage of clay substance from 30%.
The main distinguishing characteristic of clay is its weakness to moisture, due to which it quickly turns into a dough-like mass and prevents further seepage of liquid into the soil. The layers of the studied rock can be located at a significant depth, which increases the risk of soil swelling in winter due to the freezing of stagnant water.
Installation of strip base
When constructing structures on sandy loam and loamy soils, which are characterized by a low level of groundwater, a strip foundation is an ideal solution. The presented base is a reinforced concrete strip installed under all load-bearing structural elements. Arrangement of this type of house support allows you to subsequently create a basement and basement, as well as an underground garage.
Execution of work
Marking the area for a strip foundation
The construction of a strip foundation for a house involves the following operations:
- Transferring markings from a sketch to a section. Along the perimeter of the stretched signal ropes, it is necessary to make a pit with a depth exceeding the soil freezing level. In some areas with harsh climatic conditions, this figure can be from 1.5 to 2 m. The width of the pit is set based on the dimensions of the foundation with a margin of distance for the future placement of waterproofing, thermal insulation sheets and the facade layer, if they are implemented.
- The bottom of the prepared pit is leveled and a gravel-sand mixture is sprinkled into a layer thickness of 15-20 cm, followed by compaction.
- The walls of the pit are covered with waterproofing, which can be used as ordinary rolled roofing felt.
- The bottom is filled with a 5-7 cm layer of concrete and a supporting substrate is formed (drying time from 10 to 15 days depending on the ambient temperature).
- Installation of formwork with reinforced mesh placed inside the gutter.
- We are pouring concrete. The pouring process is carried out in portions, 20-25 cm of concrete with its uniform distribution until completely filled.
- After waiting for the hardening period, which usually takes about 3-4 weeks, we begin waterproofing work.
If the base is left to shrink over the winter, the concrete structural elements are covered with plastic film or any available means of protection.
Tape base is one of the most common types
The advantages of this method are:
- uniform load distribution due to the large support area;
- practicality and durability;
- Possibility of equipping a basement or basement.
Flaws:
- significant time and labor costs;
- inflated cost of materials;
- Possibility of implementation exclusively on sandy loam or loamy soils.
Construction cost
The average cost of shallow tape is 15,000 rubles per 1 m³. Or 3,000 rubles per 1 linear meter. The price includes:
- excavation;
- sand cushion (200 mm);
- formwork installation;
- arrangement of reinforcement frame;
- pouring concrete;
- removal of formwork;
- concrete grade B25;
- fittings with a diameter of 12 (3 bundles of 4 pieces);
- formwork;
- sand;
- cleaning the area;
- delivery.
Scheme of a shallow strip foundation.
The price varies from 3,000 to 18,000 rubles per cubic meter. m. The price is based on the structure of the building that will stand on it. A light structure (wooden or frame house, foam block garage, etc.) requires the cheapest foundation, and if it is a two-story brick or concrete house with a reinforced concrete floor, then the cost will be maximum.
During construction the following work is carried out:
- Excavation – 1100 rub/m³.
- Installation of a sand cushion (200 mm) – 900 rubles/m³.
- Monolithic work (tying reinforcement, installing formwork, pouring concrete with a mixer) – 5,200 rubles/m³.
- Concrete grade B25 - from 3,500 to 4,5000 rubles/m³.
- Fittings – 32 rubles per 1 linear. m.
- Sand for a pillow - from 3,000 to 4,500 rubles per 8 m³.
Video description
The following video will show you how to install driven piles:
- bored, formed directly on the construction site by drilling deep wells around the perimeter of the future house. The bottom of each well is covered with a layer of crushed stone, large-section asbestos or metal pipes are lowered into it, a reinforcing frame is installed in the pipes and they are filled with high-grade concrete with mandatory compaction with an in-depth vibrator;
To install the grillage, reinforcement is released from the piles or embedded fasteners are installed in the concrete that has not yet hardened Source himmashstroi.ru
What foundations can be built
Subject to the recommendations of SP 22.13330, even on highly intumescent soils, the construction of any type of foundation is allowed. In shallow-depth options, it is necessary to increase the thickness of the underlying layer. The pits of deep strip foundation pits and columnar foundations should be filled with inert materials that do not contain clay by default. In low grillages along the pile heads, there must be a technological gap of 20–40 cm between the ground and the beams, protected on the sides by sheet materials.
Slab foundation
The advantage of a floating slab is the largest possible support surface. Load-bearing capacity is provided by default; this design copes with uneven heaving forces without problems. However, the construction of a slab foundation on clay should be supplemented with several measures:
- underlying layer of sand, crushed stone (at low and high groundwater levels, respectively);
- ring drainage from a corrugated pipe perforated with slots in geotextiles;
- insulation of the blind area to a width of 0.6 - 1.2 m.
Heat loss through the slab, which is also a floor on the ground, is inevitable. However, this allows you to maintain positive temperatures under the entire sole. A horizontal layer of extruded polystyrene foam does not allow the clay soil adjacent to the house to freeze; drains remove moisture.
There is a modification of the slab foundation USHP (insulated Swedish slab), in which polystyrene foam is laid under a reinforced concrete structure. The USHP has a heated floor contour in the upper part. In this case, there is no heat loss through reinforced concrete. However, the insulation retains the geothermal heat of the subsoil; freezing under the house is also impossible.
Strip foundation
If the customer needs a usable basement floor, the choice of a recessed strip foundation is made by default
In this case, it practically does not matter whether construction is carried out on clay or sandy soils. There is no swelling under the sole at depths below freezing
The underlying layer has a minimum thickness of 20 cm and serves solely to level the bottom of the pit.
However, the deep-laying tape has a huge area of external surfaces:
- In winter, swelling soil presses on the underground walls from all sides;
- the interior does not allow for internal backfilling to compensate for soil pressure.
Therefore, the tape is made wider (from 40 - 60 cm), the pit sinuses are filled with sand, crushed stone, and ASG to provide a layer of at least 40 cm near the load-bearing structures.
In shallow-depth MZLF tapes, on the contrary, the area of the side faces is minimal, and tangential swelling forces are practically absent. But the uneven heaving of the soil under the sole is clearly expressed. Therefore, the construction technology changes somewhat:
- high-quality drainage at the level of the sole of the MZLF;
- insulation of the blind area + thermal insulation of the outer edges of the tape (base);
- increasing the thickness of the underlying layer to 60 - 80 cm under the concrete.
There are several reasons for this:
- a trench with non-crumbling sides can be dug exclusively in clay;
- It is impossible to make perfectly smooth walls in the ground, so the engagement with the soil will be maximum;
- During freezing, serious pull-out loads will inevitably arise.
In addition, when pouring into a trench, it is more difficult to ensure the tightness of the waterproofing layer. When laying reinforcement cages on a film laid in a slotted foundation, punctures and tears are inevitable. In this case, you can use extruded polystyrene foam as permanent formwork by securing it to the walls of the trench (suitable only for clay soils, since other soils can easily crumble at the most inopportune moment).
Pile foundation
The ideal option for complex geology and terrain of the site is the construction of a pile-grillage foundation. Regardless of the composition of the soil, the piles penetrate through heaving, unstable horizons and rest on a layer with a high bearing capacity.
Types of foam block foundations
- Tape;
- Monolithic;
- Columnar;
- Pile.
These are variations in the arrangement of the foundation, based on the use of foam blocks. Note that one of the most rational and correct decisions is to create a high-quality strip foundation, which can be:
- Reinforced concrete;
- Recessed;
- Shallow.
It is quite obvious that before laying the foundation, the area will need to be cleared. Next comes the planning process. If you find moles on the territory of a land plot, you can find out how to deal with them on the website
Columnar foundation
One of the most rational solutions is the use of a columnar foundation, which is based on high-quality materials, as well as on an additional reinforcing belt made of durable reinforcement. Such a foundation can last quite a significant amount of time, while for clay soil, a columnar foundation is the most rational and correct solution.
Pile foundation
Among the many variations of foundation arrangement, the pile option can be considered the most unique and correct. The whole point is that a pile foundation can be installed on any soil, while obtaining high quality, prospects for endurance, strength and reliability.
Today, many unique methods of arranging this type of foundation have appeared based on the use of the following piles;
- Rack piles;
- Screw piles;
- Hanging piles;
- Piles with reinforced concrete grillage.
Which clay foundation is better?
So, in order to decide on the type, you need to know:
- Soil type
- Soil moisture.
- Ground water level.
- Soil freezing level.
Do not try to determine all these parameters yourself; this is only for geological engineers and laboratory workers.
It is possible to build different types of foundations on the same soil. This depends on the planned load on the soil and the presence of a basement. In any case, when planning large loads, a strip foundation with a recess is used.
To build a house, two main types of foundations are used - strip and tile, as well as their varieties. The strip foundation type is budget-friendly, but also less reliable. It is suitable for small structures, preferably made of wood. The slab foundation is one of the most reliable. On the basis of such a foundation, a house of any size can be built.
In the case of clay soils, a slab foundation is most often used. It is quite expensive, but on heavily clayey soil any other foundation is unsuitable. The slab foundation is made in the form of a concrete monolithic slab, due to which the load is distributed evenly over the entire area. Clay soils often float. If there is a slab foundation, it deforms along with the soil, which prevents cracks from appearing in buildings. Sand and gravel must be poured under the concrete slab.
Which foundation is better to choose for a house made of timber on clay soil? An excellent option for wooden houses is a strip foundation, since it is quite reliable and inexpensive.
Which foundation is better for a house made of aerated concrete on clay soil? Aerated concrete is a lightweight material, for which, just like for a house made of timber, a strip foundation is perfect.
A slab foundation is also suitable for loam or sandy loam if the groundwater level is not deep. In this case, if the level of hard rock is not deep, piles are driven into them so that a small part of them is above the foundation from above.
Thanks to this, the foundation on clay is better secured. Unfortunately, if this technology is used, then having a basement is impossible. The piles must be tied with timber or channel bars. The first option is applicable for wooden buildings, and the second – for buildings made of stone or foam concrete.
Foundation deformations. Main causes, solutions and prevention of the problem
The main factors that influence the deformation of the foundation are divided into external and internal in relation to the soil. External ones include: the impact of groundwater and lateral pressure. To the internal ones - soil heaving.
Subsidence. One of the most common deformations that occurs due to soil erosion by groundwater. Washing out can occur not only under the foundation, but also at a considerable depth from it. Groundwater does not flow in voids; it seeps through sandy rocks. They can be either cemented or uncemented with natural cement. If it is just unconsolidated sand, then the probability of washing out is high, and under high pressure this area can sink.
Lateral pressure. It occurs when the foundation is deep and entails the appearance of significant cracks, both in the foundation and in the building itself. The solution is to construct the foundation in such a way that it expands upward. Thanks to this, the pressure from the side will be minimal.
Heaving. A very common phenomenon in permafrost areas. It was thanks to heaving that the concept of a “hut on chicken legs” arose. In such an area, in order not to expose the building to danger, all structures are erected on legs. Although, this phenomenon can also be observed in areas with a normal climate, if the foundation lies above the soil freezing level. When water freezes, it increases in size, causing the soil to also increase in size. This is called heaving. This problem can only be solved by insulating the soil with special materials. This factor should not be ignored, since it entails the appearance of large cracks in the house and its gradual destruction.
Remember, in order to decide on the type of foundation, first of all you need to know the characteristics of the soil. These characteristics are obtained exclusively through geotechnical research and laboratories. Determining the type of soil and the level of groundwater is dangerous for the strength of the future structure.
Creation of a drainage system
If the groundwater level is high, especially if it is located above the freezing level, it is recommended to carry out drainage work before laying the foundation. They consist of forming trenches filled with gravel or a system of pipes with holes located in the ground at a slope around the future structure. Such drainage will ensure the removal of water from the foundation.
Types and types of clay soils. Main characteristics
Clay soils are classified as cohesive soils, while sandy soils are classified as non-cohesive soils. Cohesion is the ability of soil not to crumble in both wet and dry conditions. Depending on the granulometric composition, cohesive soils are divided into:
- Clays. The fraction is no larger than 0.01 mm with a percentage by weight of at least 50%.
- Loams. The fraction is not larger than 0.01mm with a percentage of 30-50% and the presence of a fraction larger than 0.01mm up to 70%.
- Sandy loam. The fraction is no larger than 0.01 m with a percentage of less than 30%.
- Loess. Fraction 0.002-0.05mm, content of clay particles 5-30% with porosity 40-55%.
For building a foundation, clay is best, loess is worst. Moreover, these soils are not always in a “clean” state. For example, loess-like loams are widespread.
An extremely important parameter that greatly influences the bearing capacity of cohesive soils is the consistency index. It depends on water saturation and is measured in fractions of a unit. The lower the value, the harder (drier) the soil.
Indicators of consistency of cohesive soils.
Types of soil mixed with clay
- Clay refers to soil in which at least 30% clay predominates.
- Loam is characterized by no more than 10% clay in the soil.
- Sandy loam contains from 5 to 10% clay.
There are also glacial clay and alluvial clay. The first type of this material is characterized by excellent load-bearing capacity. It is characterized by high strength under significant concrete loads.
But this ability is preserved only if it is deep.
Alluvial clay can be found near bodies of water. Due to its high plasticity, one should refrain from building on this site. It is not suitable for a foundation. Otherwise, it may soon float, which will cause cracks on the walls of the house.
As a last resort, building a house on stilts is allowed.
Heaving soils - choosing a foundation
For the construction of load-bearing structures of any building on moving soils, the following types of foundations can be considered:
The organization of an expensive slab base will be effective for brick or heavy wooden structures that occupy large areas. It is predominantly of regular square or rectangular shape, but if necessary, complex perimeter figures are also designed;
Universal slab foundationSource keysdom.ru
- Pile - screw or reinforced concrete. Here, too, you need to know exactly the depth of freezing of the soil in order to place the piles below this mark. Effective for the construction of small buildings in marshy and watery areas. A special reinforcement frame is constructed on the surface of the piles, which is filled with a composite mortar just below the soil level.
- Columnar. It is used only for light and ultra-light commercial buildings, has a shallow depth and is not considered as a foundation for a residential building.
- Concrete strip foundation buried below the frozen soil level.
- Less expensive and in demand is a shallow or non-buried strip foundation on heaving soils. It must be used very thoughtfully, having previously calculated all the loads in order to eliminate the influence of heaving forces.
Strip foundation is the most familiar option for many, which “takes root” on many types of soil. Source pinterest.com
The type of base chosen will depend on the size and shape of the building, the arsenal of equipment used, as well as the financial capabilities of the customer.
Modern TIS technologies involve the use of support-column elements connected by a grillage. To organize such construction, special equipment and electricity are not used, it is possible to hide communications and minimize the slope of the construction site. A similar technique is relevant for frame, stone or brick construction.
Slab reinforced concrete load-bearing structures, which are effective for arranging a low base and are applicable in the case of a simple building structure, can also resist freezing.
The use of a strip foundation involves the installation of a construction reinforcing strip along the perimeter of the building and in the area of construction of load-bearing walls. Such developments are less expensive, however, they are superior in reliability to the above options.
Pile type foundation
Often applicable options for making a foundation on clay soil for a house using pile technology are the pile-tape or pile-grillage type. In all respects, the presented methods are similar to making a columnar brick foundation.
During the calculations, the permissible load is determined for each pile. Depending on the depth of placement and the weight of the future building, the following types of piles are used in practice:
- screw (by screwing in screw piles, you can bypass clay layers of soil and build a foundation on harder rocks; the installation process is carried out both manually and through the use of special equipment);
- bored (installed directly on the site of the house: a recess is dug or drilled, a sand cushion and a waterproofing layer are installed, asbestos pipes are placed, inside which the reinforcing mesh is laid, and they are filled with concrete);
- driven (installed by using drilling machines).
For small houses, piles are placed along the perimeter of the load-bearing walls, and in the case of the construction of massive buildings, pile supports are mounted at the closest possible distances along the perimeter of the entire grillage part.
Subsequently, reinforced concrete beams or slabs are laid on the piles, which will evenly distribute the total weight of the structure onto each of the supports.
Pile foundation is excellent for unstable soils
Advantages:
- practicality and long service life;
- resistance to significant loads;
- relatively low financial costs;
- quick installation;
- possibility of repeated use of pile supports;
- installation can be carried out in any natural conditions.
Flaws:
- inability to equip the base and basement without additional excavation work;
- the need to attract special equipment;
- susceptibility of piled structural elements to corrosion processes.
We recommend watching a video showing in detail the installation of pile foundations.
Base requirements
To avoid foundation deformations, it is necessary to have information about the reasons for their occurrence. The main ones are:
- drawdown;
- bulging;
- displacement with shift.
The reason for foundation subsidence is the discrepancy between the actual supporting area and its norm. The occurrence of buckling and lateral shear is associated with incorrect foundation depth when the foundation is exposed to frozen soil.
Which clay foundation will best withstand all loads, taking into account horizontal and vertical vibrations when the soil freezes? There are not many requirements for such a foundation:
- it is prohibited to lay a foundation made of block elements;
- mandatory use of a reinforcing frame over the entire area;
- the presence of a wider sole (when compared with the upper part of the foundation);
- use of material for waterproofing the sole.
Scope of application of strip foundations
The easiest way to deal with heaving soils is to install a pile foundation below the freezing mark. If it is impossible to carry out such construction, an alternative solution is shallow foundations, which will require significantly smaller volumes of building mixtures, amounts of reinforcement and labor costs.
It is effective to use shallow burial technology when groundwater is located at a depth of more than 1.5 m. Ribbon structures on steep slopes, where lateral pressure must be taken into account, make it possible to compensate for the uneven impact of soil movement in the longitudinal and cross sections.
The foundation on heaving soils is suitable for the construction of frame and timber buildings, the use of foam concrete and aerated concrete materials. If it is necessary to construct a shallow foundation or build powerful structures on soft soils, strip foundations are a priority. Such construction methods are applicable for clay and sandy loam soils, loose rocks, as well as water-saturated surface layers.
Strip base of a house with a brick plinthSource domastroim.ru
Criterias of choice
Scheme of a columnar foundation.
In order to choose which type is suitable for clay soil, the specific characteristics of the soil are first determined, such as:
- specific gravity of clay particles;
- soil moisture;
- the depth of its freezing;
- ground water level;
- load of the building on the soil.
The presence of clay particles in the soil is determined in a fairly simple way. You need to take some earth and make a “sausage” out of it. If nothing happens when you crush a handful of soil, then the soil is sandy. The soil in the loam will initially take shape, but after a while it will begin to crack and fall apart into pieces. The presence of a plastic lump of earth that does not undergo changes indicates that we have clay soil.
Types of columnar foundation.
Soil moisture is determined by placing it in the air. If the soil takes a long time to dry out, the soil is wet. On cold winter days, such soil will be subject to frost heave, which can lead to destruction due to freeze-thaw cycles.
The depth of soil freezing is calculated using reference data. In the western and southern parts of the Russian Federation, the average level of soil freezing is 0.8 m, and in the northern it reaches 2.4 m. To reduce the effect of frozen soil on the foundation, it can be insulated with expanded clay or foam plastic.
The groundwater level is determined by drilling a hole or using a well (if it is located near a construction site). In the case where groundwater is located below the soil freezing level, a shallow strip foundation can be laid.
Otherwise, you should use the method of artificial drainage of groundwater. Drainage ditches and drainage systems are used for this purpose. If it is impossible to lower the groundwater level, it will be necessary to make a structure such as a foundation on piles.
Foundation layers.
The choice of foundation is also influenced by the load of the house on the ground. Installation of light frame houses can be carried out on any type of soil. For buildings that have walls two bricks thick and a complex gable roof, the foundation must lie deep and be of substantial size.
The foundation laid in clay soil must have increased resistance to soil transformation. The most suitable options for building houses on clay soils are to lay a strip or pile foundation.
For high-quality laying of one of the two types, we will need the following tools and materials:
Scheme of a homemade concrete mixer from a barrel.
- concrete mixer;
- mini-excavator;
- welding machine;
- hacksaw;
- hammer;
- Boer;
- winch;
- Bulgarian;
- nails;
- level;
- plumb line;
- square;
- buckets;
- shovels (scoop and bayonet);
- jackhammer;
- tamping;
- scrap;
- roulette;
- trowel;
- sand;
- crushed stone;
- gravel;
- fittings;
- boards for formwork;
- concrete solution;
- screw piles;
- beam;
- channel.
Ways to resist heaving
Scheme of interaction between properly constructed foundations and heaving soils.
If the foundation is being built on problematic soil, measures are taken, among which the following should be highlighted. In some cases, it makes sense to replace the soil located at the base with a non-heaving one. Crushed stone and sand are poured under the foundation. Backfilling is also made from non-heaving materials. This technique is used when it is necessary to reduce lateral heaving. The next method is with smooth wall structures. Soil heaving is not neutralized by a layer of waterproofing on the side walls.
For many types of foundations, the option of arranging a foundation in the form of an expanded monolith is suitable. Laying thermal insulation of the soil relative to the perimeter part of the building is effective only if there is a heating system and a normally insulated basement floor. The fact is that with good heating, structures in combination with thermal insulation help reduce heaving forces.
The only exception is non-heaving soils. High water content in the soil causes it to erode. Sometimes groundwater contains aggressive substances that can destroy reinforcing products and concrete structures. These problems can be solved with waterproofing. The installation of a drainage system also helps to reduce heaving in the foundation area.
Scheme of a columnar foundation.
The main solution to the problem of building a reliable one is to sufficiently deepen the foundation, which will be below the freezing level of the soil. If the base strength is insufficient, the material may be displaced or deformed. When laying the foundation to a great depth, construction will require large expenses for materials. As a rule, a good foundation on heaving soils reliably resists the effects of heaving and evenly distributes the deformation phenomena of all foundation elements.
A shallow foundation, characterized by a small backfill depth, helps to cope with this problem. This backfill helps to dampen the tangential forces of soil heaving, since the foundation is a monolithic structure. In order for such a base to cope with its functions, a special pillow is placed under it, consisting of materials that are not subject to heaving. It can be medium-fraction crushed stone or sand. After pouring the concrete, the outer side of the foundation is laid with non-heaving materials and covered with earth. Next, the main ones built on heaving soils will be described.
Strengthening clay soil
Preparing a foundation pit in a clay area
There are several methods by which you can artificially increase the bearing capacity of clay soils and expand the choice of foundations:
- The electrical method involves using the effect of electroosmosis: for this, a constant electric current with a field strength of 1 V/cm and a density of 1-5 A/m² is passed into the soil. Due to this, the clay dries out, becomes dense and loses its ability to heave.
- The electrochemical method differs only in that, simultaneously with the electric current, chemical additives (for example, calcium chloride, etc.) are introduced into the ground through the pipe, which is the cathode. Thanks to this improved technology, the process of soil strengthening is accelerated and improved significantly.
- The mechanical method can be divided into several types:
- Laying soil cushions is replacing a weak layer of soil with a new, more reliable one. To do this, the old soil is removed, and another is poured in its place and compacted layer by layer.
- Driving soil piles - strong soil is poured into the holes obtained after extraction and compacted layer by layer.
- Compacting pits using special tampers suspended on a crane boom, or tamping machines, vibratory rollers and slabs.
As you have already seen, it is possible and necessary to erect buildings on clay
But here it is important to remember its positive sides and disadvantages, skillfully use the first and try to avoid the second. Preliminary strengthening of the soil also plays an important role, so it is better to complete this labor-intensive but useful step
Engineering and reclamation methods of heaving control
Diagram of pile formation stages.
- Raising the general level of the construction site using backfill from non-heaving soils (coarse or medium sand). This will reduce the depth of freezing of heaving soil and reduce the overall degree of its swelling. This method is especially effective on soils where it is very...
- Deep drainage device. In rooms without basements, this method is ineffective, and the installation of such a system will be quite expensive. However, for houses with a technical underground or basement floor, such drainage will not only reduce the level of heaving, but also prevent flooding of the buried part of the house with groundwater.
- Reducing soil heaving by compacting it with a heavy tamper, which reduces its porosity. For individual construction, this method is quite labor-intensive and quite expensive, since it requires the use of powerful mechanisms and equipment.
Is it possible to build a reliable foundation for a house if the site has clay soil?
Clay soil consists of scaly elements prone to moisture accumulation.
A variety of heaving soils are clay, loam, and clay in combination with sand.
Clay, loam, and clay in combination with sand are a type of heaving soil characterized by an unpredictable character:
- dry clay soil is characterized by friability, which complicates the construction of a foundation on clay soil;
- waterlogged soil is susceptible to frost heaving, which gradually destroys the foundation on clay soil.
These factors negatively affect the strength characteristics of the foundation.
You should take seriously the choice of the optimal foundation option and pay special attention to the following factors:
- characteristics of clay soil. Sampling for laboratory research is carried out by making pits to the calculated depth. It is advisable to analyze samples in the spring months, when the moisture in the soil rises close to its surface;
- soil freezing level. Literary sources and professional websites provide information on the maximum possible depth of soil freezing in various regions, which makes it possible to determine the type and level of foundation depth;
The choice of the optimal foundation option should be taken seriously
the proximity of aquifers and the ability of clay soil to absorb moisture. The depth of water layers is determined by drilling, and the tendency of clay to absorb moisture is determined in laboratory conditions. The samples are moistened and the drying time is subsequently monitored.
Laboratory analysis of soil raised from various depths will provide a complete understanding of the characteristics and structure of clay soil, which is divided into the following types:
- clay soil. The concentration of pure clay reaches 1/3 of the total volume of soil. Such soil is characterized by increased flowability and high plasticity;
- loams. Along with 10% clay, such soils contain a sand fraction. Depending on the sand and clay content, they are divided into light, medium and heavy;
- sandy loam. The clay concentration does not exceed 1/5 of the total volume. Due to the increased concentration of sand, sandy loams are unsuitable for construction.
A laboratory analysis of soil raised from various depths will allow you to get a complete understanding of the characteristics and structure of clay soil.
Clay is divided into the following types:
- glacial. It has an increased load capacity and is suitable for the construction of foundations;
- alluvial. It is characterized by increased plasticity, which makes the construction of foundations difficult.
Professional builders answer the question in the affirmative about the possibility of building a reliable foundation on a site with clay soil
It is important to choose the right type of foundation for the specific conditions of the construction site. If water layers are located close to each other and are above the freezing level, a drainage system should be installed before constructing the foundation.
It will ensure effective removal of moisture from the base of the building.
Professional builders answer the question in the affirmative about the possibility of building a reliable foundation on a site with clay soil
What is the difference between heaving and non-heaving bases?
According to GOST 25100-2011, there are 5 groups of soils that differ in the level of heaving:
- Excessively heaving (soil expansion level is more than 12%);
- Highly heaving – 12%;
- Medium heaving – about 8%;
- Low heaving – about 4%;
- Non-heaving – less than 4%.
The last category is considered conditional, since soil that does not contain water practically does not exist in nature. Such foundations include only granite and coarse rocks, but in our conditions such soils are extremely rare.
When talking about what heaving soil is and how to define it, it is worth taking into account its composition and groundwater level.
Types and characteristics of clay soils
Not a single building, even the most insignificant one, is placed directly on the ground - it needs a foundation. Its main purpose is to ensure the stability of the structure, its stationary position. Without fulfilling this condition, you cannot expect that the house, garage or bathhouse will last long. Uneven movements will certainly lead to the appearance of cracks, faults, stresses in fastening points, and failures. And even if the house does not fall apart, it will eventually become uninhabitable.
The risk of obtaining such a result is especially high when choosing an unsuitable foundation on complex soils, which include clay soils. This is due to their composition and related properties.
Any large construction project should begin with a soil analysis Source magmageo.ru
You can do without a project tied to a site only when constructing secondary buildings, such as a utility block or a gazebo. Moreover, by the time of their construction, the main buildings are already ready, and the completed excavation work allows us to judge possible risks. For permanent buildings, a project with all calculations is required. Especially on heaving soils.
To understand which foundation is best for clay soil, you need to know about its properties.
There is such a thing as frost heaving of the soil. In simple terms, this means that it is saturated with water and holds it, and during severe frosts this water freezes, increasing in volume. Accordingly, the soil also becomes more voluminous, so it begins to bulge upward along with all the structures located in it.
It is easy to imagine what will happen to the house if the foundation underneath it moves, and even unevenly.
Heaving forces easily squeeze even heavy structures out of the groundSource eurolos.pro
Clay soils have the ability to retain water. They consist of small lamellar particles, impenetrable to moisture, which is retained between them. On the other hand, large volumes of water are capable of eroding clay and transporting it with its flow, which leads to the exposure of foundation elements and its freezing.
However, the percentage of such particles in the soil may vary not only in one area, but also in neighboring areas. And its characteristics and what kind of foundation to make on clay soil largely depend on this:
- Clay content less than 5% does not affect soil permeability. Such soils are called sandy. They allow water to pass through perfectly and become compacted under load, so any foundation can be built on them.
- 5-10% of clay in sand is sandy loam, which in a dry state is also a reliable base for the foundation and is little susceptible to heaving. But when saturated with water, it becomes fluid and can move with its flow. Such soil is called quicksand; it is formed when groundwater is high. It is undesirable to build on it, but if there is no other choice, use a pile foundation.
Pile foundation on quicksandSource stroyfora.ru
Loams are light, medium and heavy depending on the percentage of clay in the sand (from 10 to 50%). Which foundation is better on loamy soil, which is extremely susceptible to frost heaving, depends on its homogeneity, density, freezing mark, level of the formation, its thickness and groundwater level. If it is high, emergency subsidence of a building on a shallow strip foundation is inevitable. If the aquifers are located much below the freezing point, the heaving will not be so pronounced. But you also need to take into account factors such as the level of precipitation, the proximity of a natural reservoir and many others.
Clay as a natural material and its features
On clay soils, you can make house foundations in any way. The use of one or another base depends on the individual characteristics of the site and the financial capabilities of the owner. Soil analysis will help to accurately determine the type of foundation
When choosing the optimal type of base, the following features must be taken into account:
- the amount of clay in the soil;
- freezing limit;
- ground water level.
The determination of all of these parameters is carried out by conducting a qualitative soil analysis. If the groundwater horizon overlaps with the level of soil freezing, it is advisable to equip a primitive drainage system for water drainage before laying the foundation of the house.
Drainage is realized by digging trenches around the perimeter of the future placement of foundation elements. On clay soils, as a rule, the following types of foundations are installed:
- tape;
- pile;
- shallow slab;
- deep placement (in regions with extremely low temperatures).
The main feature of clay is the ability to quickly erode under the influence of water, without letting it penetrate deeper. Layers of clay can lie at sufficient depth, and water that penetrates them freezes and swells the soil at low temperatures. Therefore, clayey soils are called heaving soils, and before starting construction it is strongly recommended to conduct studies of the composition and homogeneity of the soils on the site. Otherwise, the clay may behave unexpectedly, quite quickly turning a buried foundation into an above-ground one.
In general, a distinction is made between river (alluvial) and glacial clays. The first lies near reservoirs, in lowlands and has high plasticity. Construction on such areas is contraindicated, and in exceptional cases houses have a pile foundation. Concrete foundations can be confidently erected on glacial layers, but only if they are deep.
Features of the technology for laying foundations on clay
Foundations buried to shallow depths are most often laid by hand. In this case, the main thing is not to make mistakes in approximate calculations, taking into account, first of all, the degree of heaving and the bearing capacity of the soil. Based on these calculations, the dimensions of the foundation and the thickness of the cushion made of sand, crushed stone, gravel or slag are selected.
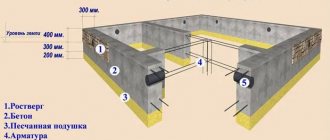
The recommended depth for laying a strip shallow foundation on clay in the conditions of our country is from 50 to 100 cm. The approximate dimensions of such a foundation are shown in Fig. 2. The above-ground part of the base should not be larger than its underground part, but may be smaller than it. The most common option is the depth and height of the foundation above the ground of 40-50 cm.
When laying the foundation, a trench is first dug. A pillow made of the selected protective material is placed at its bottom and carefully compacted. Then formwork is placed for a monolithic foundation or spacers for a prefabricated foundation, after which the mixture is poured for a monolithic foundation or blocks for a precast foundation are installed. A monolithic strip foundation should be reinforced with reinforcing metal mesh.
Before insulation, the base should be waterproofed. Foam boards are most often used as insulation. They are light, cheap, and perfectly retain air, preventing the foundation from freezing in the most severe frosts. Other thermal insulation materials are often more expensive.
Although a shallow clay foundation is not such a cheap structure, the most important thing is that with high-quality work, a building installed on it can last for many decades.
Slab technology
For clay soils, this option is also acceptable, since the total specific gravity of the entire house is evenly distributed over the slab support. In case of erosion or seasonal fluctuations of the soil, the entire foundation will be subject to displacement, and not its individual constituent elements.
Slab base suitable for clay soils
Installation procedure:
- As in the previous version, a 40-50 cm sand and gravel cushion is initially installed around the perimeter of the entire base. If groundwater is close to the ground, it is necessary to construct a drainage system with pipes sloping from the base.
- A thin layer of concrete is poured and time is given for it to harden.
- Formwork is formed, the inside of which is covered with a waterproofing layer.
- Reinforced metal mesh is laid.
- The final concreting of the base is carried out. It would be a good idea to add fine gravel to the solution during pouring.
To obtain a monolithic structure, concrete must be poured as quickly as possible.
Advantages:
- resistance to shrinkage and seismic influences;
- practicality;
- resistance to soil erosion by melt and groundwater.
Flaws:
- significant costs;
- the need to attract special equipment;
- inability to equip basements and basements.
Watch the video on how to build a slab base with your own hands.